
The Southern Oregon AVA is an American Viticultural Area which lies in Southern Oregon, United States. The Southern Oregon AVA was established in 2005 and was created to include the land of two smaller AVAs: the Rogue Valley AVA and the Umpqua Valley AVA. Southern Oregon AVA was established to allow the two principal winegrowing regions in the southern part of the state to market themselves jointly. This creation of a "super-AVA" is a departure from the trend in the Willamette Valley AVA or northern Oregon of establishing smaller AVAs specific to a particular locale's climate or soil conditions.
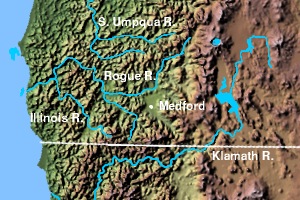
The Rogue Valley AVA is an American Viticultural Area located in southern Oregon. The federal government approved this appellation in 1991. It is entirely contained within the larger Southern Oregon AVA and includes the drainage basin of the Rogue River and several tributaries, including the Illinois River, the Applegate River, and Bear Creek. Most wineries in the region are found in the valleys formed by one of these three tributaries, rather than along the Rogue River itself. The region is 70 miles (113 km) wide by 60 miles (97 km) long ; there are fewer than 20 wineries with only 1,100 acres (450 ha) planted. Each river valley has a unique terroir, and grows different varieties of grapes. Overall, however, this region is the warmest and driest of Oregon's wine-growing regions.

Temecula Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in the Temecula Valley, located in southwestern Riverside County, California against the eastern slopes of the Santa Ana Mountains. It was initially established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury as "Temecula" on October 23, 1984 based on submitted petitions from by the Rancho Califomia/Temecula Winegrowers Association and Callaway Vineyard and Winery, Temecula, California in 1982. It was renamed "Temecula Valley" by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) in 2004, approving the 2001 petition by Temecula Valley Winegrowers Association. The petition stated the name change would provide a more accurate description of the Temecula geography and greater clarity as to its location for wine consumers and the public. The petition did not request any change to the established AVA boundaries. This was the first American Viticultural Area to change its name after the initial approval. Temecula Valley encompasses 33,000 acres (52 sq mi) and 5,000 acres (8 sq mi) is located in a "protected" area referred to as the Citrus/Vineyard Zone. This area is generally located in and around the Rancho California Road area with Riverside County. County guidelines strictly enforce the number of acres needed to build a winery, lodging and other limited housing and commercial ventures.

Sonoma County wine is wine made in Sonoma County, California, in the United States.

Paso Robles is the third American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo (SLO) County, California. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury on November 3, 1983 based on a petition submitted by Martin-Brothers Winery. The area encompasses 609,673 acres (953 sq mi) with approximately 18,500 acres (7,487 ha) cultivated with wine grapes known for their heritage varietal Zinfandel, Cabernet Sauvignon, and Rhône-style wines.
The Mendocino Ridge AVA is a coastal, cool climate and high altitude American Viticultural Area located entirely within the coastal zone of Mendocino County, California. The boundaries of the AVA encompass the coastal ridges adjacent to the Pacific Ocean that reach inland toward the Anderson Valley. Roughly 36 miles of the southernmost portion of the Mendocino Coast make up the western boundary of the AVA, with the Sonoma County line as the southern boundary, the Navarro River as the northern boundary and Anderson Valley as the inland boundary running northwest–southeast. The Mendocino Ridge AVA "is essentially a northern extension of the true Sonoma Coast viticultural area." However, the Mendocino Ridge AVA designation is unique in that it is limited by elevation, reserved only for vineyards at or above 1200 feet. This is why the Mendocino Ridge AVA has been nicknamed "Islands in the Sky®," because the vineyards sitting at 1200 feet or higher are often perched above thick fog moving inland from the Pacific Ocean blanketing the coast and the valleys between the ridge tops, making the tips of the mountains look like islands protruding from a sea of fog. In this overlapping, "[t]he Mendocino Ridge AVA floats above the Anderson Valley and Mendocino appellations." Mendocino Ridge is the only non-contiguous AVA in the United States; all others are contiguous landmasses with all vineyards inside the boundaries designated as part of the AVA, whereas Mendocino Ridge in comparison only includes the higher altitude growing sites. "There are 262,400 acres within the outer boundaries of the Mendocino Ridge viticultural area, but the actual viticultural area encompasses only 87,466 acres which lie above 1,200 feet elevation. Of these 87,466 acres, approximately 1,500 to 2,000 acres of the ridge tops are suitable for vineyards. The side-slopes are very steep and covered with timber, making them unfit for planting". Estimates of planted acres range from 233 to 410, which accounts for about 0.3% of the total area. These planted acres are scattered among 16 remote vineyards.
Arroyo Grande Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo County, California approximately 12 miles (19 km) southeast of the county seat San Luis Obispo. Arroyo Grande Valley was recognized on February 5, 1990 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) as the state's 60th AVA based on the petition filed in 1987 by Don Talley of Talley Vineyards and William S. Greenough of Saucelito Canyon Vineyard for the establishment of the "Arroyo Grande Valley" viticultural area in San Luis Obispo County. The 16 miles (26 km) long, approximately 67 square miles valley appellation benefits from its east-northeast orientation allowing the breeze from the Pacific Ocean to moderate the climate of the area. The valley is divided by a fog line produced by the cool maritime layer where Zinfandel, Petite Sirah and Rhône varietals are grown on the higher elevations near Lopez Lake and the cooler mid-valley vineyards being home to Chardonnay and Pinot noir. On April 8, 2022, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) approved the designation of the expansive San Luis Obispo (SLO) Coast AVA overlapping the boundaries of Edna Valley and Arroyo Grande Valley viticultural areas because they share common features. However, these two previously established areas still have unique characteristics to retain their viticultural area distinctions within SLO Coast. Edna Valley lies immediately to the northwest, the Los Padres National Forest straddles the north leg boundary, the Santa Maria Valley AVA lies to the southeast of Arroyo Grande Valley, and the Pacific Ocean communities of Oceano, Grover City and Arroyo Grande abut its southwestern border.

Santa Cruz Mountains AVA is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) centered on the Santa Cruz Mountains. Its territory spans three California counties, Santa Clara, Santa Cruz and San Mateo and was established January 4, 1982 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury. Santa Cruz Mountains AVA was among the first AVA to be defined by its mountainous topography. Based on elevation, it largely follows the fog line along the coast, extending down to 800 feet (240 m) on the eastern slope toward San Francisco Bay, 400 feet (120 m) on the western slope to the Pacific Ocean and extending along the ridge crest line at 3,000 feet (910 m) elevation plus.

Sierra Foothills is a vast American Viticultural Area (AVA) encompassing the foothill "belt" of the Sierra Nevada in north-central California, United States. It was established on December 18, 1987 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after evaluating the petition filed by the Sierra Foothills Winery Association of Somerset, California for the establishment of a "Sierra Foothills" viticultural area in portions of Yuba, Nevada, Placer, El Dorado, Amador, Calaveras, Tuolumne and Mariposa Counties. Wine grapes were introduced to the area in the nineteenth century during the California Gold Rush. Over 150 vineyards/wineries are located within its boundaries.

The Dry Creek Valley AVA is an American Viticultural Area in Sonoma County, California, located northwest of the town of Healdsburg. The valley is formed by Dry Creek, a tributary of the Russian River, and is approximately 16 miles (25.7 km) long and 2 miles (3.2 km) wide. The appellation benefits from the proximity of the Lake Sonoma reservoir for irrigation in this relatively dry area.
The Northern Sonoma AVA is an American Viticultural Area in Sonoma County, California, United States. The appellation covers most of the county with the notable exceptions of the Los Carneros AVA and Sonoma Valley AVA wine regions, which are located in the southern portion of the county. The creation of this AVA was largely based on the petitioning of the E & J Gallo Winery as part of their expansion of their Gallo of Sonoma brand. The viticultural area incorporates the Alexander Valley AVA, Chalk Hill AVA, Dry Creek Valley AVA, Knights Valley AVA, Russian River Valley AVA, Sonoma Coast AVA, and parts of the Green Valley of Russian River Valley AVA and Rockpile AVA valleys.

St. Helena is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located within Napa Valley, centered in and around the town of St. Helena, California. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) on October 11, 1995, after the ATF received a petition from Mr. Charles A. Carpy, Chairman of the St. Helena Appellation Committee, proposing to establish a new viticultural area in Napa County to be known as "St. Helena."
The Chiles Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Napa County, California and a sub-region within Napa Valley AVA. It was established as California's 81st AVA by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) on April 19, 1999 after the ATF received the petition from Mr. Volker Eisele, owner of the Volker Eisele Vineyard and Winery proposing a new viticultural area in Napa County to be known as "Chiles Valley District".
Leona Valley AVA is an American Viticulture Area (AVA) in northeastern Los Angeles County, California. It is located in Leona Valley within the Sierra Pelona Mountains of Southern California.

The El Dorado AVA is an American Viticultural Area located in El Dorado County, California, United States. Wine grape growers in the region produce a large diversity of varietals, notable varietals are Zinfandel, Barbera, Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot and Petite Sirah and there are significant plantings of Rhône varietals. Located in the foothills of the Sierra Nevada mountains, vineyards are found primarily at elevations between 600 feet (183 m) and 3,500 feet (1,067 m) above sea level and some of the historic and revered vineyards are planted above 2,000 feet (610 m) elevation. The region benefits from the cool breezes that come off the mountains and push hot air off the vines and down to the valley. The soils of the region are magma based with high levels of acidity.

California Shenandoah Valley is a American Viticultural Area (AVA) located within portions of Amador County and El Dorado County, California. The area was established on January 27, 1983 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), Treasury after approving the petition from the Amador County Wine Grape Growers Association proposing a viticultural area in Amador County, California, to be known as "Shenandoah Valley." It lies within the vast multi-county Sierra Foothills viticultural area boundaries and borders the northwest boundary of Fiddletown viticultural area which received recognition later the same year. In the petition, the area consists of approximately 10,000 acres (16 sq mi) with about1,200 acres (486 ha) under vine. The petition requested ATF for the Shenandoah Valley viticultural area to be situated to the north and west of Fiddletown, and to the north and east of Plymouth.
The Fair Play AVA is an American Viticultural Area in El Dorado County, California, United States. It is entirely contained within the boundaries of the El Dorado AVA and the Sierra Foothills AVA. The boundaries of the Fair Play AVA include rolling hills at elevations between 2,000 feet (610 m) and 3,000 feet (914 m) above sea level, making it the California appellation with the second highest average elevation after the Squaw Valley-Miramonte appellation. The soils are decomposed granite as part of the Sierra Nevada Foothills region, and the area is within the Cosumnes River watershed. The most popular red wine grape variety is Zinfandel, although varieties popular in southern Rhone Valley France and Italy, such as Syrah, Grenache, Mourvedre, Sangiovese and Barbera are quite commonly planted here. White wine is less popular in this AVA, but significant plantings of Viognier and Grenache Blanc, along with Chardonnay are the more popular white varietals.

Lake County wine is a appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Lake County, California and located north of Napa County. Although each region within Lake County has unique viticultural attributes, all are influenced by Clear Lake, the largest inland body of water in California. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB). TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.

Santa Barbara County wine is an appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Santa Barbara County, California which is located approximately 50 miles (80 km) north of Los Angeles County. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) of the Treasury Department. TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.

Monterey County wine is a appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown in Monterey County, California which lies entirely within the expansive multi-county Central Coast viticultural area. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB). TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.













