
The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is the surveying method developed and used in the United States to plat, or divide, real property for sale and settling. Also known as the Rectangular Survey System, it was created by the Land Ordinance of 1785 to survey land ceded to the United States by the Treaty of Paris in 1783, following the end of the American Revolution. Beginning with the Seven Ranges in present-day Ohio, the PLSS has been used as the primary survey method in the United States. Following the passage of the Northwest Ordinance in 1787, the Surveyor General of the Northwest Territory platted lands in the Northwest Territory. The Surveyor General was later merged with the United States General Land Office, which later became a part of the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM). Today, the BLM controls the survey, sale, and settling of lands acquired by the United States.

The Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty, was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined the boundary between the U.S. and Mexico. It settled a standing border dispute between the two countries and was considered a triumph of American diplomacy. It came during the successful Spanish American wars of independence against Spain.
A township in some states of the United States is a small geographic area.

The territory of the United States and its overseas possessions has evolved over time, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.
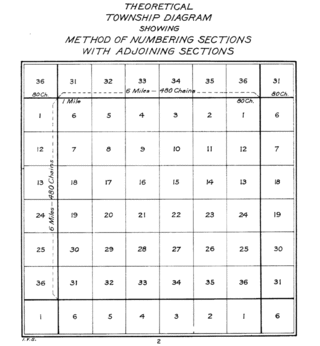
In U.S. land surveying under the Public Land Survey System (PLSS), a section is an area nominally one square mile, containing 640 acres, with 36 sections making up one survey township on a rectangular grid.

In surveying, a baseline is generally a line between two points on the Earth's surface and the direction and/or distance between them.

The Honey War was a bloodless territorial dispute in 1839 between Iowa Territory and Missouri over their border.
An arpent is a unit of length and a unit of area. It is a pre-metric French unit based on the Roman actus. It is used in Quebec, some areas of the United States that were part of French Louisiana, and in Mauritius and the Seychelles.
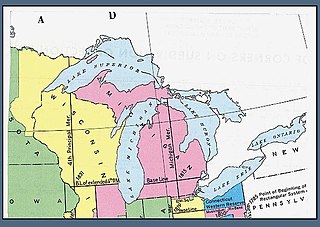
The Michigan meridian is the principal meridian used as a reference in the Michigan Survey, the survey of the U.S. state of Michigan in the early 19th century. It is located at 84 degrees, 21 minutes and 53 seconds west longitude. It forms the boundary between several counties in the state.
Joseph Cromwell Brown was an American surveyor known for establishing the Fifth Principal Meridian's baseline that governs the surveys of all or part of present-day Arkansas, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, and South Dakota. The Fifth Principal Meridian was established in 1815 to survey the territory of the Louisiana Purchase, an area of 830,000 square miles (2,100,000 km2).
John C. Sullivan was a surveyor who established the Indian Boundary Line and the Sullivan Line which were to form the boundary between Native Americans and white settlers in Indian Territory from Iowa to Texas.

The Sullivan Line originally marked in 1816 forms three quarters of the border between Missouri and Iowa and an extension of it forms the remainder. The line was initially created to establish the limits of Native American territory ; disputes over the boundary were to erupt into the Honey War.

The Louisiana Purchase State Park, located in eastern Arkansas, commemorates the initial point from which public lands acquired through the 1803 Louisiana Purchase were subsequently surveyed.
The Choctaw meridian is a meridian that governs the surveys in most of central Mississippi, USA. It begins on the Choctaw baseline, latitude 31° 54' 40" north, longitude 90° 14' 45" west from Greenwich and runs north to the south boundary of the Chickasaw cession, at latitude 34° 19' 40" north. The surveys of Mississippi by the United States General Land Office begun in 1831 "used the 'Old Choctaw Line' as the 'base meridian' of their efforts to transform the landscape from a landscape of imperial violence to a field of national development."

The fourth principal meridian, set in 1815, is the principal meridian for land surveys in northwestern Illinois and west-central Illinois, and its 1831 extension is the principal meridian for land surveys in Wisconsin and northeastern Minnesota. It is part of the Public Land Survey System that covers most of the United States.

Saint Helena meridian begins at the initial point of the Washington meridian, in latitude 31° north, and longitude 91° 09′ 15″ west of Greenwich, passing one mile east of Baton Rouge, extends south to the Mississippi River, and governs the surveys in the Greensburg and southeastern districts of Louisiana, east of the Mississippi River.

The Louisiana meridian, in longitude 92° 24′ 15″ west of Greenwich, extends from the Gulf of Mexico to the north boundary of Louisiana, and with the baseline through the initial point conforming to the parallel of 31° north latitude, governs all the surveys in the state west of the Mississippi River.
The Black Hills meridian, longitude 104°03′ west from Greenwich, with the baseline in latitude 44° north, is the principal meridian that governs surveys in the state of South Dakota north and west of White River, and west of the Missouri River, the north and west boundaries of the Lower Brule Indian Reservation, and the west boundary of range 79 west, of the Fifth Principal Meridian system. It is named for the Black Hills of South Dakota and Wyoming.

In surveying, an initial point is a datum that marks the beginning point for a cadastral survey. The initial point establishes a local geographic coordinate system for the surveys that refer to that point.
The Washington Meridian is one of the 38 principal meridians governing cadastral surveys in the United States. The meridian line was surveyed and established in 1803 by surveyor Isaac Briggs. Briggs named the meridian the Washington Meridian, likely because the meridian passed near his offices in the community of Washington, Mississippi.











