
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency within the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands covering 193 million acres (780,000 km2) of land. The major divisions of the agency are the Chief's Office, National Forest System, State and Private Forestry, Business Operations, as well as Research and Development. The agency manages about 25% of federal lands and is the sole major national land management agency not part of the U.S. Department of the Interior.

The United States secretary of the treasury is the head of the United States Department of the Treasury, and is the chief financial officer of the federal government of the United States. The secretary of the treasury serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters pertaining to economic and fiscal policy. The secretary is, by custom, a member of the president's cabinet and, by law, a member of the National Security Council, and fifth in the U.S. presidential line of succession.

The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and the U.S. Mint. These two agencies are responsible for printing all paper currency and minting coins, while the treasury executes currency circulation in the domestic fiscal system. It collects all federal taxes through the Internal Revenue Service; manages U.S. government debt instruments; licenses and supervises banks and thrift institutions; and advises the legislative and executive branches on matters of fiscal policy. The department is administered by the secretary of the treasury, who is a member of the Cabinet. The treasurer of the United States has limited statutory duties, but advises the Secretary on various matters such as coinage and currency production. Signatures of both officials appear on all Federal Reserve notes.

The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of the U.S. people and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America". Before the separate federal Department of Education was created in 1979, it was called the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW).
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, or simply a nonprofit, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, as opposed to an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a profit for its owners. A nonprofit organization is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. Depending on the local laws, charities are regularly organized as non-profits. A host of organizations may be nonprofit, including some political organizations, schools, hospitals, business associations, churches, foundations, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an entity may incorporate as a nonprofit entity without having tax-exempt status.

The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alexandria, Virginia, after a 2005 move from the Crystal City area of neighboring Arlington, Virginia.
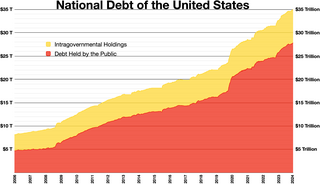
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

Michael J. Rogers is an American law enforcement officer and politician who served as the U.S. representative for Michigan's 8th congressional district from 2001 to 2015. A member of the Republican Party, he chaired the United States House Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence from 2011 to 2015.

The Architect of the Capitol is the federal agency responsible for the maintenance, operation, development, and preservation of the United States Capitol Complex. It is an agency of the legislative branch of the federal government and is accountable to the United States Congress and the Supreme Court. Both the agency and the head of the agency are called "Architect of the Capitol". The head of the agency is appointed by a vote of a congressional commission for a ten-year term. Prior to 2024, the president of the United States appointed the Architect upon confirmation vote by the United States Senate, and was accountable to the president.
In the United States, a continuing resolution is a type of appropriations legislation. An appropriations bill is a bill that appropriates money to specific federal government departments, agencies, and programs. The money provides funding for operations, personnel, equipment, and activities. Regular appropriations bills are passed annually, with the funding they provide covering one fiscal year. The fiscal year is the accounting period of the federal government, which runs from October 1 to September 30 of the following year.

Fund accounting is an accounting system for recording resources whose use has been limited by the donor, grant authority, governing agency, or other individuals or organisations or by law. It emphasizes accountability rather than profitability, and is used by nonprofit organizations and by governments. In this method, a fund consists of a self-balancing set of accounts and each are reported as either unrestricted, temporarily restricted or permanently restricted based on the provider-imposed restrictions.
Global Impact is a non-profit organization offering advisory and infrastructure services that drive strategic philanthropy for nonprofit, public, and private sector clients. Global Impact has raised more than $2.5 billion for global charities since its inception in 1956. Global Impact employs over 150 staff and is part of Global Impact Ventures, alongside Geneva Global, Capital for Good, and the GI Social Welfare Fund. Global Impact has operations around the world, including Global Impact United Kingdom and Global Impact Canada.
A fiscal year is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many jurisdictions require company financial reports to be prepared and published on an annual basis but generally with the reporting period not aligning with the calendar year. Taxation laws generally require accounting records to be maintained and taxes calculated on an annual basis, which usually corresponds to the fiscal year used for government purposes. The calculation of tax on an annual basis is especially relevant for direct taxes, such as income tax. Many annual government fees—such as council tax and license fees, are also levied on a fiscal year basis, but others are charged on an anniversary basis.
Fiscal sponsorship refers to the practice of non-profit organizations offering their legal and tax-exempt status to groups—typically projects—engaged in activities related to the sponsoring organization's mission. It typically involves a fee-based contractual arrangement between a project and an established non-profit. Originally, this concept was developed at the request of the Department of Housing and Urban Development to enable distribution of funds to local charitable groups in the 1950s and has been a practice ever since.
Form 990 is a United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS) form that provides the public with information about a nonprofit organization. It is also used by government agencies to prevent organizations from abusing their tax-exempt status. Some nonprofits, such as hospitals and other healthcare organizations, have more comprehensive reporting requirements.
Ballotpedia is a nonprofit and nonpartisan online political encyclopedia that covers federal, state, and local politics, elections, and public policy in the United States. The website was founded in 2007. Ballotpedia is sponsored by the Lucy Burns Institute, a nonprofit organization based in Middleton, Wisconsin. Originally a collaboratively edited wiki, Ballotpedia is now written and edited entirely by a paid professional staff. As of 2014, Ballotpedia employed 34 writers and researchers; it reported an editorial staff of over 50 in 2021.
SourceAmerica is a U.S. nonprofit agency, located in Vienna, Virginia, that creates employment opportunities for people with disabilities through its national network of affiliated nonprofit agencies.

FundRazr is a free crowdfunding and online fundraising platform released in 2009. FundRazr operates internationally in 35+ countries with the largest markets being United States, Canada, United Kingdom and Australia. It allows users to run a wide-range of crowdfunding campaigns by creating fundraising pages and sharing it via social media, messaging apps, email and more to raise money for over 100 types of causes such as nonprofit, medical care, education, community help, poverty alleviation, arts, memorials, and animal rescue causes. FundRazr also works with more than 4000 nonprofits, charities and social enterprises with an advanced fundraising toolset for free. The digital fundraising platform provides 8 different campaign types. They include microproject fundraising, peer-to-peer campaigns, wishlist campaigns, recurring donations, branded sponsorship campaigns, DIY projects, sweepstake campaigns, and storefront campaigns.
The Office of Refugee Resettlement (ORR) is a program of the Administration for Children and Families, an office within the United States Department of Health and Human Services, created with the passing of the United States Refugee Act of 1980. The Office of Refugee Resettlement offers support for refugees seeking safe haven within the United States, including victims of human trafficking, those seeking asylum from persecution, survivors of torture and war, and unaccompanied alien children. The mission and purpose of the Office of Refugee Resettlement is to assist in the relocation process and provide needed services to individuals granted asylum within the United States.
Ascension is a large private Catholic healthcare system in the United States. Ascension had 142,000 employees, 142 hospitals, and 40 senior living facilities operating in 19 states and the District of Columbia as of the end of 2021. Ascension is the largest nonprofit and largest Catholic health system in the United States. It also operates a conglomerate of for-profit firms, including subsidiaries involved in private equity, venture capital, insurance, medical software, and pharmacy delivery. From 2014 to 2017 it co-owned a facility in the Cayman Islands.









