
A day is approximately the period of time during which the Earth completes one rotation around its axis. A solar day is the length of time which elapses between the Sun reaching its highest point in the sky two consecutive times. Days on other planets are defined similarly and vary in length due to differing rotation periods, that of Mars being slightly longer and sometimes called a sol.

An equinox is commonly regarded as the instant of time when the plane of Earth's equator passes through the geometric center of the Sun's disk. This occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September. In other words, it is the moment at which the center of the visible Sun is directly above the equator.

An hour is a unit of time conventionally reckoned as 1⁄24 of a day and scientifically reckoned as 3,599–3,601 seconds, depending on conditions. There are 60 minutes in an hour, and 24 hours in a day.
Daylight saving time (DST), also daylight savings time or daylight time and summer time, is the practice of advancing clocks during warmer months so that darkness falls later each day according to the clock. The typical implementation of DST is to set clocks forward by one hour in the spring and set clocks back by one hour in autumn to return to standard time. As a result, there is one 23-hour day in late winter or early spring and one 25-hour day in the autumn.

The flag of Scotland consists of a white saltire defacing a blue field. The Saltire, rather than the Royal Standard of Scotland, is the correct flag for all private individuals and corporate bodies to fly. It is also, where possible, flown from Scottish Government buildings every day from 8:00 am until sunset, with certain exceptions.

Night or nighttime is the period of ambient darkness from sunset to sunrise during each 24-hour day, when the Sun is below the horizon. The exact time when night begins and ends depends on the location and varies throughout the year. When night is considered as a period that follows evening, it is usually considered to start around 8 pm and to last to about 4 am. Night ends with coming of morning at sunrise.

The National Day of Sweden is a national holiday observed annually in Sweden on 6 June. Prior to 1983, the day was celebrated as Swedish Flag Day. At that time, the day was renamed the Swedish National Day by the Riksdag.

The midnight sun is a natural phenomenon that occurs in the summer months in places north of the Arctic Circle or south of the Antarctic Circle, when the sun remains visible at the local midnight. When the midnight sun is seen in the Arctic, the sun appears to move from left to right, but in Antarctica the equivalent apparent motion is from right to left. This occurs at latitudes from 65°44' to 90° north or south, and this doesn't stop exactly at the Arctic Circle or the Antarctic Circle, due to refraction.

The national flag of the United Kingdom is the Union Jack, also known as the Union Flag.

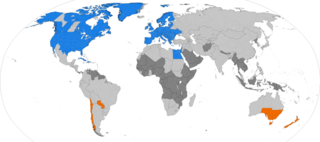
Flag days in Finland are days of the year when the national flag is flown nationwide, either by law or by custom. The flag of Finland is generally flown only on special occasions to celebrate or honour someone or something. Any citizen has a right to fly the flag on their own property if they deem it appropriate, for example in celebration birthdays or weddings. On certain days of the year the state officially flies the flag, and recommends all private citizens to do so as well.

Commonwealth Day is the annual celebration of the Commonwealth of Nations, often held on the second Monday in March. It is marked by an Anglican service in Westminster Abbey, normally attended by Queen Elizabeth II as Head of the Commonwealth along with the Commonwealth Secretary-General and Commonwealth High Commissioners in London. The Queen delivers an address to the Commonwealth, which is broadcast throughout the world.
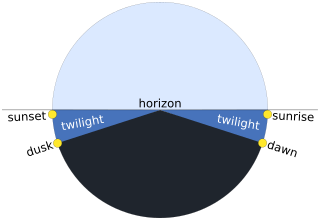
Twilight on Earth is the illumination of the lower atmosphere when the Sun is not directly visible because it is below the horizon. Twilight is produced by sunlight scattering in the upper atmosphere, illuminating the lower atmosphere so that Earth's surface is neither completely lit nor completely dark. The word twilight is also used to denote the periods of time when this illumination occurs.

Half-mast or half-staff refers to a flag flying below the summit of a ship mast, a pole on land, or a pole on a building. In many countries this is seen as a symbol of respect, mourning, distress, or, in some cases, a salute. Most English-speaking countries use the term half-mast in all instances. In the United States, this refers officially only to flags flown on ships, with half-staff used on land.

Zmanim are specific times of the day in Jewish law.
Fasting is very common among Jains and as a part of festivals. Most Jains fast at special times such as birthdays, anniversaries, during festivals, and on holy days. Paryushan is the most prominent festival, lasting eight days in Svetambara Jain tradition and ten days in Digambar Jain tradition during the monsoon. The monsoon is a time for Jains to observe most of the religious procedures. However, a Jain may fast at any time. Jain saints usually perform fasts every now and then but at times it becomes a compulsion for them when they have committed an error in relation to the preachings of Mahavira. Variations in fasts encourage Jains to do whatever they can to maintain whatever self control is possible for the individual. According to Jain texts, abstaining from the pleasures of the five senses such as sounds and dwelling in the self in deep concentration is fasting (upavāsa).

The winter solstice, hiemal solstice or hibernal solstice occurs when one of the Earth's poles has its maximum tilt away from the Sun. It happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere. For that hemisphere, the winter solstice is the day with the shortest period of daylight and longest night of the year, when the Sun is at its lowest daily maximum elevation in the sky. At the pole, there is continuous darkness or twilight around the winter solstice. Its opposite is the summer solstice. Also the Tropic of Cancer or Tropic of Capricorn depending on the hemispheres winter solstice the sun goes 90 degrees below the horizon at solar midnight to the nadir.

On Earth, daytime is the period of the day during which a given location experiences natural illumination from direct sunlight. Daytime occurs when the Sun appears above the local horizon, that is, anywhere on the globe's hemisphere facing the Sun. In direct sunlight the movement of the sun can be recorded and observed using a sundial that casts a shadow that slowly moves during the day. Other planets and natural satellites that rotate relative to a luminous primary body, such as a local star, also experience daytime, but this article primarily discusses daytime on Earth.
The observance of Jewish law (halakhah) in the polar regions of Earth presents unique problems. Many mitzvot, such as Jewish prayer and the Sabbath, rely on the consistent cycle of day and night in 24-hour periods that is commonplace in most of the world. However, north of the Arctic Circle a single period of daylight can last for a month or more during the summer, and the night lasts for a similar length of time in the winter. The question for religious Jews that live in or visit these regions is how to reconcile the observed length of days in the polar regions with common practice elsewhere in the world. Should a "day" be defined solely based on sunrise and sunset, even if these events do not occur for long stretches of time; or should the definition of a polar "day" be consistent with the length of a day in the rest of the world?

A clock position, or clock bearing, is the direction of an object observed from a vehicle, typically a vessel or an aircraft, relative to the orientation of the vehicle to the observer. The vehicle must be considered to have a front, a back, a left side and a right side. These quarters may have specialized names, such as bow and stern for a vessel, or nose and tail for an aircraft. The observer then measures or observes the angle made by the intersection of the line of sight to the longitudinal axis, the dimension of length, of the vessel, using the clock analogy.

The national flag of Ireland, frequently referred to in Ireland as 'the tricolour' and elsewhere as the Irish tricolour, is the national flag and ensign of the Republic of Ireland. The flag itself is a vertical tricolour of green, white and orange. The proportions of the flag are 1:2.


















