
Powys is a county and preserved county in Wales. It borders Gwynedd, Denbighshire, and Wrexham to the north; the English ceremonial counties of Shropshire and Herefordshire to the east; Monmouthshire, Blaenau Gwent, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Rhondda Cynon Taf, and Neath Port Talbot to the south; and Carmarthenshire and Ceredigion to the west. The largest settlement is Newtown, and the administrative centre is Llandrindod Wells.

The coat of arms of England is the coat of arms historically used as arms of dominion by the monarchs of the Kingdom of England, and now used to symbolise England generally. The arms were adopted c.1200 by the Plantagenet kings and continued to be used by successive English and British monarchs; they are currently quartered with the arms of Scotland and Ireland in the coat of arms of the United Kingdom. Historically they were also quartered with the arms of France, representing the English claim to the French throne, and Hanover.

Until 1974, Brecknockshire, also formerly known as the County of Brecknock, Breconshire, or the County of Brecon, was an administrative county in the south of Wales, later classed as one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales. Named after its county town of Brecon, the county was mountainous and primarily rural.

Until 1974, Montgomeryshire was an administrative county in mid Wales, later classed as one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales. It was named after its county town, Montgomery, which in turn was named after one of William the Conqueror's main counsellors, Roger de Montgomerie, who was the 1st Earl of Shrewsbury.

Radnorshire was an administrative county in mid Wales, later classed as one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales and from 1974 to 1996 a district. It covered a sparsely populated area, and was bounded to the north by Montgomeryshire and Shropshire, to the east by Herefordshire, to the south by Brecknockshire and to the west by Cardiganshire.

Montgomery is a town and community in Powys, Wales. It is the traditional county town of the historic county of Montgomeryshire to which it gives its name, and it is within the Welsh Marches border area. The town centre lies about 1 mile (1.6 km) west of the England–Wales border. Montgomery Castle was started in 1223 and its parish church in 1227. Other locations in the town include The Old Bell Museum, the Offa's Dyke Path, the Robber's Grave and the town wall. The large Iron Age hill fort of Ffridd Faldwyn is sited northwest of the town and west of the Castle.

The Kingdom of Powys was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain. It very roughly covered the northern two-thirds of the modern county of Powys and part of today's English West Midlands. More precisely, and based on the Romano-British tribal lands of the Ordovices in the west and the Cornovii in the east, its boundaries originally extended from the Cambrian Mountains in the west to include the modern West Midlands region of England in the east. The fertile river valleys of the Severn and Tern are found there, and this region is referred to in later Welsh literature as "the Paradise of Powys".

Powis Castle is a medieval castle, fortress and grand country house near Welshpool, in Powys, Wales. The seat of the Herbert family, earls of Powis, the castle is known for its formal gardens and for its interiors, the former having been described as "the most important", and the latter "the most magnificent", in the country. The castle and gardens are under the care of the National Trust. Powis Castle is a Grade I listed building, while its gardens have their own Grade I listing on the Cadw/ICOMOS Register of Parks and Gardens of Special Historic Interest in Wales.

The Royal Badge of Wales was approved in May 2008. It is based on the arms borne by the 13th-century Welsh prince Llywelyn ab Iorwerth, with the addition of St Edward's Crown atop a continuous scroll which, together with a wreath consisting of the plant emblems of the four countries of the United Kingdom, surrounds the shield. The motto which appears on the scroll, PLEIDIOL WYF I'M GWLAD, is taken from the national anthem of Wales; it was also an element of the Welsh designs for £1 coins minted from 1985 until 2000. The badge formerly appeared on the covers of Assembly Measures; since the 2011 referendum, it now appears on the cover of Acts passed by the Senedd and its escutcheon, ribbon and motto are depicted on the Welsh Seal.

Brochwel son of Cyngen, better known as Brochwel Ysgithrog, was a king of Powys in eastern Wales. The unusual epithet Ysgithrog has been translated as "of the canine teeth", "the fanged" or "of the tusk".

Powys Wenwynwyn or Powys Cyfeiliog was a Welsh kingdom which existed during the high Middle Ages. The realm was the southern portion of the former princely state of Powys which split following the death of Madog ap Maredudd of Powys in 1160: the northern portion (Maelor) went to Gruffydd Maelor and eventually became known as Powys Fadog; while the southern portion (Cyfeiliog) going to Owain Cyfeiliog and becoming known, eventually, as Powys Wenwynwyn after Prince Gwenwynwyn ab Owain, its second ruler.

The London County Council was granted a coat of arms in 1914 and a heraldic badge in 1956. The coat of arms can still be seen on buildings constructed by the council before its abolition in 1965.
Heraldry in Wales has a tradition distinct from that of English and Scottish heraldry. There is evidence that heraldry was already being used in Wales by the middle of the thirteenth century; for instance, in Gwynedd, two sons of Llywelyn the Great are recorded as having borne coats of arms in this period. Following the integration of Wales into England in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, the Welsh heraldic tradition became merged into that of England.
Owen de la Pole, also known as Owain ap Gruffydd ap Gwenwynwyn, was the heir presumptive to the Welsh principality of Powys Wenwynwyn until 1283 when it was abolished by the Parliament of Shrewsbury. He became the 1st Lord of Powis after the death of his father Gruffydd ap Gwenwynwyn c. 1287. He is not related to the English de la Pole family descended from William de la Pole, Chief Baron of the Exchequer in the following century, later Earls and Dukes of Suffolk.
Sir Gruffudd Vychan, also spelt in English sources as Griffith Vaughan, was a Welsh knight who supported the rebellion of Prince Owain Glyndŵr against the English, and captured the Lollard John Oldcastle, who was later immortalized by Shakespeare as John Falstaff. He was finally executed after the murder of Sir Christopher Talbot, son of John Talbot, 1st Earl of Shrewsbury.

Attributed arms are Western European coats of arms given retrospectively to persons real or fictitious who died before the start of the age of heraldry in the latter half of the 12th century. Once coats of arms were the established fashion of the ruling class, society expected a king to be armigerous. Arms were assigned to the knights of the Round Table, and then to biblical figures, to Roman and Greek heroes, and to kings and popes who had not historically borne arms. Individual authors often attributed different arms for the same person, although the arms for major figures eventually became fixed.

Ial or Yale was a commote of medieval Wales within the cantref of Maelor in the Kingdom of Powys. When the Kingdom was divided in 1160, Maelor became part of the Princely realm of Powys Fadog, and belonged to the Royal House of Mathrafal. Yale eventually merged with another commote and became the Lordship of Bromfield and Yale, later a royal lordship under the Tudors and Stuarts.
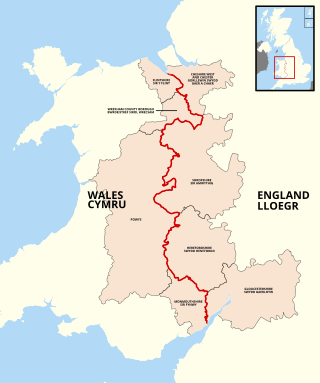
The England–Wales border, sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for 160 miles (260 km) from the Dee estuary, in the north, to the Severn estuary in the south, separating England and Wales.

The royal standards of England were narrow, tapering swallow-tailed heraldic flags, of considerable length, used mainly for mustering troops in battle, in pageants and at funerals, by the monarchs of England. In high favour during the Tudor period, the Royal English Standard was a flag that was of a separate design and purpose to the Royal Banner. It featured St George's Cross at its head, followed by a number of heraldic devices, a supporter, badges or crests, with a motto—but it did not bear a coat of arms. The Royal Standard changed its composition frequently from reign to reign, but retained the motto Dieu et mon droit, meaning God and my right; which was divided into two bands: Dieu et mon and Droyt.
This is a list of the coats of arms of the local authorities in Wales.
















