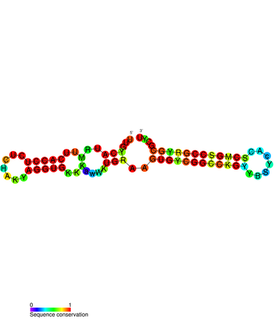
The fertility factor allows genes to be transferred from one bacterium carrying the factor to another bacterium lacking the factor by conjugation. The F factor was the first plasmid to be discovered. Unlike other plasmids, F factor is constitutive for transfer proteins due to a mutation in the gene finO. The F plasmid belongs to a class of conjugative plasmids that control sexual functions of bacteria with a fertility inhibition (Fin) system.
Addiction modules are toxin-antitoxin systems. Each consists of a pair of genes that specify two components: a stable toxin and an unstable antitoxin that interferes with the lethal action of the toxin. Found first in E. coli on low copy number plasmids, addiction modules are responsible for a process called the postsegregational killing effect. When bacteria lose these plasmid(s), the cured cells are selectively killed because the unstable antitoxin is degraded faster than the more stable toxin. The term "addiction" is used because the cell depends on the de novo synthesis of the antitoxin for cell survival. Thus, addiction modules are implicated in maintaining the stability of extrachromosomal elements.
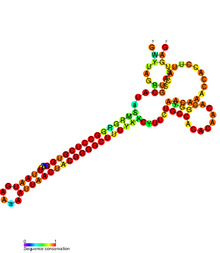
Sib RNA refers to a group of related non-coding RNA. They were originally named QUAD RNA after they were discovered as four repeat elements in Escherichia coli intergenic regions. The family was later renamed Sib when it was discovered that the number of repeats is variable in other species and in other E. coli strains.

In molecular biology the ArcZ RNA is a small non-coding RNA (ncRNA). It is the functional product of a gene which is not translated into protein. ArcZ is an Hfq binding RNA that functions as an antisense regulator of a number of protein coding genes.
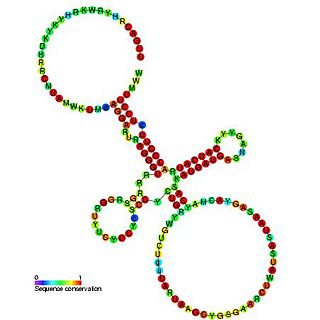
The hok/sok system is a postsegregational killing mechanism employed by the R1 plasmid in Escherichia coli. It was the first type I toxin-antitoxin pair to be identified through characterisation of a plasmid-stabilising locus. It is a type I system because the toxin is neutralised by a complementary RNA, rather than a partnered protein.
A killer yeast is a yeast, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is able to secrete one of a number of toxic proteins which are lethal to susceptible cells. These "killer toxins" are polypeptides that kill sensitive cells of the same or related species, often functioning by creating pores in target cell membranes. These yeast cells are immune to the toxic effects of the protein due to an intrinsic immunity. Killer yeast strains can be a problem in commercial processing because they can kill desirable strains. The killer yeast system was first described in 1963. Study of killer toxins helped to better understand the secretion pathway of yeast, which is similar to those of more complex eukaryotes. It also can be used in treatment of some diseases, mainly those caused by fungi.
In a screen of the Bacillus subtilis genome for genes encoding ncRNAs, Saito et al. focused on 123 intergenic regions (IGRs) over 500 base pairs in length, the authors analyzed expression from these regions. Seven IGRs termed bsrC, bsrD, bsrE, bsrF, bsrG, bsrH and bsrI expressed RNAs smaller than 380 nt. All the small RNAs except BsrD RNA were expressed in transformed Escherichia coli cells harboring a plasmid with PCR-amplified IGRs of B. subtilis, indicating that their own promoters independently express small RNAs. Under non-stressed condition, depletion of the genes for the small RNAs did not affect growth. Although their functions are unknown, gene expression profiles at several time points showed that most of the genes except for bsrD were expressed during the vegetative phase, but undetectable during the stationary phase. Mapping the 5' ends of the 6 small RNAs revealed that the genes for BsrE, BsrF, BsrG, BsrH, and BsrI RNAs are preceded by a recognition site for RNA polymerase sigma factor σA.
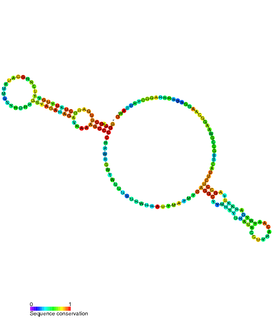
PtaRNA1 is a family of non-coding RNAs. Homologs of PtaRNA1 can be found in the proteobacteria families, Betaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria. In all cases the PtaRNA1 is located anti-sense to a short protein-coding gene. In Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria, this gene is annotated as XCV2162 and is included in the plasmid toxin family of proteins.
Bacterial small RNAs (sRNA) are small RNAs produced by bacteria; they are 50- to 500-nucleotide non-coding RNA molecules, highly structured and containing several stem-loops. Numerous sRNAs have been identified using both computational analysis and laboratory-based techniques such as Northern blotting, microarrays and RNA-Seq in a number of bacterial species including Escherichia coli, the model pathogen Salmonella, the nitrogen-fixing alphaproteobacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti, marine cyanobacteria, Francisella tularensis, Streptococcus pyogenes, the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus, and the plant pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae. Bacterial sRNAs affect how genes are expressed within bacterial cells via interaction with mRNA or protein, and thus can affect a variety of bacterial functions like metabolism, virulence, environmental stress response, and structure.

The TisB-IstR toxin-antitoxin system is the first known toxin-antitoxin system which is induced by the SOS response in response to DNA damage.

A toxin-antitoxin system is a set of two or more closely linked genes that together encode both a "toxin" protein and a corresponding "antitoxin". Toxin-antitoxin systems are widely distributed in prokaryotes, and organisms often have them in multiple copies. When these systems are contained on plasmids – transferable genetic elements – they ensure that only the daughter cells that inherit the plasmid survive after cell division. If the plasmid is absent in a daughter cell, the unstable antitoxin is degraded and the stable toxic protein kills the new cell; this is known as 'post-segregational killing' (PSK).
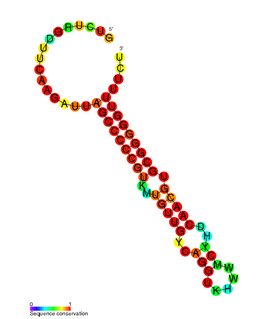
RdlD RNA is a family of small non-coding RNAs which repress the protein LdrD in a type I toxin-antitoxin system. It was discovered in Escherichia coli strain K-12 in a long direct repeat (LDR) named LDR-D. This locus encodes two products: a 35 amino acid peptide toxin (ldrD) and a 60 nucleotide RNA antitoxin. The 374nt toxin mRNA has a half-life of around 30 minutes while rdlD RNA has a half-life of only 2 minutes. This is in keeping with other type I toxin-antitoxin systems.
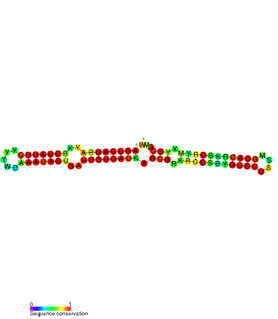
The SymE-SymR toxin-antitoxin system consists of a small symbiotic endonuclease toxin, SymE, and a non-coding RNA symbiotic RNA antitoxin, SymR, which inhibits SymE translation. SymE-SymR is a type I toxin-antitoxin system, and is under regulation by the antitoxin, SymR. The SymE-SymR complex is believed to play an important role in recycling damaged RNA and DNA. The relationship and corresponding structures of SymE and SymR provide insight into the mechanism of toxicity and overall role in prokaryotic systems.
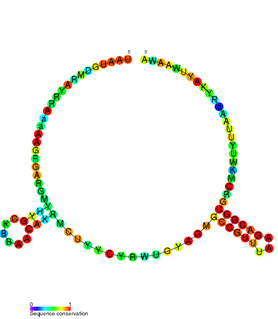
The TxpA/RatA toxin-antitoxin system was first identified in Bacillus subtilis. It consists of a non-coding 222nt sRNA called RatA and a protein toxin named TxpA.

The par stability determinant is a 400 bp locus of the pAD1 plasmid which encodes a type I toxin-antitoxin system in Enterococcus faecalis. It was the first such plasmid addiction module to be found in gram-positive bacteria.
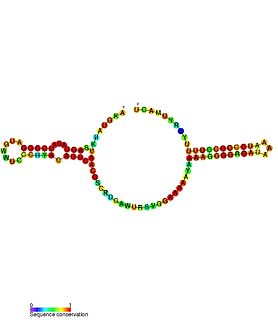
Escherichia coli contains a number of small RNAs located in intergenic regions of its genome. The presence of at least 55 of these has been verified experimentally. 275 potential sRNA-encoding loci were identified computationally using the QRNA program. These loci will include false positives, so the number of sRNA genes in E. coli is likely to be less than 275. A computational screen based on promoter sequences recognised by the sigma factor sigma 70 and on Rho-independent terminators predicted 24 putative sRNA genes, 14 of these were verified experimentally by northern blotting. The experimentally verified sRNAs included the well characterised sRNAs RprA and RyhB. Many of the sRNAs identified in this screen, including RprA, RyhB, SraB and SraL, are only expressed in the stationary phase of bacterial cell growth. A screen for sRNA genes based on homology to Salmonella and Klebsiella identified 59 candidate sRNA genes. From this set of candidate genes, microarray analysis and northern blotting confirmed the existence of 17 previously undescribed sRNAs, many of which bind to the chaperone protein Hfq and regulate the translation of RpoS. UptR sRNA transcribed from the uptR gene is implicated in suppressing extracytoplasmic toxicity by reducing the amount of membrane-bound toxic hybrid protein.
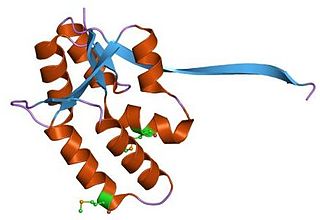
VapBC is the largest family of type II toxin-antitoxin system genetic loci in prokaryotes. VapBC operons consist of two genes: VapC encodes a toxic PilT N-terminus (PIN) domain, and VapB encodes a matching antitoxin. The toxins in this family are thought to perform RNA cleavage, which is inhibited by the co-expression of the antitoxin, in a manner analogous to a poison and antidote.
The SrnB-SrnC toxin-antitoxin system of the F plasmid is homologous to the hok/sok system of R1. Like the hok/sok system, it performs a post-segregational killing function, ensuring that all surviving daughter cells inherit the F plasmid. The system consists of srnB' mRNA which is relatively stable and codes for the toxic protein SrnB, srnB mRNA, a regulatory element and srnC mRNA, an antitoxin with complementarity to srnB.
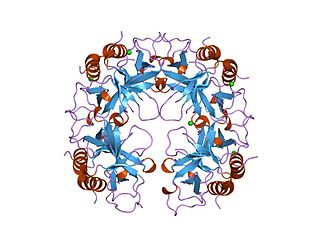
The CcdA/CcdB Type II Toxin-antitoxin system is one example of the bacterial toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems that encode two proteins, one a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation (toxin) and the other its specific antidote (antitoxin). These systems preferentially guarantee growth of plasmid-carrying daughter cells in a bacterial population by killing newborn bacteria that have not inherited a plasmid copy at cell division.
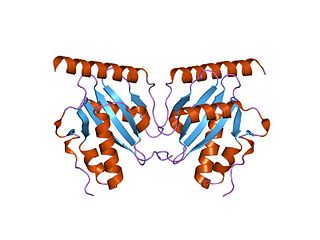
The parDE type II toxin-antitoxin system is one example of the bacterial toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems that encode two proteins, one a potent inhibitor of cell proliferation (toxin) and the other its specific antidote (antitoxin). These systems preferentially guarantee growth of plasmid-carrying daughter cells in a bacterial population by killing newborn bacteria that have not inherited a plasmid copy at cell division.