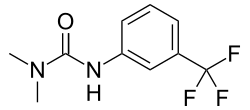
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name N,N-Dimethyl-N′-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]urea | |
| Other names 1,1-Dimethyl-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]urea; 1,1-Dimethyl-3-(α,α,α-trifluoro-m-tolyl)-urea; 3-(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea; 3-(m-Trifluoromethylphenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea; C 2059; Ciba 2059; Cotoran; Cotoran 85DF; Fluomethuron; Lanex; N-(3-Trifluoromethylphenyl)-N′,N′-Dimethylurea; N-(m-Trifluoromethylphenyl)-N′,N′-Dimethylurea; Pakhtaran | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.819 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H11F3N2O | |
| Molar mass | 232.206 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.39 g/cm3 [1] |
| Melting point | 163 to 164 °C (325 to 327 °F; 436 to 437 K) [1] |
| 90 ppm (0.0105%) at 20 °C [1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Fluometuron is an herbicide. In the United States it was approved for use on cotton and sugarcane crops in 1974, but since 1986 is only approved for use on cotton. [2]
Fluometron's herbicide resistance class is Group C, (Australia), C2 (global), Group 7, (numeric, i.e. Group 5, due to a merger). It is photosynthesis inhibitor. [3]