Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales causing plant fungal diseases.
Fusarium oxysporum, an ascomycete fungus, comprises all the species, varieties and forms recognized by Wollenweber and Reinking within an infrageneric grouping called section Elegans. It is part of the family Nectriaceae.

In botanical nomenclature, a form is one of the "secondary" taxonomic ranks, below that of variety, which in turn is below that of species; it is an infraspecific taxon. If more than three ranks are listed in describing a taxon, the "classification" is being specified, but only three parts make up the "name" of the taxon: a genus name, a specific epithet, and an infraspecific epithet.
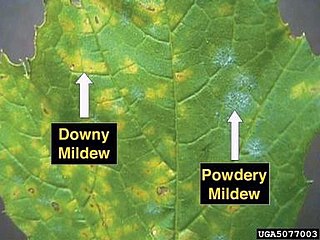
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of ascomycete fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as the signs of the causal pathogen are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. This mycelial layer may quickly spread to cover all of the leaves. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.

Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

In biological taxonomy, race is an informal rank in the taxonomic hierarchy for which various definitions exist. Sometimes it is used to denote a level below that of subspecies, while at other times it is used as a synonym for subspecies. It has been used as a higher rank than strain, with several strains making up one race. Races may be genetically distinct populations of individuals within the same species, or they may be defined in other ways, e.g. geographically, or physiologically. Genetic isolation between races is not complete, but genetic differences may have accumulated that are not (yet) sufficient to separate species.
In botany, an infraspecific name is the scientific name for any taxon below the rank of species, i.e. an infraspecific taxon or infraspecies. A "taxon", plural "taxa", is a group of organisms to be given a particular name. The scientific names of botanical taxa are regulated by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN). This specifies a three part name for infraspecific taxa, plus a connecting term to indicate the rank of the name. An example of such a name is Astrophytum myriostigma subvar. glabrum, the name of a subvariety of the species Astrophytum myriostigma.

Stem rust, also known as cereal rust, black rust, red rust or red dust, is caused by the fungus Puccinia graminis, which causes significant disease in cereal crops. Crop species that are affected by the disease include bread wheat, durum wheat, barley and triticale. These diseases have affected cereal farming throughout history. The annual recurrence of stem rust of wheat in North Indian plains was discovered by K.C. Mehta. Since the 1950s, wheat strains bred to be resistant to stem rust have become available. Fungicides effective against stem rust are available as well.

Wheat leaf rust is a fungal disease that affects wheat, barley, rye stems, leaves and grains. In temperate zones it is destructive on winter wheat because the pathogen overwinters. Infections can lead up to 20% yield loss. The pathogen is a Puccinia rust fungus. It is the most prevalent of all the wheat rust diseases, occurring in most wheat-growing regions. It causes serious epidemics in North America, Mexico and South America and is a devastating seasonal disease in India. P. triticina is heteroecious, requiring two distinct hosts.

Blumeria graminis is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on grasses, including cereals. It is the only species in the genus Blumeria. It has also been called Erysiphe graminis and Oidium monilioides or Oidium tritici.
This is a glossary of some of the terms used in phytopathology.

Ug99 is a lineage of wheat stem rust, which is present in wheat fields in several countries in Africa and the Middle East and is predicted to spread rapidly through these regions and possibly further afield, potentially causing a wheat production disaster that would affect food security worldwide. In 2005 the noted green revolution pioneer Norman Borlaug brought great attention to the problem, and most subsequent efforts can be traced to his advocacy. It can cause up to 100% crop losses and is virulent against many resistance genes which have previously protected wheat against stem rust.
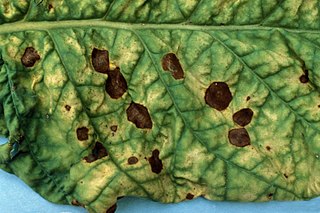
Alternaria alternata is a fungus causing leaf spots, rots, and blights on many plant parts, and other diseases. It is an opportunistic pathogen on over 380 host species of plant.
Alternaria citri is a fungal plant pathogen that causes black rot in citrus plants.
Alternaria dauci is a plant pathogen. The English name of the disease it incites is "carrot leaf blight".

Cochliobolus carbonum is one of more than 40 species of filamentous ascomycetes belonging to the genus Cochliobolus. This pathogen has a worldwide distribution, with reports from Australia, Brazil, Cambodia, Canada, China, Congo, Denmark, Egypt, India, Kenya, New Zealand, Nigeria, Solomon Islands, and the United States. Cochliobolus carbonum is one of the most aggressive members of this genus infecting sorghum, corn and apple. As one of the most devastating pathogens of sweet corn, C. carbonum causes Northern leaf spot and ear rot disease while the asexual stage causes Helminthosporium corn leaf spot. Cochliobolus carbonum is pathogenic to all organs of the corn plant including root, stalk, ear, kernel, and sheath. However, symptoms of infection show distinct manifestations in different plant parts: whole plant - seedling blight affects the whole plant, leaf discoloration and mycelial growth, black fungal spores and lesions appear on inflorescences and glumes, and grain covered with very dark brown to black mycelium which gives a characteristic charcoal appearance due to the production of conidia.

Puccinia coronata is a plant pathogen and causal agent of oat and barley crown rust. The pathogen occurs worldwide, infecting both wild and cultivated oats. Crown rust poses a threat to barley production, because the first infections in barley occur early in the season from local inoculum. Crown rusts have evolved many different physiological races within different species in response to host resistance. Each pathogenic race can attack a specific line of plants within the species typical host. For example, there are over 290 races of P. coronata. Crops with resistant phenotypes are often released, but within a few years virulent races have arisen and P. coronata can infect them.
Ruth Florence Allen (1879–1963) was an American botanist and plant pathologist and the first woman to earn her Ph.D. in botany from the University of Wisconsin. Her doctorate research focused on the reproduction and cell biology of ferns, particularly the phenomenon of apogamy. Later in her career, Allen shifted her focus to plant pathology. Her major contribution to the field of mycology was furthering the understanding of rust fungi, a group of economically important plant pathogens. Allen completed many studies on Puccinia graminis, once considered a catastrophically damaging disease-causing agent in cereal crops before the discovery of current management measures.
Puccinia coronata f. sp. avenae is the variation of the crown rust fungus which infects oat plants. Almost every growing region of oat has been affected by this pathogen at one point or another. During particularly bad epidemics, the worldwide crop yields have been reduced by up to 40%. One reason why Pca has such a prominent effect is that the conditions which favor oat production also favor the growth and inoculation of the rusts: Meaning that years in which the highest yields of crops are expected are the same years in which losses are the highest as well. Pca urediniospores germinate the best at temperature between 10–30 °C (50–86 °F) with germ-tube growth optimized at 20 °C (68 °F).