
Elizabethton is a city in, and the county seat of Carter County, Tennessee, United States. Elizabethton is the historical site of the first independent American government located west of both the Eastern Continental Divide and the original Thirteen Colonies.

Tazewell is a town in and the county seat of Claiborne County, Tennessee, United States. The population was 2,165 at the 2000 census, 2,218 at the 2010 census, and 2,348 at the 2020 census. The town is named for Tazewell, Virginia, which itself was named for Henry Tazewell (1753–1799), a U.S. senator from Virginia.

Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County, Tennessee, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state's third-most-populous city after Nashville and Memphis. It is the principal city of the Knoxville metropolitan area, which had a population of 879,773 in 2020.

East Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of Tennessee defined in state law. Geographically and socioculturally distinct, it comprises approximately the eastern third of the U.S. state of Tennessee. East Tennessee consists of 33 counties, 30 located within the Eastern Time Zone and three counties in the Central Time Zone, namely Bledsoe, Cumberland, and Marion. East Tennessee is entirely located within the Appalachian Mountains, although the landforms range from densely forested 6,000-foot (1,800 m) mountains to broad river valleys. The region contains the major cities of Knoxville and Chattanooga, Tennessee's third and fourth largest cities, respectively, and the Tri-Cities, the state's sixth largest population center.

The Wilderness Road was one of two principal routes used by colonial and early national era settlers to reach Kentucky from the East. Although this road goes through the Cumberland Gap into southern Kentucky and northern Tennessee, the other is sometimes called the "Cumberland Road" because it started in Fort Cumberland in Maryland. Despite Kentucky Senator Henry Clay's advocacy of this route, early in the 19th century, the northern route was selected for the National Road, connecting near Washington, Pennsylvania into the Ohio Valley of northern Kentucky and Ohio.

Fountain City is a neighborhood in northern Knoxville, Tennessee, in the southeastern United States. Although not a census-designated place, the populations of the two ZIP codes that serve Fountain City— 37918 and 37912— were 36,815 and 18,695, respectively, as of the 2000 U.S. census. At the time of its annexation by the city of Knoxville in 1962, Fountain City was the largest unincorporated community in the United States.

The Overmountain Men were American frontiersmen from west of the Blue Ridge Mountains which are the leading edge of the Appalachian Mountains, who took part in the American Revolutionary War. While they were present at multiple engagements in the war's southern campaign, they are best known for their role in the American victory at the Battle of Kings Mountain in 1780. The term "overmountain" arose because their settlements were west of, or "over", the Blue Ridge, which was the primary geographical boundary dividing several of the 13 American states from the Native American lands to the west. The Overmountain Men hailed from parts of Virginia, North Carolina, and what is now Tennessee and Kentucky.

Fort Nashborough, also known as Fort Bluff, Bluff Station, French Lick Fort, Cumberland River Fort and other names, was the stockade established in early 1779 in the French Lick area of the Cumberland River valley, as a forerunner to the settlement that would become the city of Nashville, Tennessee. The fort was not a military garrison. The log stockade was square in shape and covered 2 acres (8,100 m2). It contained 20 log cabins and was protection for the settlers against wild animals and Indians. James Robertson and John Donelson are considered the founders, and colloquially, the "founders of Tennessee". The fort was abandoned in 1794, but the settlement, now the town of Nashville, became the capital of the new state of Tennessee in 1796.

Tennessee is one of the 50 states of the United States. What is now Tennessee was initially part of North Carolina, and later part of the Southwest Territory. It was admitted to the Union on June 1, 1796, as the 16th state. Tennessee earned the nickname "The Volunteer State" during the War of 1812, when many Tennesseans helped with the war effort, especially during the Americans victory at the Battle of New Orleans in 1815. The nickname became even more applicable during the Mexican–American War in 1846, after the Secretary of War asked the state for 2,800 soldiers, and Tennessee sent over 30,000 volunteers.

The Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals since prehistoric times, and Cherokees gathered there. As Europeans began settling the Trans-Appalachian frontier, the shoals proved strategic militarily, as well as shaped the economies of Tennessee and Kentucky. Today, the shoals are protected as a National Historic Landmark and are maintained as part of Sycamore Shoals State Historic Park.

A longhunter was an 18th-century explorer and hunter who made expeditions into the American frontier for as much as six months at a time.

The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American settlers on the frontier. Most of the events took place in the Upper South region. While the fighting stretched across the entire period, there were extended periods with little or no action.

Gregory Bald is a mountain in the Great Smoky Mountains. It has an elevation of 4,949 feet above sea level. The mountain's majestic summit makes it a popular hiking destination. Another feature that attracts many visitors are the flame azaleas that bloom over the bald every summer. The azaleas reach peak bloom around mid-to-late June.
Avery's Trace was the principal road used by settlers travelling from the Knoxville area in East Tennessee to the Nashville area from 1788 to the mid-1830s.

The Tellico Blockhouse was an early American outpost located along the Little Tennessee River in what developed as Vonore, Monroe County, Tennessee. Completed in 1794, the blockhouse was a US military outpost that operated until 1807; the garrison was intended to keep peace between the nearby Overhill Cherokee towns and encroaching early Euro-American pioneers in the area in the wake of the Cherokee–American wars.
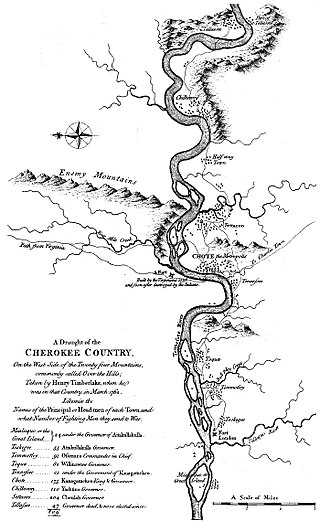
Overhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 18th-century European traders and explorers from British colonies along the Atlantic coast, as they had to cross the mountains to reach these settlements.

Chilhowee was a prehistoric and historic Native American site in present-day Blount and Monroe counties in Tennessee, in what were the Southeastern Woodlands. Although now submerged by the Chilhowee Lake impoundment of the Little Tennessee River, the Chilhowee site was home to a substantial 18th-century Overhill Cherokee town. It may have been the site of the older Creek village "Chalahume" visited by Spanish explorer Juan Pardo in 1567. The Cherokee later pushed the Muscogee Creek out of this area.
North Knoxville is the section of Knoxville, Tennessee, USA, that lies north of the city's downtown area. It is concentrated around Broadway (US-441), Clinton Highway (US-25W), Tazewell Pike (TN-331), Washington Pike, and adjacent roads, and includes the neighborhoods of Fountain City, Inskip-Norwood, Oakwood-Lincoln Park, Old North Knoxville, Fourth and Gill, North Hills, and Whittle Springs. North Knoxville is bisected by Sharp's Ridge, a 7-mile (11 km) elongate ridge that rises prominently above the surrounding terrain.

Buchanan's Station was a fortified stockade established around 1784 in Tennessee. Founded by Major John Buchanan, the settlement was located in what is today the Donelson neighborhood of Nashville, Tennessee. On September 30, 1792, it was the site of the critical Battle of Buchanan's Station during the Cherokee–American wars of the late eighteenth century. The assault by a combined force of around 300 Chickamauga Cherokee, Muscogee Creek, and Shawnee, nominally led by Chief John Watts, was repelled by 15 gunmen under Major Buchanan defending the station. Although smaller raids continued in the region, it was the last major Native American attack on the American settlements in the Cumberland.
The Battle of Island Flats was the opening battle of the American War of Independence in the west. The battle was fought in July 1776, and pitted the American regional Patriot militia against the British allied Cherokee forces in the Overmountain region of the American frontier.

















