
Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

Whitehorse is the capital of Yukon, and the largest city in Northern Canada. It was incorporated in 1950 and is located at kilometre 1426 on the Alaska Highway in southern Yukon. Whitehorse's downtown and Riverdale areas occupy both shores of the Yukon River, which rises in British Columbia and meets the Bering Sea in Alaska. The city was named after the White Horse Rapids for their resemblance to the mane of a white horse, near Miles Canyon, before the river was dammed.

Yukon is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It is the third-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 45,148 as of 2023. However, Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement in any of the three territories.

Beaver Creek is a community in Yukon, Canada. Located at kilometre 1870.6 of the Alaska Highway, 1 NM southeast of Beaver Creek Airport and close to the Alcan - Beaver Creek Border Crossing, it is Canada's westernmost community. The community's main employers are a Canada Border Services Agency port, the White River First Nation and a number of tourist lodges.
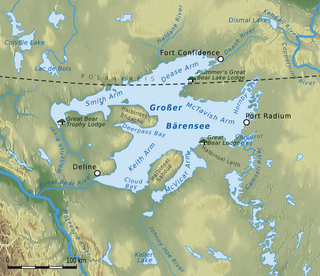
Great Bear Lake is a lake in the boreal forest of Canada. It is the largest lake entirely in Canada, the fourth-largest in North America, and the eighth-largest in the world. The lake is in the Northwest Territories, on the Arctic Circle between 65 and 67 degrees of northern latitude and between 118 and 123 degrees western longitude, 156 m (512 ft) above sea level.

Dawson City, officially the City of Dawson, is a city in the Canadian territory of Yukon. It is inseparably linked to the Klondike Gold Rush (1896–1899). Its population was 1,577 as of the 2021 census, making it the second-largest city in Yukon.

Bennett Lake is a lake in the Province of British Columbia and Yukon Territory in northwestern Canada, at an elevation of 642 m (2,106 ft). It is just north of the border with the United States state of Alaska, near the Alaskan port of Skagway.

White Pass, also known as the Dead Horse Trail, is a mountain pass through the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains on the border of the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia, Canada. It leads from Skagway, Alaska, to the chain of lakes at the headwaters of the Yukon River.

The Liard River of the North American boreal forest flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows 1,115 km (693 mi) southeast through British Columbia, marking the northern end of the Rocky Mountains and then curving northeast back into Yukon and Northwest Territories, draining into the Mackenzie River at Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The river drains approximately 277,100 km2 (107,000 sq mi) of boreal forest and muskeg.

Watson Lake is a town in Yukon, Canada, located at mile 635 on the Alaska Highway close to the British Columbia border. It has a population of 790 in 2016. The town is named for Frank Watson, an American-born trapper and prospector, who settled in the area at the end of the 19th century.
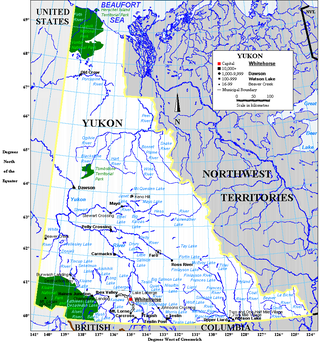
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenery, snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.

Ross River is an unincorporated community in Yukon, Canada. It lies at the junction of the Ross River and the Pelly River, along the Canol Road, not far from the Campbell Highway. Primary access to the Campbell Highway is via a nine-mile access road. Formerly it was accessed along a six-mile Canol Road section that is no longer maintained. It is serviced by Ross River Airport, used mainly for charter and scheduled flights to and from Whitehorse and Watson Lake.
Marsh Lake is an unincorporated community on the Alaska Highway on the shores of Marsh Lake southeast of Whitehorse in Canada's Yukon. The area was organized in 2001, as a local area council to help the residents with some form of municipal government.

The Northwest Territories is a territory in Northern Canada, specifically in Northwestern Canada between Yukon Territory and Nunavut including part of Victoria Island, Melville Island, and other islands on the western Arctic Archipelago. Originally a much wider territory enclosing most of central and northern Canada, the Northwest Territories was created in 1870 from the Hudson's Bay Company's holdings that were sold to Canada from 1869-1870. In addition, Alberta and Saskatchewan were formed from the territory in 1905. In 1999, it was divided again: the eastern portion became the new territory of Nunavut. Yellowknife stands as its largest city and capital. It has a population of 42,800 and has an area of 532,643 sq mi (1,379,540 km2). The current territory lies west of Nunavut, north of latitude 60° north, and east of Yukon.

The Ogilvie Mountains are a mountain range in the Yukon Territory of northwestern Canada.

Swift River is a settlement in the Canadian territory of Yukon, primarily a service stop on the Alaska Highway at historical mile 733. The radius of the area is estimated to be about 22.71 square kilometres ). The only permanent population owns and operates, or is employed at, the area's commercial highway establishment. Other residents are transient, working at the Yukon government's highway maintenance camp.

The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a group of volcanoes and associated lava flows in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located on the Tahltan Highland, it is 40 kilometres southeast of Telegraph Creek and 85 kilometres southwest of Dease Lake. The complex encompasses a broad, steep-sided lava plateau that extends over 1,000 square kilometres. Its highest summit is 2,786 metres in elevation, making the MEVC the highest of four large complexes in an extensive north–south trending volcanic region. It is obscured by an ice cap characterized by several outlet glaciers that stretch out to lower altitudes.
The Yukon Plateau is a plateau located in the Yukon Territory, comprising much of the central and southern Yukon Territory and the far northern part of British Columbia, Canada between Tagish Lake (W) and the Cassiar Mountains (E) and north of the Nakina River.
Snafu Lake is a lake of southern Yukon, Canada, about 25 to 30 km north of the border with British Columbia. It is drained by Snafu Creek.
















