
VideoLAN is a non-profit organization which develops software for playing video and other media formats. It originally developed two programs for media streaming, VideoLAN Client (VLC) and VideoLAN Server (VLS), but most of the features of VLS have been incorporated into VLC, with the result renamed VLC media player.

Asterisk is a software implementation of a private branch exchange (PBX). In conjunction with suitable telephony hardware interfaces and network applications, Asterisk is used to establish and control telephone calls between telecommunication endpoints such as customary telephone sets, destinations on the public switched telephone network (PSTN) and devices or services on voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) networks. Its name comes from the asterisk (*) symbol for a signal used in dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) dialing.

Netatalk is a free, open-source implementation of the Apple Filing Protocol (AFP). It allows Unix-like operating systems to serve as file servers for Macintosh computers running macOS or Classic Mac OS.

SipXecs is a free software enterprise communications system. It was initially developed by Pingtel Corporation in 2003 as a voice over IP telephony server located in Boston, MA. The server was later extended with additional collaboration capabilities as part of the SIPfoundry project. Since its extension, sipXecs now acts as a software implementation of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), making it a full IP-based communications system.
The following tables compare general and technical information between a number of notable IRC client programs which have been discussed in independent, reliable prior published sources.

Watcom C/C++ is an integrated development environment (IDE) product from Watcom International Corporation for the C, C++, and Fortran programming languages. Watcom C/C++ was a commercial product until it was discontinued, then released under the Sybase Open Watcom Public License as Open Watcom C/C++. It features tools for developing and debugging code for DOS, OS/2, Windows, and Linux operating systems, which are based upon 16-bit x86, 32-bit IA-32, or 64-bit x86-64 compatible processors.
Ports collections are the sets of makefiles and patches provided by the BSD-based operating systems, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and OpenBSD, as a simple method of installing software or creating binary packages. They are usually the base of a package management system, with ports handling package creation and additional tools managing package removal, upgrade, and other tasks. In addition to the BSDs, a few Linux distributions have implemented similar infrastructure, including Gentoo's Portage, Arch's Arch Build System (ABS), CRUX's Ports and Void Linux's Templates.
A Bluetooth stack is software that is an implementation of the Bluetooth protocol stack.

FreePBX is a web-based open-source graphical user interface (GUI) that manages Asterisk, a voice over IP (VoIP) and telephony server.

Jitsi is a collection of free and open-source multiplatform voice (VoIP), video conferencing and instant messaging applications for the Web platform, Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS and Android. The Jitsi project began with the Jitsi Desktop. With the growth of WebRTC, the project team focus shifted to the Jitsi Videobridge for allowing web-based multi-party video calling. Later the team added Jitsi Meet, a full video conferencing application that includes web, Android, and iOS clients. Jitsi also operates meet.jit.si, a version of Jitsi Meet hosted by Jitsi for free community use. Other projects include: Jigasi, lib-jitsi-meet, Jidesha, and Jitsi.
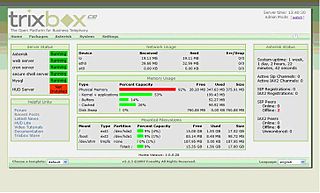
trixbox was a software PBX based on Asterisk.

Elastix is a unified communications server software that brings together IP PBX, email, IM, faxing and collaboration functionality. It has a Web interface and includes capabilities such as a call center software with predictive dialing.

Jami is a SIP-compatible distributed peer-to-peer softphone and SIP-based instant messenger for Linux, Microsoft Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. Jami was developed and maintained by the Canadian company Savoir-faire Linux, and with the help of a global community of users and contributors, Jami positions itself as a potential free Skype replacement.
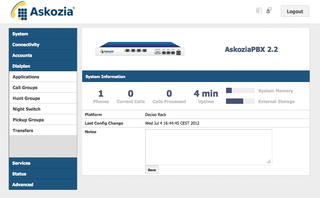
AskoziaPBX is a closed source telephone system firmware. It is a fork of the m0n0wall project and uses the Asterisk private branch exchange (PBX) software to realize all telephony functions.
GNU SIP Witch is free SIP server software with peer-to-peer capabilities from the GNU Project. It is the GNU implementation of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), which is used for the routing of calls.

OBS Studio is a free and open-source, cross-platform screencasting and streaming app. It is available for Windows, macOS, Linux distributions, and BSD. The OBS Project raises funds on Open Collective and Patreon.
ZeroTier, Inc. is a software company with a freemium business model based in Irvine, California. ZeroTier provides proprietary software, SDKs and commercial products and services to create and manage virtual software-defined networks. The company's flagship end-user product ZeroTier One is a client application that enables devices such as PCs, phones, servers and embedded devices to securely connect to peer-to-peer virtual networks.












