
Shuffling is a procedure used to randomize a deck of playing cards to provide an element of chance in card games. Shuffling is often followed by a cut, to help ensure that the shuffler has not manipulated the outcome.

The Magician (I), also known as The Magus or The Juggler, is the first trump or Major Arcana card in most traditional Tarot decks. It is used in game playing and divination; in the English-speaking world, the divination meaning is much better-known.

The cups and balls is a performance of magic with innumerable adaptations. Street gambling variations performed by conmen were known as Bunco Booths. A typical cups and balls routine includes many of the most fundamental effects of magic: the balls can vanish, appear, transpose, reappear and transform. Basic skills, such as misdirection, manual dexterity, sleight of hand, and audience management are also essential to most cups and balls routines. As a result, mastery of the cups and balls is considered by many as the litmus test of a magician's skill with gimmick style tricks. Magician John Mulholland wrote that Harry Houdini had expressed the opinion that no one could be considered an accomplished magician until he had mastered the cups and balls. Professor Hoffman called the cups and balls "the groundwork of all legerdemain".
Sleight of hand refers to fine motor skills when used by performing artists in different art forms to entertain or manipulate. It is closely associated with close-up magic, card magic, card flourishing and stealing. Because of its heavy use and practice by magicians, sleight of hand is often confused as a branch of magic; however, it is a separate genre of entertainment and many artists practice sleight of hand as an independent skill. Sleight of hand pioneers with worldwide acclaim include Dan and Dave, Ricky Jay, Derek DelGaudio, David Copperfield, Yann Frisch, Norbert Ferré, Dai Vernon, Cardini, Tony Slydini and Helder Guimarães.
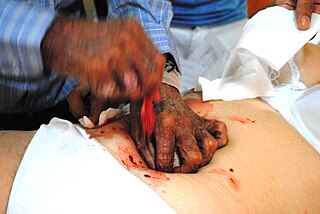
Psychic surgery is a pseudoscientific medical fraud in which practitioners create the illusion of performing surgery with their bare hands and use sleight of hand, fake blood, and animal parts to convince the patient that diseased lesions have been removed and that the incision has spontaneously healed.

Tweezers are small hand tools used for grasping objects too small to be easily handled with the human fingers. Tweezers are thumb-driven forceps most likely derived from tongs used to grab or hold hot objects since the dawn of recorded history. In a scientific or medical context, they are normally referred to as just "forceps", a name that is used together with other grasping surgical instruments that resemble pliers, pincers and scissors-like clamps.

Card manipulation is the branch of magic that deals with creating effects using sleight of hand techniques involving playing cards. Card manipulation is often used in magical performances, especially in close-up, parlor, and street magic. Some of the most recognized names in this field include Dai Vernon, Tony Slydini, Ed Marlo, S.W. Erdnase, Richard Turner, John Scarne, and Ricky Jay. Before becoming world-famous for his escapes, Houdini billed himself as "The King of Cards". Among the more well-known card tricks relying on card manipulation are Ambitious Card, and Three-card Monte, a common street hustle also known as Find the Lady.

Coin magic is the manipulating of coins to entertain audiences. Because coins are small, most coin tricks are considered close-up magic or table magic, as the audience must be close to the performer to see the effects. Though stage conjurers generally do not use coin effects, coin magic is sometimes performed onstage using large coins. In a different type of performance setting, a close-up coin magician will use a large video projector so the audience can see the magic on a big screen. Coin magic is generally considered harder to master than other close-up techniques such as card magic, as it requires great skill and grace to perform convincingly, and this requires much practice to acquire.

A thumb tip is a magician's prop designed to fit over and appear to be the magician's thumb used for vanishing, producing, or switching small objects. A classic effect is to have a silk handkerchief or other small object pressed into the top of the left fist. After pushing it well in with the right thumb, the left fist is opened to show the silk has disappeared. Alternatively, a lit cigarette, liquid, salt or other small objects can be made to disappear in a similar manner.
This is a glossary of conjuring terms used by magicians.
In the retention of vision vanish, the magician places a coin or small object between the fingers and the thumb of the right hand. The left hand is palm up with the palm slightly tilted towards the audience. The right approaches and displays the object on the left palm for a second or so, held on opposite sides of a diameter. Then the right hand moves away empty as the fingers of the left hand close over the object. After a brief pause the left hand is shown empty and the coin has disappeared. In some versions the right hand can also be seen empty, leaving no clue as to where the coin went.

Palming is a technique for holding or concealing an object in the hand. It is used frequently by magicians to conceal a card, coin, or other object. When it is done skillfully, the hand containing the palmed object is perceived to be completely empty.

The hat-trick is a classic magic trick where a performer will produce an object out of an apparently empty top hat.

Close-up magic is magic performed in an intimate setting usually no more than 3 meters from one's audience and is usually performed while sitting at a table.

The Tarbell Course in Magic is a notable encyclopedia of magic amongst professional and amateur magicians. It has eight volumes; the first five were part of the original home-study correspondence course compiled in 1928 by Dr. Harlan Tarbell, the remaining three volumes being added on later.

Chink-a-chink is a simple close-up magic coin trick in which a variety of small objects, usually four, appear to magically transport themselves from location to location when covered by the performer's hands, until the items end up gathered together in the same place. Variations, especially the Sympathetic Coins also known as Coins-n-Cards, have been performed since the 1800s. Popular modern variations are Shadow Coins and Matrix. A variation using playing cards as the objects is known as Sympathetic Aces.

In music performance and education, thumb position, not a traditional position, is a string instrument playing technique used to facilitate playing in the upper register of the double bass, cello, and related instruments, such as the electric upright bass. To play passages in this register, the player shifts his or her hand out from behind the neck and curves the hand, using the side of the thumb to press down the string; in effect, the side of the thumb becomes a movable nut (capo).
The Bamberg Magical Dynasty were a Dutch family of magicians. Six generations of Dutch magicians were named Bamberg. The Bambergs were an upper middle-class unorthodox Jewish family. The oldest sons were magicians and carried on the tradition to next the generation. This tradition was not always exclusive to just the oldest son; Theo Bamberg's two younger brothers were also magicians. Three Bambergs were court magicians entertaining the royal family. This chain was unbroken for 165 years, from the 18th to the 20th centuries.

Magic, which encompasses the subgenres of illusion, stage magic, and close up magic, among others, is a performing art in which audiences are entertained by tricks, effects, or illusions of seemingly impossible feats, using natural means. It is to be distinguished from paranormal magic which are effects claimed to be created through supernatural means. It is one of the oldest performing arts in the world.















