In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder.

gzip is a file format and a software application used for file compression and decompression. The program was created by Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler as a free software replacement for the compress program used in early Unix systems, and intended for use by GNU. Version 0.1 was first publicly released on 31 October 1992, and version 1.0 followed in February 1993.

In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes".

In computer science, a heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property: In a max heap, for any given node C, if P is a parent node of C, then the key of P is greater than or equal to the key of C. In a min heap, the key of P is less than or equal to the key of C. The node at the "top" of the heap is called the root node.
In computer science, an online algorithm is one that can process its input piece-by-piece in a serial fashion, i.e., in the order that the input is fed to the algorithm, without having the entire input available from the start.
In cryptography, RC4 is a stream cipher. While it is remarkable for its simplicity and speed in software, multiple vulnerabilities have been discovered in RC4, rendering it insecure. It is especially vulnerable when the beginning of the output keystream is not discarded, or when nonrandom or related keys are used. Particularly problematic uses of RC4 have led to very insecure protocols such as WEP.
In connection-oriented communication, a data stream is the transmission of a sequence of digitally encoded signals to convey information. Typically, the transmitted symbols are grouped into a series of packets.
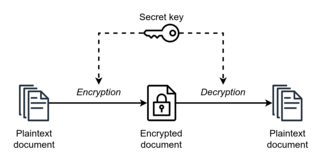
Symmetric-key algorithms are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both the encryption of plaintext and the decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical, or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys. The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link. The requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric-key encryption, in comparison to public-key encryption. However, symmetric-key encryption algorithms are usually better for bulk encryption. With exception of the one-time pad they have a smaller key size, which means less storage space and faster transmission. Due to this, asymmetric-key encryption is often used to exchange the secret key for symmetric-key encryption.
Lempel–Ziv–Welch (LZW) is a universal lossless data compression algorithm created by Abraham Lempel, Jacob Ziv, and Terry Welch. It was published by Welch in 1984 as an improved implementation of the LZ78 algorithm published by Lempel and Ziv in 1978. The algorithm is simple to implement and has the potential for very high throughput in hardware implementations. It is the algorithm of the Unix file compression utility compress and is used in the GIF image format.
A cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (CSPRNG) or cryptographic pseudorandom number generator (CPRNG) is a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) with properties that make it suitable for use in cryptography. It is also loosely known as a cryptographic random number generator (CRNG).
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is the process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar. The term parsing comes from Latin pars (orationis), meaning part.

A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm that has special properties desirable for a cryptographic application:
In cryptography, MISTY1 is a block cipher designed in 1995 by Mitsuru Matsui and others for Mitsubishi Electric.
eSTREAM is a project to "identify new stream ciphers suitable for widespread adoption", organised by the EU ECRYPT network. It was set up as a result of the failure of all six stream ciphers submitted to the NESSIE project. The call for primitives was first issued in November 2004. The project was completed in April 2008. The project was divided into separate phases and the project goal was to find algorithms suitable for different application profiles.
SNOW 1.0, SNOW 2.0, and SNOW 3G are word-based synchronous stream ciphers developed by Thomas Johansson and Patrik Ekdahl at Lund University.
Rabbit is a high-speed stream cipher from 2003. The algorithm and source code was released in 2008 as public domain software.
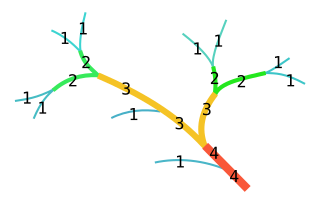
In mathematics, the Strahler number or Horton–Strahler number of a mathematical tree is a numerical measure of its branching complexity.

Cryptography, or cryptology, is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications.
In computer science, streaming algorithms are algorithms for processing data streams in which the input is presented as a sequence of items and can be examined in only a few passes, typically just one. These algorithms are designed to operate with limited memory, generally logarithmic in the size of the stream and/or in the maximum value in the stream, and may also have limited processing time per item.
In computer science, data stream clustering is defined as the clustering of data that arrive continuously such as telephone records, multimedia data, financial transactions etc. Data stream clustering is usually studied as a streaming algorithm and the objective is, given a sequence of points, to construct a good clustering of the stream, using a small amount of memory and time.






