
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. Heating and cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delivery are among the most common uses for plumbing, but it is not limited to these applications. The word derives from the Latin for lead, plumbum, as the first effective pipes used in the Roman era were lead pipes.

A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes, or more generally tubing. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical.

Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes.

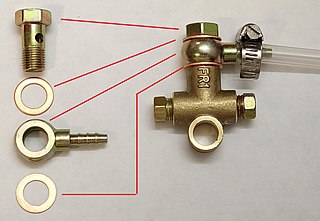
A compression fitting is a fitting used in plumbing and electrical conduit systems to join two tubes or thin-walled pipes together. In instances where two pipes made of dissimilar materials are to be joined, the fittings will be made of one or more compatible materials appropriate for the connection. Compression fittings for attaching tubing (piping) commonly have compression rings, called ferrules or olives, in them, and are sometimes referred to as flareless fittings. There are also flare fittings that do not require ferrules/olives.
An air line is a tube, or hose, that contains and carries a compressed air supply. In industrial usage, this may be used to inflate car or bicycle tyres or power tools worked by compressed air, for breathing apparatus in hazardous environments and to operate many other pneumatic systems.
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.
Manifold vacuum, or engine vacuum in a petrol engine is the difference in air pressure between the engine's intake manifold and Earth's atmosphere.

An exhaust system is used to guide reaction exhaust gases away from a controlled combustion inside an engine or stove. The entire system conveys burnt gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes. Depending on the overall system design, the exhaust gas may flow through one or more of the following:
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes.

Autogas or LPG is liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) used as a fuel in internal combustion engines in vehicles as well as in stationary applications such as generators. It is a mixture of propane and butane.

A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; a hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than the solid members.

The Bowin P3 is a monocoque racing car that was produced in 1968 by Bowin. The P3 was designed for the Australian National Formula and the Australian 1½ Litre Formula. After the capacity limit for Australian Formula 2 was increased from 1100cc to 1600cc at the beginning of 1969, the P3 found a new home in that class. The car was designed by John Joyce, founder of Bowin and assisted by Ray Parson, better known as a mechanic.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.

The Meillerwagen was a German World War II trailer used to transport a V-2 rocket from the 'transloading point' of the Technical Troop Area to the launching point, to erect the missile on the Brennstand, and to act as the service gantry for fuelling and launch preparation.
Motorcycle components and systems for a motorcycle are engineered, manufactured, and assembled in order to produce motorcycle models with the desired performance, aesthetics, and cost. The key components of modern motorcycles are presented below.
A banjo fitting is actually called a hose connecting bolt, or internally relieved bolt, and a spherical union for fluid transfer. It is typically used to connect a fluid line to a rigid, internally threaded hydraulic component. The bolt is assembled through the center of the union, usually with face seals on either side of the union, to create a fluid path between the external ports on the union and bolt. A flexible hose or a rigid pipe may be connected to the union port.
A truckmount carpet cleaner is a carpet and upholstery cleaning unit that is generally mounted to the floor of a van or trailer. Its cleaning method is hot water extraction. The operator would park the van near the premises, connect the vacuum hose and solution line hose into the machine, bring the hoses into the building, and connect a carpet cleaning wand to the end of the hoses.
Braided stainless steel brake lines are flexible hoses fitted to a hydraulic brake system. The intent of braided stainless steel brake lines is to improve brake system effectiveness and longevity as compared to an equivalent system fitted with flexible rubber hoses through near-elimination of hose expansion.

Copper tubing is available in two basic types of tube—plumbing tube and air conditioning/refrigeration (ACR) tube, and in both drawn (hard) and annealed (soft) tempers. Because of its high level of corrosion resistance, it is used for water distribution systems, oil fuel transfer lines, non-flammable medical-gas systems, and as a refrigerant line in HVAC systems. Copper tubing is joined using flare connection, compression connection, pressed connection, or solder.












