
Cullin 1, also known as CUL1, is a human protein and gene from cullin family. This protein plays an important role in protein degradation and protein ubiquitination.
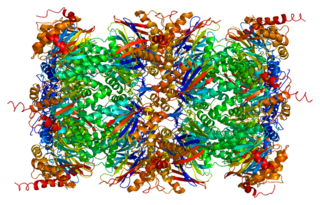
Proteasome subunit beta type-4 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB4 gene.

26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 10 or gankyrin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMD10 gene. First isolated in 1998 by Tanaka et al.; Gankyrin is an oncoprotein that is a component of the 19S regulatory cap of the proteasome. Structurally, it contains a 33-amino acid ankyrin repeat that forms a series of alpha helices. It plays a key role in regulating the cell cycle via protein-protein interactions with the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK4. It also binds closely to the E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2, which is a regulator of the degradation of p53 and retinoblastoma protein, both transcription factors involved in tumor suppression and found mutated in many cancers. Gankyrin also has an anti-apoptotic effect and is overexpressed in certain types of tumor cells such as hepatocellular carcinoma.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS6 gene.

26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMD5 gene.

COP9 constitutive photomorphogenic homolog subunit 5 (Arabidopsis), also known as COPS5 or Csn5, is a gene conserved from humans to Saccharomyces cerevisiae.

26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 4, also as known as 26S Proteasome Regulatory Subunit Rpn10, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMD4 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 19S proteasome complex.
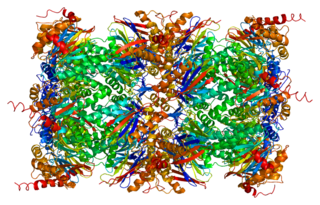
Proteasome subunit beta type-5 also known as 20S proteasome subunit beta-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PSMB5 gene. This protein is one of the 17 essential subunits that contributes to the complete assembly of 20S proteasome complex. In particular, proteasome subunit beta type-5, along with other beta subunits, assemble into two heptameric rings and subsequently a proteolytic chamber for substrate degradation. This protein contains "chymotrypsin-like" activity and is capable of cleaving after large hydrophobic residues of peptide. The eukaryotic proteasome recognized degradable proteins, including damaged proteins for protein quality control purpose or key regulatory protein components for dynamic biological processes. An essential function of a modified proteasome, the immunoproteasome, is the processing of class I MHC peptides.

26S protease regulatory subunit 4, also known as 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunit Rpt2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMC1 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of a complete assembled 19S proteasome complex. Six 26S proteasome AAA-ATPase subunits together with four non-ATPase subunits form the base sub complex of 19S regulatory particle for proteasome complex.

40S ribosomal protein S27a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27A gene.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS2 gene. It encodes a subunit of the COP9 signalosome.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS3 gene. It encodes a subunit of the COP9 signalosome.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS4 gene.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS8 gene.

Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide—protein glycosyltransferase subunit 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPN1 gene.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 7a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS7A gene.

Kappa-casein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSN3 gene.

COP9 signalosome complex subunit 7b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COPS7B gene.

26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14, also known as 26S proteasome non-ATPase subunit Rpn11, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMD14 gene. This protein is one of the 19 essential subunits of the complete assembled 19S proteasome complex. Nine subunits Rpn3, Rpn5, Rpn6, Rpn7, Rpn8, Rpn9, Rpn11, SEM1, and Rpn12 form the lid sub complex of the 19S regulatory particle of the proteasome complex.

COP9 signalosome (CSN) is a protein complex with isopeptidase activity. It catalyses the hydrolysis of NEDD8 protein from the cullin subunit of Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL). Therefore, it is responsible for CRL deneddylation – at the same time, it is able to bind denedyllated cullin-RING complex and retain them in deactivated form. COP9 signalosome thus serves as a sole deactivator of CRLs. The complex was originally identified in plants, and subsequently found in all eukaryotic organisms including human. Human COP9 signalosome consists of 8 subunits - CSN1, CSN2, CSN3, CSN4, CSN5, CSN6, CSN7, CSN8. All are essential for full function of the complex and mutation in some of them is lethal in mice.






















