Related Research Articles

Hyperpigmentation is the darkening of an area of skin or nails caused by increased melanin.
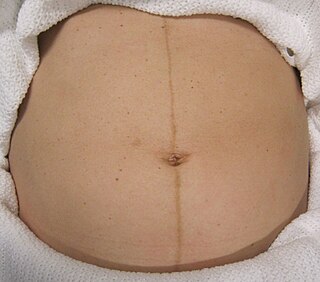
Linea nigra, often referred to as a pregnancy line, is a linear hyperpigmentation that commonly appears on the abdomen. The brownish streak is usually about a centimeter (0.4 in) in width. The line runs vertically along the midline of the abdomen from the pubis to the umbilicus, but can also run from the pubis to the top of the abdomen.
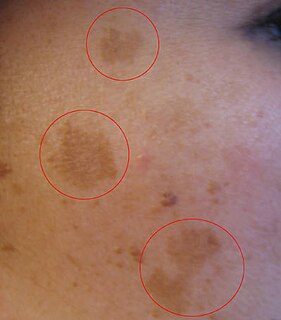
Melasma is a tan or dark skin discoloration. Melasma is thought to be caused by sun exposure, genetic predisposition, hormone changes, and skin irritation. Although it can affect anyone, it is particularly common in women, especially pregnant women and those who are taking oral or patch contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy medications.

Ochronosis is a syndrome caused by the accumulation of homogentisic acid in connective tissues. The condition was named after the yellowish (ocher-like) discoloration of the tissue seen on microscopic examination. Macroscopically, though, the affected tissues appear bluish-grey because of a light-scattering phenomenon known as the Tyndall effect. The condition is most often associated with alkaptonuria, but can occur from exogenous administration of phenol complexes such as hydroquinone. It was first described by Rudolf Virchow in 1865.

A lentigo is a small pigmented spot on the skin with a clearly defined edge, surrounded by normal-appearing skin. It is a harmless (benign) hyperplasia of melanocytes which is linear in its spread. This means the hyperplasia of melanocytes is restricted to the cell layer directly above the basement membrane of the epidermis where melanocytes normally reside. This is in contrast to the "nests" of multi-layer melanocytes found in moles. Because of this characteristic feature, the adjective "lentiginous" is used to describe other skin lesions that similarly proliferate linearly within the basal cell layer.

Cysteamine is a chemical compound that can be biosynthesized in mammals, including humans, by the degradation of coenzyme A. The intermediate pantetheine is broken down into cysteamine and pantothenic acid. It is the biosynthetic precursor to the neurotransmitter hypotaurine.
α-Hydroxy acids, or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), are a class of chemical compounds that consist of a carboxylic acid substituted with a hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon. They may be naturally occurring or synthetic. AHAs are well known for their use in the cosmetics industry. They are often found in products that aid in the reduction of wrinkles, that soften strong, defining lines, and that improve the overall look and feel of the skin. They are also used as chemical peels. AHAs have effective results through continuous treatment in the cosmeceutical industry.

Skin whitening, also known as skin lightening and skin bleaching, is the practice of using chemical substances in an attempt to lighten the skin or provide an even skin color by reducing the melanin concentration in the skin. Several chemicals have been shown to be effective in skin whitening, while some have proven to be toxic or have questionable safety profiles. This includes mercury compounds which may cause neurological problems and kidney problems.
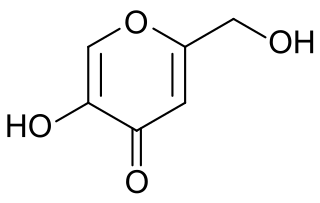
Kojic acid is a chelation agent produced by several species of fungi, especially Aspergillus oryzae, which has the Japanese common name koji. Kojic acid is a by-product in the fermentation process of malting rice, for use in the manufacturing of sake, the Japanese rice wine. It is a mild inhibitor of the formation of pigment in plant and animal tissues, and is used in food and cosmetics to preserve or change colors of substances. It forms a bright red complex with ferric ions.
Huia melasma is a species of frogs in the family Ranidae. It is endemic to western and northern Thailand and known from Kanchanaburi, Prachuap Kiri Khan, and Chiang Mai Provinces.

Starksia melasma, the black spot blenny, is a species of labrisomid blenny known only from reefs around Desecheo Island, Puerto Rico and St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. This species can reach a length of 2.1 cm (0.83 in).
The cream containing the drug combination fluocinolone acetonide/hydroquinone/tretinoin is used for the treatment of melasma. It is marketed by Galderma.

Trichopsetta is a genus of small lefteye flounders native to the western Atlantic Ocean.

Eviota melasma, commonly called headspot eviota or melasma pygmy goby among various other vernacular names, is a species of marine fish in the family Gobiidae.

Hemilophini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae.
Cameron K. Rokhsar is an associate clinical professor of dermatology at Mount Sinai Hospital and the founder and medical director of the New York Cosmetic, Skin, and Laser Surgery Center. He is a fellowship-trained cosmetic and mohs surgeon, a specialist in laser surgery including laser resurfacing and laser treatment of wrinkles and scars.

Chiang Dao Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. Established on 25 August 1978, the sanctuary covers 521 km2 of the Doi Chiang Dao and southern mountainous regions of the Daen Lao Range, north of the Thanon Thong Chai Range. The tallest summit is 2,175 m high Doi Chiang Dao.
Gagarinia aureolata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Lane in 1950. It is known from Brazil.
Gagarinia borgmeieri is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Bondar in 1938. It is known from French Guiana and Brazil.
Gagarinia mniszechii is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Chabrillac in 1857. It is known from Brazil.
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Gagarinia melasma. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.