The politics of Spain takes place under the framework established by the Constitution of 1978. Spain is established as a social and democratic sovereign country wherein the national sovereignty is vested in the people, from which the powers of the state emanate.

In Spain, an autonomous community is a first-level political and administrative division, created in accordance with the Spanish constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy of the nationalities and regions that make up Spain.

The politics of Iran take place in a framework that officially combines elements of theocracy and presidential democracy. The December 1979 constitution, and its 1989 amendment, define the political, economic, and social order of the Islamic Republic of Iran, declaring that Shia Islam of the Twelver school of thought is Iran's official religion.

The federal government of the United States is the national government of the United States, a federal republic in North America, composed of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories and several island possessions. The federal government is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executive and judicial, whose powers are vested by the U.S. Constitution in the Congress, the president and the federal courts, respectively. The powers and duties of these branches are further defined by acts of Congress, including the creation of executive departments and courts inferior to the Supreme Court.

The Spanish Constitution is the democratic law that is supreme in the Kingdom of Spain. It was enacted after its approval in a constitutional referendum, and it is the culmination of the Spanish transition to democracy. The Constitution of 1978 is one of about a dozen of other historical Spanish constitutions and constitution-like documents; however, it is one of two fully democratic constitutions. It was sanctioned by King Juan Carlos I on 27 December, and published in the Boletín Oficial del Estado on 29 December, the date in which it became effective. The promulgation of the constitution marked the culmination of the Spanish transition to democracy after the death of general Francisco Franco, on 20 November 1975, who ruled over Spain as a military dictator for nearly 40 years. This led to the country undergoing a series of political, social and historical changes that transformed the Francoist regime into a democratic state.

The President of the Dominican Republic is both the head of state and head of government of the Dominican Republic. The presidential system was established in 1844, following the proclamation of the republic during the Dominican War of Independence. The President of the Dominican Republic is styled Your Excellency, Mr. President during his time in office. His official residence is the National Palace.

The Congress of the Republic of Colombia is the name given to Colombia's bicameral national legislature.

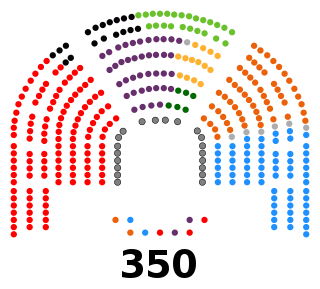
The Congress of the Dominican Republic is the bicameral legislature of the government of the Dominican Republic, consisting of two houses, the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Both senators and deputies are chosen through direct election. There are no term limits for either chamber.

The Tennessee General Assembly (TNGA) is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Tennessee. It is a part-time bicameral legislature consisting of a Senate and a House of Representatives. The Speaker of the Senate carries the additional title and office of Lieutenant Governor of Tennessee. In addition to passing a budget for state government plus other legislation, the General Assembly appoints three state officers specified by the state constitution. It is also the initiating body in any process to amend the state's constitution.
A balanced budget amendment is a constitutional rule requiring that a state cannot spend more than its income. It requires a balance between the projected receipts and expenditures of the government.

The Constitution of the State of Texas is the document that describes the structure and function of the government of the U.S. state of Texas.
The Golden Rule is a guideline for the operation of fiscal policy. The Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending. In layman's terms this means that on average over the ups and downs of an economic cycle the government should only borrow to pay for investment that benefits future generations. Day-to-day spending that benefits today's taxpayers should be paid for with today's taxes, not with leveraged investment. Therefore, over the cycle the current budget must balance or be brought into surplus.
The Constitution of the State of Arkansas is the governing document of the U.S. state of Arkansas. It was adopted in 1874, shortly after the Brooks-Baxter War. It replaced the 1868 constitution adopted by the legislature following the end of the American Civil War and under which Arkansas rejoined the Union.

The Constitution of Argentina is the basic governing document of Argentina, and the primary source of existing law in Argentina. Its first version was written in 1853 by a Constitutional Assembly gathered in Santa Fe, and the doctrinal basis was taken in part from the United States Constitution. It was then reformed in 1860, 1866, 1898, 1949, 1957, and the current version is the reformed text of 1994.

The Chairman of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation, also called Speaker (спикер), is the presiding officer of the lower house of the Russian parliament. His responsibilities include overseeing the day-to-day business of the State Duma presiding and maintaining order at the regular sessions of the parliament. The Speaker also chairs the Council of the Duma which includes representatives from all the parliamentary parties and determines the legislative agenda.

The Tribunal de Cuentas is the supreme governmental accounting body of Spain responsible of the comptrolling of the public accounts and the auditing of the accountancy of the political parties, in accordance with the Constitution and its Organic Law.
The Economic Agreement is a juridical instrument that regulates the taxation and financial relations between the General Administration of the Kingdom of Spain and the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country.
The Ministry of Finance is the central specialized body of public administration, which develops and promotes the unique policy of training and managing public finances, applying financial levers in line with the requirements of the market economy. In its activity, the Ministry of Finance is governed by the Constitution of the Republic of Moldova, the laws of the Republic, the decrees of the President of the Republic of Moldova, the resolutions of the Parliament, the ordinances, the decisions and the provisions of the Cabinet of Moldova.

The Ministry of Finance or Ministry of Treasury (MH) is the department of the Government of Spain responsible responsible for planning and carrying out the government policy on public finance and budget and it applies and manages the regional and local financing systems and the provision of information on the economic-financial activity of the different Public Administrations.