Related Research Articles

Digital compositing is the process of digitally assembling multiple images to make a final image, typically for print, motion pictures or screen display. It is the digital analogue of optical film compositing.
Real-time computing (RTC) is the computer science term for hardware and software systems subject to a "real-time constraint", for example from event to system response. Real-time programs must guarantee response within specified time constraints, often referred to as "deadlines".

Chroma key compositing, or chroma keying, is a visual-effects and post-production technique for compositing (layering) two images or video streams together based on colour hues. The technique has been used in many fields to remove a background from the subject of a photo or video – particularly the newscasting, motion picture, and video game industries. A colour range in the foreground footage is made transparent, allowing separately filmed background footage or a static image to be inserted into the scene. The chroma keying technique is commonly used in video production and post-production. This technique is also referred to as colour keying, colour-separation overlay, or by various terms for specific colour-related variants such as green screen or blue screen; chroma keying can be done with backgrounds of any colour that are uniform and distinct, but green and blue backgrounds are more commonly used because they differ most distinctly in hue from any human skin colour. No part of the subject being filmed or photographed may duplicate the colour used as the backing, or the part may be erroneously identified as part of the backing.
RT-11 is a discontinued small, low-end, single-user real-time operating system for the Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-11 family of 16-bit computers. RT-11, which stands for Real-Time, was first implemented in 1970 and was widely used for real-time systems, process control, and data acquisition across the full line of PDP-11 computers. It was also used for low-cost general-use computing.
In computing, scheduling is the action of assigning resources to perform tasks. The resources may be processors, network links or expansion cards. The tasks may be threads, processes or data flows.
Disk Operating System/360, also DOS/360, or simply DOS, is the discontinued first member of a sequence of operating systems for IBM System/360, System/370 and later mainframes. It was announced by IBM on the last day of 1964, and it was first delivered in June 1966. In its time, DOS/360 was the most widely used operating system in the world.

Compositing is the process or technique of combining visual elements from separate sources into single images, often to create the illusion that all those elements are parts of the same scene. Live-action shooting for compositing is variously called "chroma key", "blue screen", "green screen" and other names. Today, most, though not all, compositing is achieved through digital image manipulation. Pre-digital compositing techniques, however, go back as far as the trick films of Georges Méliès in the late 19th century, and some are still in use.
A job scheduler is a computer application for controlling unattended background program execution of jobs. This is commonly called batch scheduling, as execution of non-interactive jobs is often called batch processing, though traditional job and batch are distinguished and contrasted; see that page for details. Other synonyms include batch system, distributed resource management system (DRMS), distributed resource manager (DRM), and, commonly today, workload automation (WLA). The data structure of jobs to run is known as the job queue.
Video quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation. Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task.
Mattes are used in photography and special effects filmmaking to combine two or more image elements into a single, final image. Usually, mattes are used to combine a foreground image with a background image. In this case, the matte is the background painting. In film and stage, mattes can be physically huge sections of painted canvas, portraying large scenic expanses of landscapes.

A front projection effect is an in-camera visual effects process in film production for combining foreground performance with pre-filmed background footage. In contrast to rear projection, which projects footage onto a screen from behind the performers, front projection projects the pre-filmed material over the performers and onto a highly reflective background surface.
Rear projection is one of many in-camera effects cinematic techniques in film production for combining foreground performances with pre-filmed backgrounds. It was widely used for many years in driving scenes, or to show other forms of "distant" background motion.

Predictive maintenance techniques are designed to help determine the condition of in-service equipment in order to estimate when maintenance should be performed. This approach promises cost savings over routine or time-based preventive maintenance, because tasks are performed only when warranted. Thus, it is regarded as condition-based maintenance carried out as suggested by estimations of the degradation state of an item.
Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) is a component of Microsoft Windows XP and later iterations of the operating systems, which facilitates asynchronous, prioritized, and throttled transfer of files between machines using idle network bandwidth. It is most commonly used by recent versions of Windows Update, Microsoft Update, Windows Server Update Services, and System Center Configuration Manager to deliver software updates to clients, Microsoft's anti-virus scanner Microsoft Security Essentials to fetch signature updates, and is also used by Microsoft's instant messaging products to transfer files. BITS is exposed through the Component Object Model (COM).
Foreground-background is a scheduling algorithm that is used to control an execution of multiple processes on a single processor. It is based on two waiting lists, the first one is called foreground because this is the one in which all processes initially enter, and the second one is called background because all processes, after using all of their execution time in foreground, are moved to background.
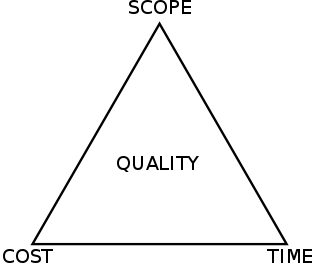
The project management triangle is a model of the constraints of project management. While its origins are unclear, it has been used since at least the 1950s. It contends that:
- The quality of work is constrained by the project's budget, deadlines and scope (features).
- The project manager can trade between constraints.
- Changes in one constraint necessitate changes in others to compensate or quality will suffer.
2D to 3D video conversion is the process of transforming 2D ("flat") film to 3D form, which in almost all cases is stereo, so it is the process of creating imagery for each eye from one 2D image.
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, an M/G/1 queue is a queue model where arrivals are Markovian, service times have a General distribution and there is a single server. The model name is written in Kendall's notation, and is an extension of the M/M/1 queue, where service times must be exponentially distributed. The classic application of the M/G/1 queue is to model performance of a fixed head hard disk.

Foreground detection is one of the major tasks in the field of computer vision and image processing whose aim is to detect changes in image sequences. Background subtraction is any technique which allows an image's foreground to be extracted for further processing.
Video matting is a technique for separating the video into two or more layers, usually foreground and background, and generating alpha mattes which determine blending of the layers. The technique is very popular in video editing because it allows to substitute the background, or process the layers individually.
References
- ↑ Nuyens, Misja; Wierman, Adam (2008). "The Foreground-Background queue: a survey" (PDF). Performance Evaluation. 65 (3–4). Retrieved 7 August 2017.