
Cattaraugus County is a county in Western New York, with one side bordering Pennsylvania. As of the United States 2020 census, the population was 77,042. The county seat is Little Valley. The county was created in 1808 and later organized in 1817.

Livingston County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 61,834. Its county seat is Geneseo. The county is named after Robert R. Livingston, who helped draft the Declaration of Independence and negotiated the Louisiana Purchase.

Olean is a city in Cattaraugus County, New York, United States. Olean is the largest city in Cattaraugus County and serves as its financial, business, transportation and entertainment center. It is one of the principal cities of the Southern Tier region of Western New York.
Mount Morris is a village in the town of Mount Morris in Livingston County, New York, United States. The village population was 2,986 at the 2010 census, out of 4,465 in the entire town. The village and town are named after Robert Morris.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Genesee River is a tributary of Lake Ontario flowing northward through the Twin Tiers of Pennsylvania and New York in the United States. The river contains several waterfalls in New York at Letchworth State Park and Rochester.
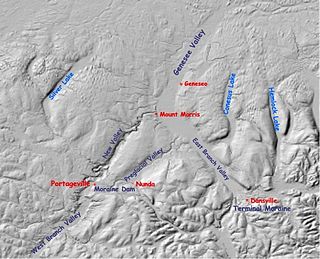
The Genesee River flows northward from its source in northern Pennsylvania to enter Lake Ontario at Rochester, New York.

Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY includes the cities of Buffalo, Niagara Falls, Jamestown, and the surrounding suburbs, as well as the outlying rural areas of the Great Lakes lowlands and Niagara Frontier, and Chautauqua-Alleghany. Many would also place Rochester and the Genesee Valley in the region, while some would also include the western Finger Lakes within the region. Others would describe the latter three areas as being in a separate Finger Lakes region.

The Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad is a short line railroad that operates in Livingston County and Monroe County in New York, United States. The railroad interchanges with CSX at Genesee Junction in Chili, New York, the Rochester and Southern Railroad (RSR) at Genesee Junction and the RSR's Brooks Avenue Yard in Gates, New York, and with the Rochester & Genesee Valley Railroad Museum at Industry, New York. Their primary freight consists of food products: grains and corn syrup. In 1997, the Livonia, Avon and Lakeville Railroad was selected as Short Line Railroad of the Year by industry trade journal Railway Age. The LAL is also the parent company for the Bath and Hammondsport Railroad, the Western New York and Pennsylvania Railroad and the Ontario Midland Railroad.

The Genesee Valley Canal is a former canal that operated in western New York between 1840 and 1878. It ran for a length of 124 miles, passing through 106 locks. Its course was later used by the Genesee Valley Canal Railroad and today comprises portions of the Genesee Valley Greenway.
The Pittsburgh, Fort Wayne and Chicago Railway was a major part of the Pennsylvania Railroad system, extending the PRR west from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, via Fort Wayne, Indiana, to Chicago, Illinois. It included the current Norfolk Southern-owned Fort Wayne Line east of Crestline, Ohio, to Pittsburgh, and the Fort Wayne Secondary, owned by CSX, from Crestline west to Tolleston in Gary, Indiana. CSX leased its entire portion in 2004 to the Chicago, Fort Wayne and Eastern Railroad (CFE). The remaining portion of the line from Tolleston into Chicago is now part of the Norfolk Southern's Chicago District, with a small portion of the original PFW&C trackage abandoned in favor of the parallel lines of former competitors which are now part of the modern NS system.
The Belvidere-Delaware Railroad was a railroad running along the eastern shore of the Delaware River from Trenton, New Jersey north via Phillipsburg, New Jersey to the small village of Manunka Chunk, New Jersey. It became an important feeder line for the Lehigh Valley Railroad's join to the Central Railroad of New Jersey, which was constructed into Phillipsburg, NJ at about the same time. This connected Philadelphia and Trenton, NJ at one end of the shortline railroad to the rapidly growing lower Wyoming Valley region, and via the Morris Canal or the CNJ, a slow or fast connection to New York City ferries crossing New York Harbor from Jersey City, NJ. In 1871 the CNJ leased various railroads in Pennsylvania, most from the Lehigh Coal & Navigation Company allowing the CNJ to penetrate to the upper Wyoming Valley, over some stretches, competing directly with the Lehigh Valley Railroad and with the Lehigh Canal and the trunk road connection of the Belvidere Delaware Railroad to New York became less profitable since Philadelphia connected more easily to Northeastern Pennsylvania thereafter without needing a double-crossing of the Delaware River; a general revenue decline ensued, leading to the Pennsylvania Railroad acquiring the rights, where it served as part of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR) system, carrying mainly anthracite coal and iron ore from northeastern Pennsylvania to population centers along the coast.

The Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad is a Class II railroad operating in New York and Pennsylvania.
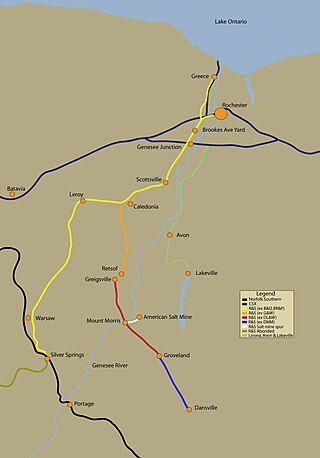
The Rochester and Southern Railroad, a subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming Inc., is a class III shortline that runs from the city of Rochester in Monroe County to Silver Springs, NY. The RSR started in 1986, when the B&O sold off its Buffalo and Rochester branches. The trackage was purchased by Genesee & Wyoming Inc., and split into two railroads, the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad and the Rochester and Southern Railroad. The Rochester branch was scrapped from Silver Springs south to Machias, New York.

New York State Route 63 (NY 63) is a state highway in the western part of New York in the United States. It extends for 82.11 miles (132.14 km) in a generally southeast–northwest direction from an intersection with NY 15 and NY 21 in the village of Wayland in Steuben County to a junction with NY 18 in the town of Yates in Orleans County, 2 miles (3.2 km) south of the Lake Ontario shoreline. The route passes through the city of Batavia and enters or comes near several villages, including Dansville and Medina.

New York State Route 408 (NY 408) is a 15.95-mile-long (25.67 km) state highway located entirely within Livingston County, New York, in the United States. It runs north–south from an intersection with NY 70 near the hamlet of Dalton in the town of Nunda to a junction with NY 63 in the town of Groveland near NY 408's exit with Interstate 390 (I-390). Most of NY 408 is a two-lane rural highway that passes through lightly developed areas; however, the last two miles (3 km) of the highway, where it runs in a due east–west direction, are heavily trafficked as NY 408 becomes a key connector road in both directions.

The P&W Subdivision is a railroad line owned and operated by CSX Transportation, the Allegheny Valley Railroad (AVR), and the Buffalo and Pittsburgh Railroad (BPRR) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The line runs from Rankin north through Pittsburgh to West Pittsburg along a former Baltimore and Ohio Railroad line, once the Pittsburgh and Western Railroad.

The Main Line of the Pennsylvania Railroad was a rail line in Pennsylvania connecting Philadelphia with Pittsburgh via Harrisburg. The rail line was split into two rail lines, and now all of its right-of-way is a cross-state corridor, composed of Amtrak's Philadelphia to Harrisburg Main Line and the Norfolk Southern Railway's Pittsburgh Line.
The New Castle Branch was a rail line owned and operated by the Pennsylvania Railroad in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. The line ran from New Castle north to Stoneboro, and is now entirely abandoned. At its south end, the line intersected the Erie and Pittsburgh Branch and Mahoningtown Branch. When the New Castle Branch ended at Stoneboro, the PRR had trackage rights east along the New York Central Railroad's Stoneboro Branch to Oil City and the Allegheny Branch, Chautauqua Branch, and Salamanca Branch.
The Western New York and Pennsylvania Railway was a railroad that operated in the U.S. states of New York and Pennsylvania.
















