
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a visual display, support electronics, power supply, housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls.

A graphics card is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called discrete or dedicated graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the CPU. A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole.

Corning Incorporated is an American multinational technology company that specializes in specialty glass, ceramics, and related materials and technologies including advanced optics, primarily for industrial and scientific applications. The company was named Corning Glass Works until 1989. Corning divested its consumer product lines in 1998 by selling the Corning Consumer Products Company subsidiary to Borden.
Applied Materials, Inc. is an American corporation that supplies equipment, services and software for the manufacture of semiconductor chips for electronics, flat panel displays for computers, smartphones, televisions, and solar products. Integral to the growth of Silicon Valley, the company also supplies equipment to produce coatings for flexible electronics, packaging and other applications. The company is headquartered in Santa Clara, California.

ViewSonic Corporation is a Taiwanese-American privately held multinational electronics company with headquarters in Brea, California, United States and a research & development center in New Taipei City, Taiwan.

Barco NV is a Belgian technology company that specializes in digital projection and imaging technology, focusing on three core markets: entertainment, enterprise, and healthcare. It employs 3600 employees located in 90 countries. The company has 400 granted patents. Barco is headquartered in Kortrijk, Belgium, and has its own facilities for Sales & Marketing, Customer Support, R&D and Manufacturing in Europe, North America and Asia-Pacific. Shares of Barco are listed on Euronext Brussels. It has a market cap of around €1.2 billion. Barco sells its ClickShare products to enable wireless projection from sender devices to receiver displays.

CSR plc was a multinational fabless semiconductor company headquartered in Cambridge, United Kingdom. Its main products were connectivity, audio, imaging and location chips. CSR was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index until it was acquired by Qualcomm in August 2015. Under Qualcomm's ownership, the company was renamed Qualcomm Technologies International, Ltd.
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.

Trident Microsystems was a fabless semiconductor company that became in the 1990s a well-known supplier of integrated circuits for video display controllers used in video cards and on motherboards for desktop PCs and laptops. In 2003, it transformed itself into being a supplier of display processors for digital televisions, and primarily LCD TVs starting from 2005, at a time when the global LCD TV market started showing strong growth.

VM Labs was a semiconductor and platform company, founded in 1995 in Los Altos, Silicon Valley, California.

Ecolab Inc. is an American corporation headquartered in Saint Paul, Minnesota. It develops and offers services, technology and systems that specialize in treatment, purification, cleaning and hygiene of water in a wide variety of applications. It helps organizations, both in private as well as public markets, treat their water for drinking use and for use in food, healthcare, hospitality-related safety and industry. Founded as Economics Laboratory in 1923 by Merritt J. Osborn, it was eventually renamed "Ecolab" in 1986.

DisplayPort (DP) is a digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers and standardized by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA). It is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor. It can also carry audio, USB, and other forms of data.
KLA Corporation is an American capital equipment company based in Milpitas, California. It supplies process control and yield management systems for the semiconductor industry and other related nanoelectronics industries. The company's products and services are intended for all phases of wafer, reticle, integrated circuit (IC) and packaging production, from research and development to final volume manufacturing.
Maxim Integrated, a subsidiary of Analog Devices, designs, manufactures, and sells analog and mixed-signal integrated circuits for the automotive, industrial, communications, consumer, and computing markets. Maxim's product portfolio includes power and battery management ICs, sensors, analog ICs, interface ICs, communications solutions, digital ICs, embedded security, and microcontrollers. The company is headquartered in San Jose, California, and has design centers, manufacturing facilities, and sales offices worldwide.

Microchip Technology Inc. is a publicly listed American corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP integrated circuits. Its products include microcontrollers, Serial EEPROM devices, Serial SRAM devices, embedded security devices, radio frequency (RF) devices, thermal, power and battery management analog devices, as well as linear, interface and wireless products.

Silicon Optix Inc was a privately held fabless semiconductor company that designed and manufactured video/image digital processing integrated circuits. Originally a division of Genesis Microchip, Silicon Optix was spun off in 2000 by Paul Russo, the CEO of Genesis Microchip at the time. Silicon Optix acquired Teranex and its patents on the GAPP, which it incorporated into some of their products.
In electronics engineering, video processing is a particular case of signal processing, in particular image processing, which often employs video filters and where the input and output signals are video files or video streams. Video processing techniques are used in television sets, VCRs, DVDs, video codecs, video players, video scalers and other devices. For example—commonly only design and video processing is different in TV sets of different manufactures.

MStar Semiconductor, Inc. was a Taiwanese fabless semiconductor company specializing in mixed-mode integrated circuit technologies, based in Hsinchu Hsien. MStar made hardware for multimedia and wireless communications, in the form of display ICs and mixed-mode ASIC/IPs, in addition to chip sets for GSM mobile handsets. MStar employed approx. 1300 in more than 10 branches worldwide. The company's revenue was around US$1067 million in 2010. The growth has been substantial, their revenue in 2005 was US$175 million. MStar is listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange under the code 3697.
Faroudja Labs was a San Francisco–based IP and research company founded by Yves Faroudja. Faroudja Labs shouldn't be confused with Faroudja Enterprises, Yves Faroudja's latest venture.
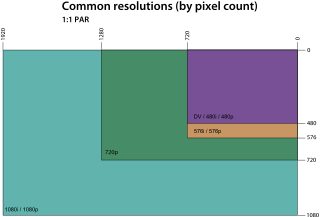
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions. A graphics display resolution can be used in tandem with the size of the graphics display to calculate pixel density. An increase in the pixel density often correlates with a decrease in the size of individual pixels on a display.












