
Frankia is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria that live in symbiosis with actinorhizal plants, similar to the Rhizobium bacteria found in the root nodules of legumes in the family Fabaceae. Frankia also initiate the forming of root nodules.
Pluralibacter gergoviae is a Gram-negative, motile, facultatively-anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. P. gergoviae is of special interest to the cosmetics industry, as it displays resistance to parabens, a common antimicrobial agent added to cosmetic products.
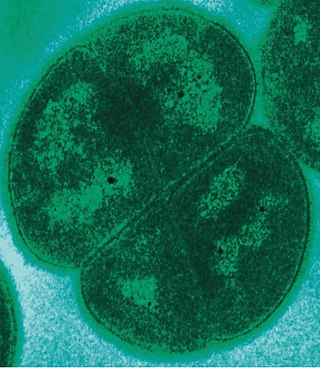
Deinococcus is in the monotypic family Deinococcaceae, and one genus of three in the order Deinococcales of the bacterial phylum Deinococcota highly resistant to environmental hazards. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them Gram-positive stains, but they include a second membrane and so are closer in structure to Gram-negative bacteria. Deinococcus survive when their DNA is exposed to high doses of gamma and UV radiation. Whereas other bacteria change their structure in the presence of radiation, such as by forming endospores, Deinococcus tolerate it without changing their cellular form and do not retreat into a hardened structure. They are also characterized by the presence of the carotenoid pigment deinoxanthin that give them their pink color. They are usually isolated according to these two criteria. In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus bacteria, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings support the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.
Streptomyces tunisiensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from forest soil in Tunis in Tunisia. Streptomyces tunisiensis has antibacterial activity.
Blastococcus is a Gram-positive, coccoid and aerobic genus of bacteria from the family of Geodermatophilaceae.
Blastococcus capsensis is a Gram-positive bacterium from the genus of Blastococcus which has been isolated from a limestone rock.
Geodermatophilus africanus is a Gram-positive, aerobic and halotolerant bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from desert sand near Ourba in the Sahara.
Geodermatophilus amargosae is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from desert soil from the Amargosa Desert in the United States.
Geodermatophilus aquaeductus is a Gram-positive, aerobic and gamma-ray resistant bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from the surface of a calcarenite stone from the ruins of the Aqueduct of Hadrian in Tunisia.
Geodermatophilus arenarius is a Gram-positive, aerobic and xerophilic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from desert sand from Ouré Cassoni in Chad.
Geodermatophilus bullaregiensis is an aerobic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from the surface of a marble monument from Bulla Regia in Tunisia.
Geodermatophilus dictyosporus is a Gram-positive and gamma-ray resistant bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from soil from the Westgard Pass in the United States.
Geodermatophilus normandii is a Gram-positive bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from desert sand from Ouré Cassoni in Chad.
Geodermatophilus poikilotrophus is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from dolomitic marble from Samara in Namibia.
Geodermatophilus saharensis is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from desert sand from Ouré Cassoni in Chad.
Geodermatophilus siccatus is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from arid sand near Ourba in Chad.
Geodermatophilus telluris is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from arid sand near Vers Ourba in Chad.
Geodermatophilus tzadiensis is a Gram-positive, aerobic and UV radiation-resistant bacterium from the genus Geodermatophilus which has been isolated from desert sand near Ouré Cassoni in Chad.
Blastococcus xanthinilyticus is a Gram-positive and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Blastococcus which has been isolated from marble dust from the Bulla Regia monument in Tunisia.
Geodermatophilus is a Gram-positive genus of bacteria from the phylum Actinomycetota.

