Related Research Articles
A fall line is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coastal plain is softer sedimentary rock. A fall line often will recede upstream as the river cuts out the uphill dense material, forming "c"-shaped waterfalls and exposing bedrock shoals. Because of these features, riverboats typically cannot travel any farther inland without portaging, unless locks are built. The rapid change in elevation of the water and resulting energy release make the fall line a good location for water mills, grist mills, and sawmills. Because of the need for a river port leading to the ocean, and a ready supply of water power, settlements often develop where rivers cross a fall line.
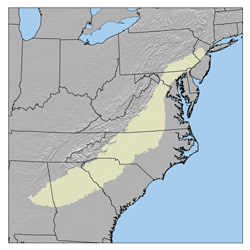
The Piedmont is a plateau region located in the Eastern United States. It sits between the Atlantic coastal plain and the main Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York in the north to central Alabama in the south. The Piedmont Province is a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division which consists of the Gettysburg-Newark Lowlands, the Piedmont Upland and the Piedmont Lowlands sections.
Carolina bays are elliptical depressions concentrated along the Atlantic seaboard within coastal Delaware, Maryland, New York, New Jersey, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, Georgia, and north Florida. In Maryland, they are called Maryland basins. Within the Delmarva Peninsula, they and other coastal ponds are also called Delmarva bays. They are named for the bay trees frequently found in them, not because of the frequent ponding of water.

The Atlantic coastal plain is a physiographic region of low relief along the East Coast of the United States. It extends 2,200 miles (3,500 km) from the New York Bight southward to a Georgia/Florida section of the Eastern Continental Divide, which demarcates the plain from the ACF River Basin in the Gulf Coastal Plain to the west. The province is bordered on the west by the Atlantic Seaboard fall line and the Piedmont plateau, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Floridian province. The Outer Lands archipelagic region forms the insular northeasternmost extension of the Atlantic coastal plain.

The Sandhills or Carolina Sandhills is a 10-35 mi wide physiographic region within the U.S. Atlantic Coastal Plain province, along the updip (inland) margin of this province in the States of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. The extent of the Carolina Sandhills is shown clearly in maps of the ecoregions of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.

The Ogeechee River is a 294-mile-long (473 km) blackwater river in the U.S. state of Georgia. It heads at the confluence of its North and South Forks, about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) south-southwest of Crawfordville and flowing generally southeast to Ossabaw Sound about 16 miles (26 km) south of Savannah. Its largest tributary is the Canoochee River, which drains approximately 1,400 square miles (3,600 km2) and is the only other major river in the basin. The Ogeechee has a watershed of 5,540 square miles (14,300 km2). It is one of the state's few free-flowing streams.

Israel's Coastal Plain is the coastal plain along Israel's Mediterranean Sea coast, extending 187 kilometres (116 mi) north to south. It is a geographical region defined morphologically by the sea, in terms of topography and soil, and also in its climate, flora and fauna. It is narrow in the north and broadens considerably towards the south, and is continuous with the exception of the short section where Mount Carmel reaches almost all the way to the sea. The Coastal Plain is bordered to the east by - north to south - the topographically higher regions of the Galilee, the low and flat Jezreel Valley, the Carmel range, the mountains of Samaria, the hill country of Judea known as the Shephelah, and the Negev Mountains in the south. To the north it is separated from the coastal plain of Lebanon by the cliffs of Rosh HaNikra, which jut out into the sea from the Galilee mountains, but to the south it continues into the Egyptian Sinai Peninsula.

Lowcountry cuisine is the cooking traditionally associated with the South Carolina Lowcountry and the Georgia coast. While it shares features with Southern cooking, its geography, economics, demographics, and culture pushed its culinary identity in a different direction from regions above the Fall Line. With its rich diversity of seafood from the coastal estuaries, its concentration of wealth in Charleston and Savannah, and a vibrant African cuisine influence, Lowcountry cooking has strong parallels with New Orleans and Cajun cuisine.

Carolina style refers to an established set of condiments for hot dogs and hamburgers, originating in the Coastal Plain and Piedmont regions of North Carolina and South Carolina. The classic combination is chili, slaw and onions; locally, mustard sometimes replaces slaw, or is added as a fourth item.
North America is the third largest continent, and is also a portion of the second largest supercontinent if North and South America are combined into the Americas and Africa, Europe, and Asia are considered to be part of one supercontinent called Afro-Eurasia.

The Geology of Georgia consists of four distinct geologic regions, beginning in the northwest corner of the state and moving through the state to the southeast: the Valley and Ridge region, also known as the Appalachian Plateau; the Blue Ridge; the Piedmont and the Coastal Plain. The Fall Line is the boundary between the Piedmont and the Coastal Plain.

The geology of Delaware consists of two physiographic provinces located in the U.S. state of Delaware. They are the Atlantic Coastal Plain and the Piedmont.
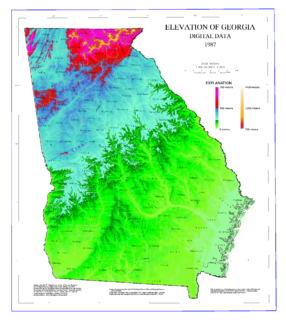
The geography of Georgia describes a state in the Southeastern United States in North America. The Golden Isles of Georgia lie off the coast of the state. The main geographical features include mountains such as the Ridge-and-valley Appalachians in the northwest, the Blue Ridge Mountains in the northeast, the Piedmont plateau in the central portion of the state and Coastal Plain in the south. The highest area in Georgia is Brasstown Bald which is 1,458 m (4,784 ft) above sea level, while the lowest is at sea level, at the Atlantic Ocean. Georgia is located at approximately 33° N 83.5° W. The state has a total area of 154,077 km2 (59,489 sq mi) and the geographic center is located in Twiggs County.
The geology of Alabama is marked by abundant geologic resources and a variety of geologic structures from folded mountains in the north to sandy beaches along the Gulf of Mexico coast. Alabama spans three continental geologic provinces as defined by the United States Geological Survey, the Atlantic Plain, Appalachian Highlands, and Interior Plains. The Geological Survey of Alabama breaks these provinces down into more specific physiographic provinces.
The Geographical Regions of South Carolina refers to the three major geographical regions of South Carolina: the Appalachian Mountains in the west, the central Piedmont region, and the eastern Atlantic Coastal Plain. The largest region in the state is the Piedmont located between the Mountains and the Carolina Sandhills, while the smallest in region in the state is the Mountains also known as the Blue Ridge Range.

Paleontology in South Carolina refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of South Carolina. Evidence suggests that at least part of South Carolina was covered by a warm, shallow sea and inhabited by trilobites during the Cambrian period. Other than this, little is known about the earliest prehistory of South Carolina because the Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, Permian, Triassic, and Jurassic, are missing from the state's local rock record. The earliest fossils of South Carolina date back to the Cretaceous, when the state was partially covered by seawater. Contemporary fossils include marine invertebrates and the remains of dinosaur carcasses that washed out to sea. On land, a wide variety of trees grew. Sea levels rose and fell throughout the ensuing Cenozoic era. Local marine life included invertebrates, fish, sharks, whales. The first scientifically accurate identification of vertebrate fossils in North America occurred in South Carolina. In 1725, African slaves digging in a swamp uncovered mammoth teeth, which they recognized as originating from an elephant-like animal.
The Black Mingo Group is a geologic group in South Carolina composed of dark grey to black clays, shales, laminated sandy shales, and yellow-red sands. The group's name comes from Black Mingo Creek where outcrops of the group are exposed. The bottom boundary is an unconformity with Cretaceous deposits. It preserves fossils dating back to the Paleogene period.
Before the foundation of the United States in 1776, Kingdom of Great Britain owned Thirteen Colonies on the eastern shore of North America. The geography and climate of the area had a significant impact on the economy and survival of the colonies.
References
- ↑ "Regions & Places in South Carolina" (PDF). USC Library. University of South Carolina . Retrieved 21 February 2017.
| This South Carolina-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This article about a specific United States geological feature is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |