Related Research Articles

Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics. The word crystallography is derived from the Ancient Greek word κρύσταλλος, and γράφειν. In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming that 2014 would be the International Year of Crystallography.

Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.

X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and various other information.
A timeline of atomic and subatomic physics.

Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of the structure of the material. The technique is similar to X-ray diffraction but due to their different scattering properties, neutrons and X-rays provide complementary information: X-Rays are suited for superficial analysis, strong x-rays from synchrotron radiation are suited for shallow depths or thin specimens, while neutrons having high penetration depth are suited for bulk samples.

The Atomic Energy Research Establishment (AERE) was the main centre for atomic energy research and development in the United Kingdom from 1946 to the 1990s. It was created, owned and funded by the British Government.

Leo James Rainwater was an American physicist who shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1975 for his part in determining the asymmetrical shapes of certain atomic nuclei.

Clifford Glenwood Shull was an American physicist.

Neutron scattering, the irregular dispersal of free neutrons by matter, can refer to either the naturally occurring physical process itself or to the man-made experimental techniques that use the natural process for investigating materials. The natural/physical phenomenon is of elemental importance in nuclear engineering and the nuclear sciences. Regarding the experimental technique, understanding and manipulating neutron scattering is fundamental to the applications used in crystallography, physics, physical chemistry, biophysics, and materials research.
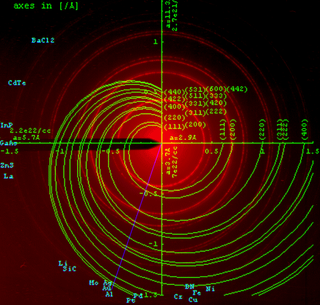
Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray, neutron, or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline samples for structural characterization of materials. An instrument dedicated to performing such powder measurements is called a powder diffractometer.

Dame Louise Napier Johnson,, was a British biochemist and protein crystallographer. She was David Phillips Professor of Molecular Biophysics at the University of Oxford from 1990 to 2007, and later an emeritus professor.
Noor Muhammad Butt ; b. 3 June 1936), SI, FPAS, also known as N. M. Butt, is a Pakistani nuclear physicist and professor of physics at the Preston University who is known for his research publications in understanding the gamma-rays burst, Mössbauer effect, diffraction, later the nanotechnology.

Sow-Hsin Chen, was a Hoklo Taiwanese physicist and Professor Emeritus at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). He was a recognized pioneer in the research of the dynamic properties of supercooled and interfacial water with the use of neutron scattering techniques. As an educator, he was recognized for his training of young scientists in the use of those same techniques. Regarding hydrogen storage, his research focused on the use of activated carbon to allow hydrogen to be stored at room temperature.
Colin George Windsor FRS is a British physicist, and was Programme Area Manager, for the United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority

Ernest Omar Wollan was an American physicist who made major contributions in the fields of neutron scattering and health physics.

Brent Fultz is an American physicist and materials scientist and one of the world's leading authorities on statistical mechanics, diffraction, and phase transitions in materials. Fultz is the Barbara and Stanley Rawn Jr. Professor of Applied Physics and Materials Science at the California Institute of Technology. He is known for his research in materials physics and materials chemistry, and for establishing the importance of phonon entropy to the phase stability of materials. Additionally, Fultz oversaw the construction of the wide angular-range chopper spectrometer (ARCS) instrument at the Spallation Neutron Source and has made advances in phonon measuring techniques.
Structural chemistry is a part of chemistry and deals with spatial structures of molecules and solids. For structure elucidation a range of different methods is used. One has to distinguish between methods that elucidate solely the connectivity between atoms (constitution) and such that provide precise three dimensional information such as atom coordinates, bond lengths and angles and torsional angles.
Nivrathi Suryanarayanashastry Satya Murthy was an Indian physicist and the head of the Nuclear Physics Division of the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre. Known for his research in molecular reaction dynamics, Murthy was an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy, National Academy of Sciences, India and Indian Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, for his contributions to physical sciences in 1980.
Quantum crystallography is a branch of crystallography that investigates crystalline materials within the framework of quantum mechanics, with analysis and representation, in position or in momentum space, of quantities like wave function, electron charge and spin density, density matrices and all properties related to them. Like the quantum chemistry, Quantum crystallography involves both experimental and computational work. The theoretical part of quantum crystallography is based on quantum mechanical calculations of atomic/molecular/crystal wave functions, density matrices or density models, used to simulate the electronic structure of a crystalline material. While in quantum chemistry, the experimental works mainly rely on spectroscopy, in quantum crystallography the scattering techniques play the central role, although spectroscopy as well as atomic microscopy are also sources of information.
Vanessa K. Peterson is a Neutron Instrument Scientist, at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO). She established an independent research program at ANSTO which specialised on improving understanding of energy systems and how they work. She manages the Echidna program, a high-resolution powder diffractometer, as well as Wombat - a high-intensity powder diffractometer. Peterson's expertise includes synchtron and laboratory x-ray techniques, as well as neutron powder diffraction, as well as single crystal x-ray diffraction.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Bacon, Prof. George Edward (5 Dec. 1917–18 March 2011)", ukwhoswho.com, accessed 15 November 2023 (subscription required); "Bacon, Prof. George Edward" in Who's Who 2007, credoreference.com, accessed 23 August 2007