
Politics in Georgia involve a parliamentary representative democratic republic with a multi-party system. The President of Georgia is the ceremonial head of state and the Prime Minister of Georgia is the head of government. The President and the Government wield executive power. Legislative power is vested in both the Government and the unicameral Parliament of Georgia.

South Ossetia, officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, or the Tskhinvali Region, is a disputed territory in the South Caucasus, in the northern part of the internationally recognised Georgian territory. It has a population of 53,000 people who live in an area of 3,900 km2, south of the Russian Caucasus, with 30,000 living in Tskhinvali. The separatist polity, Republic of South Ossetia, is recognised as a state by Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria. While Georgia lacks control over South Ossetia, the Georgian government and most members of the United Nations consider the territory part of Georgia, whose constitution designates the area as "the former autonomous district of South Ossetia", in reference to the former Soviet autonomous oblast disbanded in 1990.

There are four types of elections in Finland. Each Finnish citizen at least 18 years of age has the right to vote in each of the elections, which decide the following: the president, the parliament, the MEPs, and the municipal and city councils.

Nino Burjanadze is a Georgian politician and lawyer who served as Chairperson of the Parliament of Georgia from November 2001 to June 2008. As the first woman she has served as the acting head of state of Georgia twice; the first time from 23 November 2003 to 25 January 2004 in the wake of Eduard Shevardnadze's resignation during the Rose Revolution, and again from 25 November 2007 to 20 January 2008, when Mikheil Saakashvili stepped down to rerun in the early presidential elections. She withdrew into opposition to Saakashvili as the leader of the Democratic Movement-United Georgia party in 2008. In October 2013, she ran for president in the October 2013 election. She ran against 22 candidates and ended third with 10 percent of the vote.

Referendums in the United Kingdom are occasionally held at a national, regional or local level. National referendums can be permitted by an Act of Parliament and regulated through the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000, but they are by tradition extremely rare due to the principle of parliamentary sovereignty meaning that they cannot be constitutionally binding on either the Government or Parliament, although they usually have a persuasive political effect.
Regular elections in Croatia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation enacted by Parliament. The presidency, Parliament, county prefects and assemblies, city and town mayors, and city and municipal councils are all elective offices. Since 1990, five presidential elections have been held. During the same period, nine parliamentary elections were also held. In addition, there were six nationwide local elections. Croatia has held two elections to elect 11 members of the European Parliament following its accession to the EU on 1 July 2013.

The Hungarian Workers' Party is a communist party in Hungary led by Gyula Thürmer. Established after the fall of the communist Hungarian People's Republic, the party has yet to win a seat in the Hungarian parliament. Until May 2009 it was a member of the Party of the European Left.

This article provides information on elections and election results in Austria.

Referendums are held only occasionally by the Government of New Zealand. Referendums may be government-initiated or held in accordance with the Electoral Act 1993 or the Citizens Initiated Referenda Act 1993. Ten referendums have been held so far. Seven were government-led, and three were indicative citizen initiatives.
Referendums in Ukraine, according to the Ukrainian Constitution, are one of the lawful forms of expression of people's will.

Georgia and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) relations officially began in 1994 when Georgia joined the NATO-run Partnership for Peace. Georgia has moved quickly following the Rose Revolution in 2003 to seek closer ties and eventual membership with NATO. Georgia's powerful northern neighbor, Russia, has opposed the closer ties, including those expressed at the 2008 Bucharest summit where NATO members promised that Georgia would eventually join the organization. In the 7 December 2011 statement of the North Atlantic Council Georgia was designated as an "aspirant country".

Parliamentary elections were held in Georgia on May 21, 2008. President Mikheil Saakashvili proposed a referendum on bringing them forward from October to April after the 2007 Georgian demonstrations. The referendum was held at the same time as the early presidential election on 5 January 2008; according to exit polls, voters were largely in favour of having the elections in spring.

Presidential elections were held in Georgia on 5 January 2008, moved forward from autumn 2008 by President Mikheil Saakashvili after the 2007 demonstrations.
Denmark holds opt-outs from European Union policies in relation to security and defence, citizenship, police and justice, and the adoption of the euro. They were secured under the Edinburgh Agreement in 1992 after a referendum for the ratification of the Maastricht Treaty was rejected by Danish voters, as a package of measure to assuage concerns raised during that referendum.
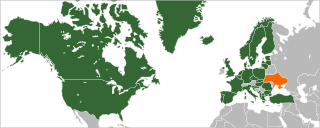
Relations between Ukraine and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) started in 1994. Ukraine applied to join the NATO Membership Action Plan (MAP) in 2008. Plans for NATO membership were shelved by Ukraine following the 2010 presidential election in which Viktor Yanukovych, who preferred to keep the country non-aligned, was elected President. Amid the Euromaidan unrest, Yanukovych fled Ukraine in February 2014. The interim Yatsenyuk Government which came to power initially said, with reference to the country's non-aligned status, that it had no plans to join NATO. However, following the Russian military invasion in Ukraine and parliamentary elections in October 2014, the new government made joining NATO a priority.
Parliamentary elections were held in Abkhazia on 23 November 1996, with a second round on 7 December. There was also a simultaneous referendum held amongst Abkhazian refugees.

The accession of Montenegro to NATO (NATO) took place on 5 June 2017. In December 2009, Montenegro was granted a Membership Action Plan, the final step in an application for membership in the organization. A formal invitation was issued by the alliance on 2 December 2015, with accession negotiations concluded with the signature by the Foreign Ministers of an Accession Protocol on 19 May 2016. Montenegro officially joined NATO on 5 June 2017.
A referendum in Slovakia was held on 23 May and 24 May 1997. Voters in Slovakia were asked four separate questions: on whether the country should join NATO, whether nuclear weapons should be allowed in Slovakia, whether foreign military bases should be allowed in Slovakia, and whether the President should be elected directly. The government left the last question off the ballot paper, leading to both referendums failing to meet the legally required turnout threshold.
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This article summarises referendum laws and practice in various countries.














