 | |
Germany | Kuwait |
|---|---|
As a country with traditionally strong contacts in the Arab world, Germany enjoys a good relationship with Kuwait. Among the EU states, Germany is Kuwait's most important trading partner. [1]
 | |
Germany | Kuwait |
|---|---|
As a country with traditionally strong contacts in the Arab world, Germany enjoys a good relationship with Kuwait. Among the EU states, Germany is Kuwait's most important trading partner. [1]
Kuwait gained independence from the United Kingdom on June 19, 1961. West Germany opened a consulate in Kuwait on November 4, 1963, which was upgraded to a consulate general on June 7, 1971. On February 3, 1973, the representation was converted into an embassy. [2] East Germany also established diplomatic relations with Kuwait in the 1970s and was represented by its own embassy in the country after 1972. In 1982, Erich Honecker, the leader of East Germany, visited Kuwait. [3] During the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait in the Gulf War, the GDR embassy, which was already in the process of being liquidated as part of German reunification, served as a place of refuge for German citizens in Kuwait. [4] They were later taken to Baghdad, detained there, and eventually brought home through the mediation of Willy Brandt. [5]
In 2007, the two countries signed an agreement to strengthen cooperation in security policy. Three years later, Emir Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah visited Germany, marking a high point in bilateral relations. German President Christian Wulff visited to participate in celebrations marking the 50th anniversary of Kuwait's independence in 2011. [6] German Foreign Minister Heiko Maas signed a memorandum of understanding to further intensify bilateral relations in 2018. [1]
The total volume of trade with Kuwait amounted to €1.0 billion in 2021, putting Kuwait in 79th place in the ranking of Germany's trading partners. [7] As Kuwait is one of the richest countries in the Arab world, it is a notable buyer of German goods and mostly imports industrial and chemical products from Germany. Due to the relatively affluent market, more than 700 brands and companies from Germany are represented in Kuwait. [8] At the same time, Kuwait is an investor in major listed German companies through its sovereign wealth fund, like Mercedes-Benz and GEA. [6] [1]
There has been an investment promotion agreement between the two countries since 1997 and a double taxation agreement since 2000. [6]
The two countries signed a bilateral cultural agreement in 1989. [1] Since 2009, Kuwaiti students have had the opportunity to study in Germany as part of an exchange program. There was a German school in Kuwait, which was not reopened after the Iraqi invasion. [6] In 2016, a U.S.-German school was opened in Kuwait, where U.S. curriculum is taught in German, Arabic, and English. [1]
German defense companies supplied various weapons to Kuwait, including fighter jets (2016), helicopters (2016), grenade weapons (2008), and submachine guns (2003). [9]


Since its independence in 1961, Kuwait has maintained strong international relations with most countries, especially nations within the Arab world. Its vast oil reserves give it a prominent voice at the global economic forums and organizations like the OPEC. Kuwait is also a major ally of ASEAN, a regional ally of China, and a major non-NATO ally.

Kuwait–Turkey relations are foreign relations between Turkey and Kuwait. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Turkey describes the current relations as being at "outstanding levels". Bilateral trade between the two countries in 2016 was estimated to be worth around US$700 million by the Turkish Deputy Prime Minister, Mehmet Simek.

Kenyan–Kuwaiti relations are bilateral relations between Kenya and Kuwait.

Kuwait and Mexico established diplomatic relations in 1975. Both nations are members of the United Nations.

Germany–Morocco relations date back to the 19th century. The German Foreign Office describes Morocco as a "central partner of the European Union and Germany in North Africa," and Germany is an important trading partner for Morocco. In the past, however, relations have not always been entirely free of tension.

Relations between Germany and Algeria are described as "good" by the German Federal Foreign Office. Germany is among Algeria's most important trading partners. The two countries concluded an energy partnership in 2015.
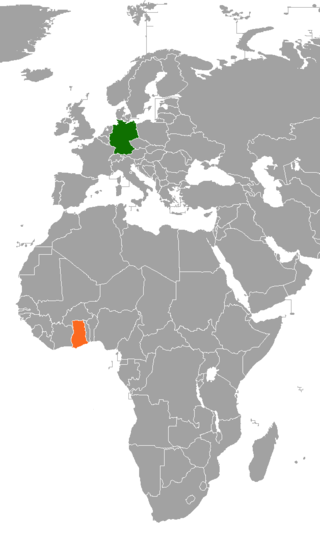
Germany–Ghana relations are good and Ghana is one of the priority countries for German development aid. Official Diplomatic Relations between the two countries were established in the 1950s, but contacts between the two societies go back much further and can be traced back to the 17th century.
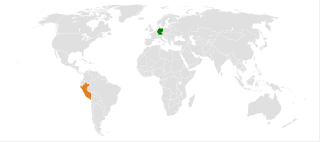
Germany–Peru relations are the bilateral relations between Germany and Peru. The relations are described by the German Foreign Office as "close and friendly". Cooperation between Germany and Peru takes place at both the bilateral and multilateral level.
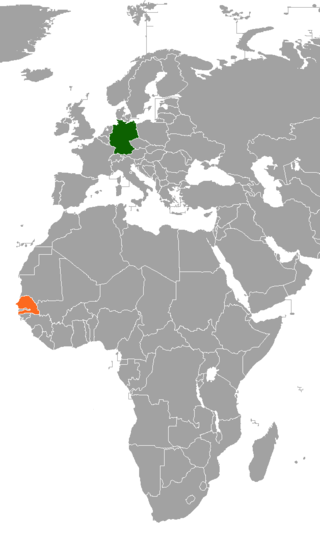
Germany–Senegal relations are the bilateral relations between Germany and Senegal. The relations are described by the German Foreign Office as "friendly." The two countries share a close partnership in development cooperation, and numerous cultural ties exist between the two countries.

On the diplomatic level, Colombia–Germany relations have existed since 1872 and thus for more than 140 years.

Germany–Mali relations gained depth and intensity in the 2010s as the German government stepped up its efforts to stabilize the Sahel region, and there were an increasing number of bilateral state visits. Germany is also increasingly engaged in security policy in Mali.
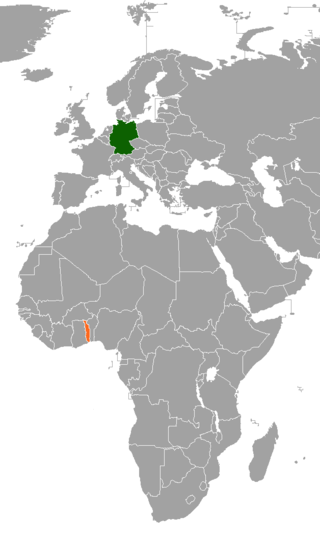
Germany–Togo relations are shaped by the shared past of both countries. From 1884 to 1914, Togo was a colony of Germany under the name of Togoland.

Germany–Mauritania relations are described as "good" by the German Foreign Office, and Germany provides development aid to Mauritania. However, state visits at the bilateral level are rare.

Eritrea–Germany relations have existed since Eritrea's independence from Ethiopia in 1993, but they are strained by the poor human rights situation in Eritrea. Among Afro-Germans, Eritreans are now among the largest groups.
Germany–Lebanon relations are "traditionally friendly" and "very close", according to the German Foreign Office. For Lebanon, Germany is one of the most important donor countries for the care of the numerous refugees in the country. Among the Arabs in Germany, the Lebanese are among the largest groups with almost 160,000 members (2021).
Germany–Oman relations are described by the German Foreign Office as "good and friendly". Germany is one of Oman's most important economic partners in areas outside the oil industry.

Germany–Madagascar relations are "traditionally friendly", according to the German Foreign Office. Diplomatic contacts have been maintained between the two countries since the 19th century. In the 21st century, relations between the two countries are predominantly characterized by development cooperation.
Germany–Yemen relations have existed since the 1960s. During the civil war in Yemen, the Federal Republic of Germany provided humanitarian aid to the country.
Ecuador–Germany relations have existed since 1922, and in the 21st century they focus on development cooperation, environmental policy, trade and investment and education.

Bahrain-Germany relations have existed since 1972 and are described as "good" by the German Foreign Office. Germany enjoys a good reputation in Bahrain, and the German economy in particular is highly regarded.