
In marine geology, a guyot, also called a tablemount, is an isolated underwater volcanic mountain (seamount) with a flat top more than 200 m (660 ft) below the surface of the sea. The diameters of these flat summits can exceed 10 km (6.2 mi). Guyots are most commonly found in the Pacific Ocean, but they have been identified in all the oceans except the Arctic Ocean. They are analogous to tables on land.

A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface, and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000–4,000 m (3,300–13,100 ft) in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least 1,000 m (3,281 ft) above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such flat-top seamounts are called "guyots" or "tablemounts".
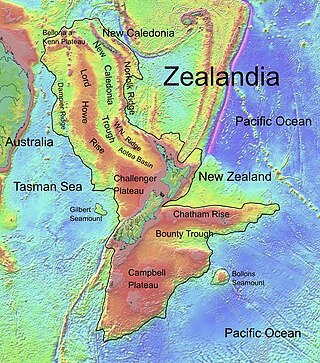
The Lord Howe Rise is a deep sea plateau which extends from south west of New Caledonia to the Challenger Plateau, west of New Zealand in the south west of the Pacific Ocean. To its west is the Tasman Basin and to the east is the New Caledonia Basin. Lord Howe Rise has a total area of about 1,500,000 km2 (580,000 sq mi), and generally lies about 750 to 1,200 metres under water. It is part of Zealandia, a much larger continent that is now mostly submerged, and so is composed of continental crust. Some have included the 3,500 m (11,500 ft) deep New Caledonia Basin as within the rise, given its continental crust origin, and this would give a larger total area of 1,950,000 km2 (750,000 sq mi).

The Lord Howe Seamount Chain formed during the Miocene. It features many coral-capped guyots and is one of the two parallel seamount chains alongside the east coast of Australia; the Lord Howe and Tasmantid seamount chains both run north-south through parts of the Coral Sea and Tasman Sea. These chains have longitudes of approximately 159°E and 156°E respectively.

The Great Meteor Seamount, also called the Great Meteor Tablemount, is a guyot and the largest seamount in the North Atlantic with a volume of 24,000 km3 (5,800 cu mi). It is one of the Seewarte Seamounts, rooted on a large terrace located south of the Azores Plateau. The crust underlying Great Meteor has an age of 85 million years, deduced from the magnetic anomaly 34 (An34) at this location.

The East Tasman Plateau is a submerged microcontinent south east of Tasmania. Its area is 50,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), and it is mostly from 2,500 to 3,000 metres deep. It is a circular piece of continental rocks surrounded by oceanic crust. Volcanism occurred there 36 million years ago. The East Tasman Plateau is separated from the island of Tasmania by 100 kilometres (62 mi) of deeper water, and the East Tasman Saddle is a higher ridge connecting the plateau to the Freycinet Peninsula region of the Tasmanian East Coast. This ridge runs north west from the plateau. South-west of the plateau is the L'Atalante Depression. The East Tasman Plateau represents a continental fragment.

The Tasmantid Seamount Chain is a 2,000 km (1,200 mi) long chain of seamounts in the South Pacific Ocean. The chain consists of over 16 extinct volcanic peaks, many rising more than 4,000 m (13,000 ft) from the seabed. It is one of the two parallel seamount chains alongside the East Coast of Australia; the Lord Howe and Tasmantid seamount chains both run north-south through parts of the Coral Sea and Tasman Sea. These chains have longitudes of approximately 159°E and 156°E respectively.

Wōdejebato is a Cretaceous guyot or tablemount in the northern Marshall Islands, Pacific Ocean. Wōdejebato is probably a shield volcano and is connected through a submarine ridge to the smaller Pikinni Atoll 74 kilometres (46 mi) southeast of the guyot; unlike Wōdejebato, Pikinni rises above sea level. The seamount rises for 4,420 metres (14,500 ft) to 1,335 metres (4,380 ft) depth and is formed by basaltic rocks. The name Wōdejebato refers to a sea god of Pikinni.
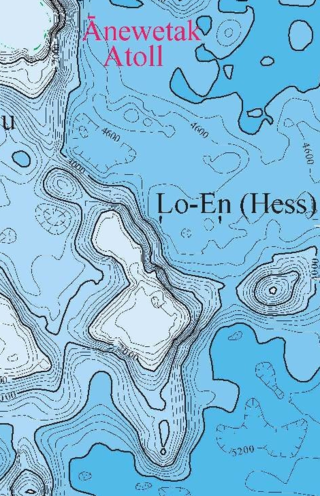
Lo-En or Hess is an Albian–Campanian guyot in the Marshall Islands. One among a number of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean, it was probably formed by a hotspot in what is present-day French Polynesia. Lo-En lies southeast of Eniwetok which rises above sea level, and Lo-En is almost connected to it through a ridge.

Ruwitūn̄tūn̄ is a guyot in the Pacific Ocean which reaches a depth of 1,215 metres (3,986 ft) below sea level. It is capped off with a summit platform covered in sediments and some volcanic pinnacles with craters. Basaltic rocks have been found on Ruwitūn̄tūn̄.

Gifford Marine Park is an Australian marine park located 700 km east of Brisbane, Queensland. Part of the Temperate East Marine Park Network, it protects 5,828 km2 around two flat-topped seamounts, located in the Lord Howe Seamount Chain.
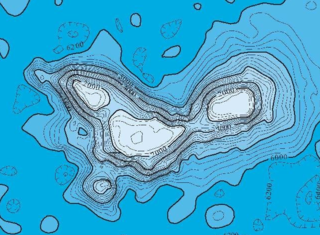
Ioah Guyot is a seamount in the Pacific Ocean, close to the Marshall Islands. Part of the Magellan Seamounts, it is a shield volcano that has erupted alkali basalt and hawaiite 87 million years ago, but may have continued erupting into the Miocene. During the Cretaceous, reefs developed on the guyot.

Pako Guyot is a guyot in the Pacific Ocean.

Ita Mai Tai is a Cretaceous-early Cenozoic seamount northwest of the Marshall Islands and north of Micronesia. One among a number of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean, it is part of the Magellan Seamounts which may have a hotspot origin although Ita Mai Tai itself may not have formed on a hotspot.

Horizon Guyot is a presumably Cretaceous guyot (tablemount) in the Mid-Pacific Mountains, Pacific Ocean. It is an elongated ridge, over 300 kilometres (190 mi) long and 4.3 kilometres (2.7 mi) high, that stretches in a northeast-southwest direction and has two flat tops; it rises to a minimum depth of 1,443 metres (4,730 ft). The Mid-Pacific Mountains lie west of Hawaii and northeast of the Line Islands.

Capricorn Seamount is a seamount in Tonga. It rises 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) to a depth of about 360 m (1,180 ft) and is capped off by a 15 km (9.3 mi) wide summit platform. It appears to be a submerged volcano of Miocene age that may be part of a volcanic chain with Niue. Capricorn Seamount is located on the eastern flank of the Tonga Trench and is in the process of breaking up; in turn the trench has been altered by the interaction with the downgoing seamount.
Gascoyne Seamount, also called Gascoyne Guyot or Gascoyne Tablemount, is a guyot in the Tasman Sea of the South Pacific Ocean.

The Taupo Bank is an extinct volcanic seamount of the Tasmantid Seamount Chain.

The Derwent Hunter Guyot is an extinct volcanic seamount of the Tasmantid Seamount Chain.

The Britannia Guyots are a line of extinct volcanic seamounts in the Tasmantid Seamount Chain.
















