Diophantus of Alexandria was a Greek mathematician, who was the author of two main works: On Polygonal Numbers, which survives incomplete, and the Arithmetica in thirteen books, most of it extant, made up of arithmetical problems that are solved through algebraic equations.

Wacław Franciszek Sierpiński was a Polish mathematician. He was known for contributions to set theory, number theory, theory of functions, and topology. He published over 700 papers and 50 books.

Kollagunta Gopalaiyer Ramanathan was an Indian mathematician known for his work in number theory. His contributions are also to the general development of mathematical research, and teaching in India.
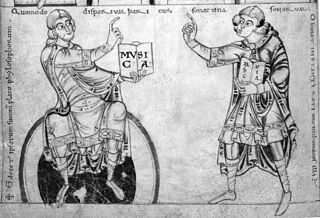
Nicomachus of Gerasa was an Ancient Greek Neopythagorean philosopher from Gerasa, in the Roman province of Syria. Like many Pythagoreans, Nicomachus wrote about the mystical properties of numbers, best known for his works Introduction to Arithmetic and Manual of Harmonics, which are an important resource on Ancient Greek mathematics and Ancient Greek music in the Roman period. Nicomachus' work on arithmetic became a standard text for Neoplatonic education in Late antiquity, with philosophers such as Iamblichus and John Philoponus writing commentaries on it. A Latin paraphrase by Boethius of Nicomachus's works on arithmetic and music became standard textbooks in medieval education.

Jacques Lefèvre d'Étaples was a French theologian and a leading figure in French humanism. He was a precursor of the Protestant movement in France. The "d'Étaples" was not part of his name as such, but used to distinguish him from Jacques Lefèvre of Deventer, a less significant contemporary who was a friend and correspondent of Erasmus. Both are also sometimes called by the German version of their name, Jacob/Jakob Faber. He himself had a sometimes tense relationship with Erasmus, whose work on Biblical translation and in theology closely paralleled his own.

Arithmetica is an Ancient Greek text on mathematics written by the mathematician Diophantus in the 3rd century AD. It is a collection of 130 algebraic problems giving numerical solutions of determinate equations and indeterminate equations.
In mathematics, a prime number p is called a Chen prime if p + 2 is either a prime or a product of two primes. The even number 2p + 2 therefore satisfies Chen's theorem.

Glenealy is one of the few roads or streets without a suffix in Hong Kong. Located in the Mid-Levels on the Hong Kong Island, Hong Kong, it starts from Ice House Street and goes uphill to Hong Kong Zoological and Botanical Gardens, across Robinson Road and ends at Hornsey Road and Conduit Road.

Arithmetica Universalis is a mathematics text by Isaac Newton. Written in Latin, it was edited and published by William Whiston, Newton's successor as Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge. The Arithmetica was based on Newton's lecture notes.

Acta Arithmetica is a scientific journal of mathematics publishing papers on number theory. It was established in 1935 by Salomon Lubelski and Arnold Walfisz. The journal is published by the Institute of Mathematics of the Polish Academy of Sciences.
The Wicklow Senior Hurling Championship is an annual club hurling competition organised by the Wicklow County Board of the Gaelic Athletic Association and contested by the top-ranking senior clubs in the county of Wicklow in Ireland, deciding the competition winners through a group and knockout format. It is the most prestigious competition in Wicklow hurling.

The R752 road is a regional road in County Wicklow, Ireland. From its junction with the R772 in Rathnew on the outskirts of Wicklow Town it takes a generally south-westerly route to its junction with the R747 in the village of Woodenbridge, where it terminates. The road is 26 km (16 mi) long.

Glenealy is a village 8 km (5 mi) west of Wicklow Town, in County Wicklow, on the R752 road. The Dublin–Rosslare railway line also passes through the village.
In mathematics, the Newton inequalities are named after Isaac Newton. Suppose a1, a2, ..., an are non-negative real numbers and let denote the kth elementary symmetric polynomial in a1, a2, ..., an. Then the elementary symmetric means, given by

Michael Stifel or Styfel was a German monk, Protestant reformer and mathematician. He was an Augustinian who became an early supporter of Martin Luther. He was later appointed professor of mathematics at Jena University.
The 2005–06 All-Ireland Senior Club Hurling Championship was the 36th staging of the All-Ireland Senior Club Hurling Championship, the Gaelic Athletic Association's premier inter-county club hurling tournament. The championship began on 30 October 2005 and ended on 17 March 2006.
Glenealy Hurling Club is a Gaelic Athletic Association club located in the parish of Glenealy and Ashford in County Wicklow, Ireland. The club was founded in 1885 as a football club but switched codes to the game of hurling in the early 1920s.

Glenea is a genus of longhorn beetles belonging to the family Cerambycidae, subfamily Lamiinae.

Summa de arithmetica, geometria, proportioni et proportionalita is a book on mathematics written by Luca Pacioli and first published in 1494. It contains a comprehensive summary of Renaissance mathematics, including practical arithmetic, basic algebra, basic geometry and accounting, written for use as a textbook and reference work.

Glenea venus is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1865. It is known from Papua New Guinea, Australia and Indonesia.













