
Peptide hormones are hormones whose molecules are peptides. Peptide hormones have shorter amino acid chain lengths than protein hormones. These hormones have an effect on the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones can be classified as either amino acid–based hormones or steroid hormones. The former are water-soluble and act on the surface of target cells via second messengers; the latter, being lipid-soluble, move through the plasma membranes of target cells to act within their nuclei.

Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to treat a number of health conditions. Its effect is opposite to that of insulin, which lowers extracellular glucose. It is produced from proglucagon, encoded by the GCG gene.

Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion.

Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans by a blood-glucose–dependent mechanism.
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, abbreviated as GIP, is an inhibiting hormone of the secretin family of hormones. While it is a weak inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, its main role, being an incretin, is to stimulate insulin secretion.
Enteroglucagon is a peptide hormone derived from preproglucagon. It is a gastrointestinal hormone, secreted from mucosal cells primarily of the colon and terminal ileum. It consists of 37 amino acids. Enteroglucagon is released when fats and glucose are present in the small intestine; which decrease the motility to allow sufficient time for these nutrients to be absorbed.

Exenatide, sold under the brand name Byetta and Bydureon among others, is a medication used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. It is used together with diet, exercise, and potentially other antidiabetic medication. It is a treatment option after metformin and sulfonylureas. It is given by injection under the skin twice daily or once weekly.

Proglucagon is a protein that is cleaved from preproglucagon. Preproglucagon in humans is encoded by the GCG gene.

Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone deriving from the tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage, which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 protein secondary structure includes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region.

Peptide YY (PYY) also known as peptide tyrosine tyrosine is a peptide that in humans is encoded by the PYY gene. Peptide YY is a short peptide released from cells in the ileum and colon in response to feeding. In the blood, gut, and other elements of periphery, PYY acts to reduce appetite; similarly, when injected directly into the central nervous system, PYY is also anorexigenic, i.e., it reduces appetite.
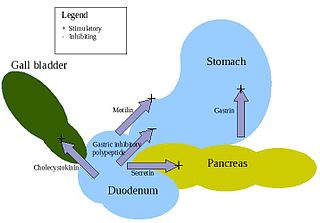
Enteroendocrine cells are specialized cells of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas with endocrine function. They produce gastrointestinal hormones or peptides in response to various stimuli and release them into the bloodstream for systemic effect, diffuse them as local messengers, or transmit them to the enteric nervous system to activate nervous responses. Enteroendocrine cells of the intestine are the most numerous endocrine cells of the body. They constitute an enteric endocrine system as a subset of the endocrine system just as the enteric nervous system is a subset of the nervous system. In a sense they are known to act as chemoreceptors, initiating digestive actions and detecting harmful substances and initiating protective responses. Enteroendocrine cells are located in the stomach, in the intestine and in the pancreas. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses in these enteroendocrine cells via their fermentation product, acetate.

The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) found on beta cells of the pancreas and on neurons of the brain. It is involved in the control of blood sugar level by enhancing insulin secretion. In humans it is synthesised by the gene GLP1R, which is present on chromosome 6. It is a member of the glucagon receptor family of GPCRs. GLP1R is composed of two domains, one extracellular (ECD) that binds the C-terminal helix of GLP-1, and one transmembrane (TMD) domain that binds the N-terminal region of GLP-1. In the TMD domain there is a fulcrum of polar residues that regulates the biased signaling of the receptor while the transmembrane helical boundaries and extracellular surface are a trigger for biased agonism.

Peptide PHI, also known as peptide histidine isoleucine, is a peptide which functions as a hormone. This peptide contains a composition of 27 amino acids with histidine on the N-terminus and isoleucine on the C-terminus. It was originally isolated from the mammalian small intestine amongst mammalian neurons called intramural neurons which function in the motor activity of the intestinal walls. An example of this was revealed in a study that demonstrated that this peptide regulates water and electrolyte transportation in the human jejunum; similar to its inhibitory effects on fluid absorption in the small intestine of pigs and rats.

The gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIP-R), also known as the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GIPR gene.
Glucagon-like peptide-2 receptor (GLP-2R) is a protein that in human is encoded by the GLP2R gene located on chromosome 17.
Secretin receptor family consists of secretin receptors regulated by peptide hormones from the glucagon hormone family. The family is different from adhesion G protein-coupled receptors.

Glucagon/gastric inhibitory polypeptide/secretin/vasoactive intestinal peptide hormones are a family of evolutionarily related peptide hormones that regulate activity of G-protein-coupled receptors from the secretin receptor family.
Albiglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist drug marketed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) for treatment of type 2 diabetes. As of 2017 it is unclear if it affects a person's risk of death. GSK has announced that it intends to withdraw the drug from the worldwide market by July 2018 for economic reasons.

Teduglutide is a 33-membered polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP-2) analog that is used for the treatment of short bowel syndrome. It works by promoting mucosal growth and possibly restoring gastric emptying and secretion. In Europe it has been granted orphan drug status and is marketed under the brand Revestive by Nycomed. It was approved by the United States under the name Gattex on 21 December 2012, where it was given status as an orphan drug.
Svetlana Mojsov is a Serbian chemist who is a research associate professor at Rockefeller University. Her research considers peptide synthesis. She discovered the glucagon-like peptide-1 and uncovered its role in glucose metabolism and the secretion of insulin. Her breakthroughs were transformed by Novo Nordisk into therapeutic agents against diabetes and obesity.














