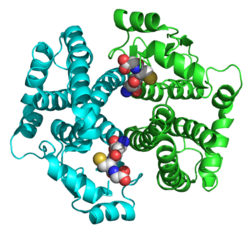
1ags: A SURFACE MUTANT (G82R) OF A HUMAN ALPHA-GLUTATHIONE S-TRANSFERASE SHOWS DECREASED THERMAL STABILITY AND A NEW MODE OF MOLECULAR ASSOCIATION IN THE CRYSTAL
1gsd: GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE A1-1 IN UNLIGANDED FORM
1gse: GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE A1-1 COMPLEXED WITH AN ETHACRYNIC ACID GLUTATHIONE CONJUGATE (MUTANT R15K)
1gsf: GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE A1-1 COMPLEXED WITH ETHACRYNIC ACID
1guh: STRUCTURE DETERMINATION AND REFINEMENT OF HUMAN ALPHA CLASS GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE A1-1, AND A COMPARISON WITH THE MU AND PI CLASS ENZYMES
1k3l: Crystal Structure Analysis of S-hexyl-glutathione Complex of Glutathione Transferase at 1.5 Angstroms Resolution
1k3o: Crystal Structure Analysis of apo Glutathione S-Transferase
1k3y: Crystal Structure Analysis of human Glutathione S-transferase with S-hexyl glutatione and glycerol at 1.3 Angstrom
1pkw: Crystal structure of human glutathione transferase (GST) A1-1 in complex with glutathione
1pkz: Crystal structure of human glutathione transferase (GST) A1-1
1pl1: Crystal structure of human glutathione transferase (GST) A1-1 in complex with a decarboxy-glutathione
1pl2: Crystal structure of human glutathione transferase (GST) A1-1 T68E mutant in complex with decarboxy-glutathione
1tdi: Crystal Structure of hGSTA3-3 in Complex with Glutathione
1usb: RATIONAL DESIGN OF A NOVEL ENZYME - EFFICIENT THIOESTER HYDROLYSIS ENABLED BY THE INCORPORATION OF A SINGLE HIS RESIDUE INTO HUMAN GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASE A1-1
1xwg: Human GST A1-1 T68E mutant
1ydk: Crystal structure of the I219A mutant of human glutathione transferase A1-1 with S-hexylglutathione