
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of the cell and another. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipids in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of the lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to the surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes.

The cytochrome complex, or cyt c, is a small hemeprotein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where it plays a critical role in cellular respiration. It transfers electrons between Complexes III and IV. Cytochrome c is highly water-soluble, unlike other cytochromes. It is capable of undergoing oxidation and reduction as its iron atom converts between the ferrous and ferric forms, but does not bind oxygen. It also plays a major role in cell apoptosis. In humans, cytochrome c is encoded by the CYCS gene.
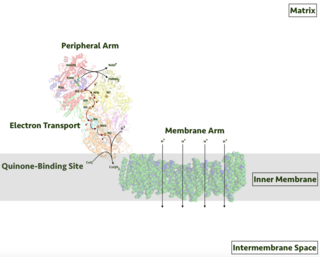
Respiratory complex I, EC 7.1.1.2 is the first large protein complex of the respiratory chains of many organisms from bacteria to humans. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and translocates protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane of bacteria.

Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane. Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane.
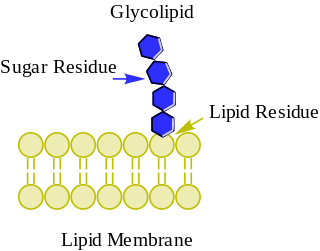
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.
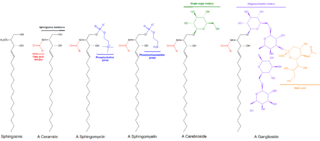
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with a terminal hydroxyl group is a ceramide. Other common groups bonded to the terminal oxygen atom include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids.

Photosystem I is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae, plants, and cyanobacteria. Photosystem I is an integral membrane protein complex that uses light energy to catalyze the transfer of electrons across the thylakoid membrane from plastocyanin to ferredoxin. Ultimately, the electrons that are transferred by Photosystem I are used to produce the moderate-energy hydrogen carrier NADPH. The photon energy absorbed by Photosystem I also produces a proton-motive force that is used to generate ATP. PSI is composed of more than 110 cofactors, significantly more than Photosystem II.

Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of sphingosine and a fatty acid joined by an amide bond. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells.
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), also called plasma lipid transfer protein, is a plasma protein that facilitates the transport of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides between the lipoproteins. It collects triglycerides from very-low-density (VLDL) or Chylomicrons and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and vice versa. Most of the time, however, CETP does a heteroexchange, trading a triglyceride for a cholesteryl ester or a cholesteryl ester for a triglyceride.
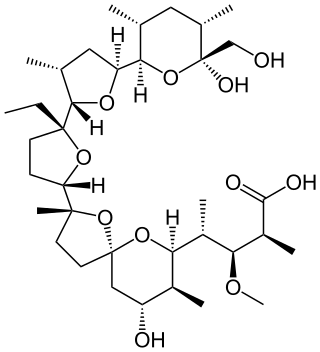
Monensin is a polyether antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces cinnamonensis. It is widely used in ruminant animal feeds.

Adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT), also known as the ADP/ATP translocase (ANT), ADP/ATP carrier protein (AAC) or mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier, exchanges free ATP with free ADP across the inner mitochondrial membrane. ANT is the most abundant protein in the inner mitochondrial membrane and belongs to mitochondrial carrier family.

The germ cell nuclear factor (GCNF), also known as RTR or NR6A1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR6A1 gene. GCNF is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.
N-acetyllactosamine synthase is a galactosyltransferase enzyme. It is a component of lactose synthase This enzyme modifies the connection between two molecule UDP-galactose and N-actyl-D-glucosamine and generates two different molecules UDP and N-acetyllactosamine as products. The main function of the enzyme is associated with the biosynthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids in both human and animals. In human, the activity of this enzyme can be found in Golgi apparatus.

Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase is a transferase enzyme which converts phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the liver. In humans it is encoded by the PEMT gene within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17.

Cytochromes c cytochromes, or heme-containing proteins, that have heme C covalently attached to the peptide backbone via one or two thioether bonds. These bonds are in most cases part of a specific Cys-X-X-Cys-His (CXXCH) binding motif, where X denotes a miscellaneous amino acid. Two thioether bonds of cysteine residues bind to the vinyl sidechains of heme, and the histidine residue coordinates one axial binding site of the heme iron. Less common binding motifs can include a single thioether linkage, a lysine or a methionine instead of the axial histidine or a CXnCH binding motif with n>2. The second axial site of the iron can be coordinated by amino acids of the protein, substrate molecules or water. Cytochromes c possess a wide range of properties and function as electron transfer proteins or catalyse chemical reactions involving redox processes. A prominent member of this family is mitochondrial cytochrome c.

Glycolipid transfer protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GLTP gene.

CYP4F22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F22 gene.
KAHRP is a protein expressed by Plasmodium falciparum infecting erythrocytes. KAHRP is a major component of knobs, feature found on Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes.
The lysosomal cystine transporter (LCT) family is part of the TOG Superfamily and includes secondary transport proteins that are derived from animals, plants, fungi and other eukaryotes. They exhibit 7 putative transmembrane α-helical spanners (TMSs) and vary in size between about 200 and 500 amino acyl residues, although most have between 300 and 400 residues.

A single-pass membrane protein also known as single-spanning protein or bitopic protein is a transmembrane protein that spans the lipid bilayer only once. These proteins may constitute up to 50% of all transmembrane proteins, depending on the organism, and contribute significantly to the network of interactions between different proteins in cells, including interactions via transmembrane alpha helices. They usually include one or several water-soluble domains situated at the different sides of biological membranes, for example in single-pass transmembrane receptors. Some of them are small and serve as regulatory or structure-stabilizing subunits in large multi-protein transmembrane complexes, such as photosystems or the respiratory chain. A 2013 estimate identified about 1300 single-pass membrane proteins in the human genome.
















