Related Research Articles
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. Within Indo-European, the three largest phyla in Europe are Romance, Germanic, and Slavic; they have more than 200 million speakers each and together account for close to 90% of Europeans. Smaller phyla of Indo-European found in Europe include Hellenic, Baltic, Albanian, Celtic, and Armenian ; Indo-Aryan, though a large subfamily of Indo-European, has a relatively small number of speakers in Europe.
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Christian non-profit organization.
The Kangjia language is a Mongolic language spoken by a Muslim population of around 300 people in Jainca (Jianzha) County, Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Qinghai province of China. As to its taxonomic affiliation, Kangjia seems to be an intermediate between Bonan language and Dongxiang language (Santa).

Chad has two official languages, Arabic and French, and over 120 indigenous languages. A vernacular version of Arabic, Chadian Arabic, is a lingua franca and the language of commerce, spoken by 40–60% of the population. The two official languages have fewer speakers than Chadian Arabic. Standard Arabic is spoken by around 615,000 speakers. French is widely spoken in the main cities such as N'Djamena and by most men in the south of the country. Most schooling is in French. The language with the most first-language speakers is probably Ngambay, with around one million speakers.
Kim Mun is a Mienic language spoken by 200,000 of the Yao people in the Chinese provinces of Guangxi, Hunan and Yunnan, with about 61,000 of the speakers in Hainan Province. There are also speakers in Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.

The Dene TháFirst Nation is a First Nations government of the South Slavey in Northern Alberta, Canada. The people call themselves Dene Dháa or 'Ordinary People' in the Dene Dháh language. Its population is centered primarily in three communities: Bushe River, Meander River, and Chateh, but approximately 600 members who live off-reserve. Dene Thá First Nation is Treaty 8 nation and a member of the North Peace Tribal Council.
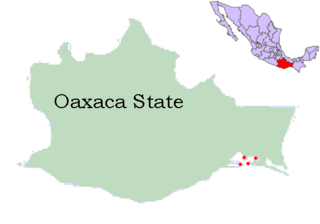
The Huave are an indigenous people of Mexico. The autodenomination term used by the Huave themselves is Ikoots or Kunajts, or Mareños. They have inhabited the Isthmus of Tehuantepec for more than 3000 years, preceding the Zapotec people in settling the area. Today they inhabit several villages on the sandspits of the Pacific Ocean and trade marine products with inland neighbors. According to the 2000 census, 13,687 people declared themselves to be Huave speakers, however, many non-speakers still identify as Huaves or Mareños. Their language is called Huave, or ombeayiüts/umbeyajts, depending on the dialect.
Demta, also known as Sowari and Muris, is a Papuan language on the north coast of Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken in Ambora, Muris Besar, Muris Kecil, and Yougafsa villages, all located in Demta District.
The Kim language of southern Chad is an Mbum language spoken by 15,000 people. It is one of the three members of the Kim languages group, together with Besme and Goundo.
Tami is an Austronesian language on the Tami Islands and in a few villages at the tip of the Huon Peninsula in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. It is not closely related to the other Huon Gulf languages, but like other North New Guinea languages in Morobe Province, its basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO).
Besme is an Adamawa language of Chad. It is one of the three members of the Kim languages group, together with Kim and Goundo.
Bawm or Bawm Chin, also known as Banjogi, is a Kuki-Chin language primarily spoken in Bangladesh. It is also spoken in adjacent regions of Northeast India and Myanmar. The Bawms that live on the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh call their settlements "Bawmram", which literally means an area or location inhabited by Bawms.
Bebele is a Bantu language of Cameroon. It is mutually intelligible with other Beti dialects such as Ewondo and Fang.
Pangkhua (Pangkhu), or Paang, is a Kuki-Chin language primarily spoken in Bangladesh. Most speakers of Pangkhu are bilingual in Bengali, and most education in Pangkhu is conducted in that language.

Chiru (Naga) is a Southern Naga language spoken mostly in Manipur. The Chiru population numbers approximately 8,599. It is an endangered spoken in three districts of Manipur: Senapati, Noney district of Manipur and Cachar district of Assam. Chiru has been recognized as a Scheduled Tribe of Manipur by the government of India since 1956 under "The Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Orders (Amendment) Act, Act No. 63 of 1956" Dated 25 September 1956. The total population of the native speakers of Chiru is only 8599. The native speakers have high proficiency in Meitei language. The language is neither used in schools nor in radio or mass media. Older people read and write in Meitei language. The younger generation of Chiru speakers prefers Roman script. The speakers of this language use Meitei language as their second language (L2) according to the Ethnologue.
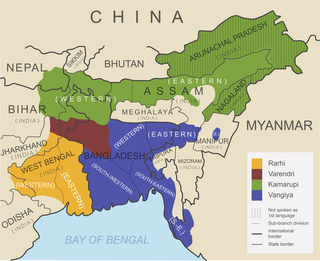
The Bengali–Assamese languages is a grouping of several languages in the eastern Indian subcontinent. This group belongs to the Eastern zone of Indo-Aryan languages. The languages in this group according to Glottolog includes Assamese, Bengali, Bishnupriya, Chakma, Chittagonian, Hajong, Kharia Thar, Kurmukar, Lodhi, Mal Paharia, Noakhailla, Rajbangshi, Rohingya, Sylheti, Tangchangya and Surjapuri.
Kol is a Munda language spoken by a minority in Bangladesh. Kim (2010) considers Kol and Koda to be Mundari cluster languages. Kol villages include Babudaing in Rajshahi Division and Rangpur Division, Bangladesh, while Koda-speaking villages include Kundang and Krishnupur.
Ná-Meo is a language of northern Vietnam, spoken by the Mieu people. Nguyen (2007) believes Na Meo may be a Hmongic language closest to Qiandong Miao.
References
- 1 2 Goundo at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)
