
The cell is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology or cellular biology.
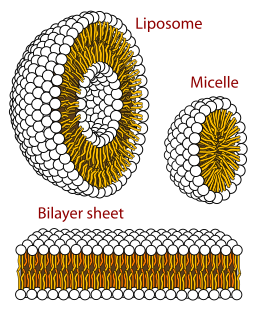
A biological membrane or biomembrane is an enclosing or separating membrane that acts as a selectively permeable barrier within living things. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipid in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes.

In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many.

Cell biology is a branch of biology that studies the structure and function of the cell, which is the basic unit of life. Cell biology is concerned with the physiological properties, metabolic processes, signaling pathways, life cycle, chemical composition and interactions of the cell with their environment. This is done both on a microscopic and molecular level as it encompasses prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences; it is also essential for research in bio-medical fields such as cancer, and other diseases. Research in cell biology is closely related to genetics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology and cytochemistry.
The cytosol, also known as intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix, is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.

The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a type of organelle found in eukaryotic cells that forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs or tube-like structures known as cisternae. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum occurs in most types of eukaryotic cells, but is absent from red blood cells and spermatozoa.

The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. In eukaryotes the organelles of the endomembrane system include: the nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, endosomes, and plasma (cell) membrane among others. The system is defined more accurately as the set of membranes that form a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport. Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of chloroplasts or mitochondria, but might have evolved from the latter.

A lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells and most plant cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, cell signaling, and energy metabolism.

A vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in all plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell.

Symbiogenesis, or endosymbiotic theory, is an evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms, first articulated in 1905 and 1910 by the Russian botanist Konstantin Mereschkowski, and advanced and substantiated with microbiological evidence by Lynn Margulis in 1967. It holds that the organelles distinguishing eukaryote cells evolved through symbiosis of individual single-celled prokaryotes . The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibly other organelles of eukaryotic cells represent formerly free-living prokaryotes taken one inside the other in endosymbiosis. In more detail, mitochondria appear to be related to Rickettsiales proteobacteria, and chloroplasts to nitrogen-fixing filamentous cyanobacteria. Among the many lines of evidence supporting symbiogenesis are that new mitochondria and plastids are formed only through binary fission, and that cells cannot create new ones otherwise; that the transport proteins called porins are found in the outer membranes of mitochondria, chloroplasts and bacterial cell membranes; that cardiolipin is found only in the inner mitochondrial membrane and bacterial cell membranes; and that some mitochondria and plastids contain single circular DNA molecules similar to the chromosomes of bacteria.
The plastid is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. Plastids were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, but A. F. W. Schimper was the first to provide a clear definition. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cells of autotrophic eukaryotes. They often contain pigments used in photosynthesis, and the types of pigments in a plastid determine the cell's color. They have a common evolutionary origin and possess a double-stranded DNA molecule that is circular, like that of prokaryotic cells.

A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of only one cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of more than one cell. Unicellular organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but the group includes the protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early protocells possibly emerging 3.8–4 billion years ago.

The soma, perikaryon, neurocyton, or cell body is the bulbous, non-process portion of a neuron or other brain cell type, containing the cell nucleus. The word 'soma' comes from the Greek 'σῶμα', meaning 'body'. Although it is often used to refer to neurons, it can also refer to other cell types as well, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia. There are many different specialized types of neurons, and their sizes vary from as small as about 5 micrometres to over 10 millimetre for some of the smallest and largest neurons of invertebrates, respectively.

A hydrogenosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle of some anaerobic ciliates, trichomonads, fungi, and animals. The hydrogenosomes of trichomonads produce molecular hydrogen, acetate, carbon dioxide and ATP by the combined actions of pyruvate:ferredoxin oxido-reductase, hydrogenase, acetate:succinate CoA transferase and succinate thiokinase. Superoxide dismutase, malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating), ferredoxin, adenylate kinase and NADH:ferredoxin oxido-reductase are also localized in the hydrogenosome. It is nearly universally accepted that hydrogenosomes evolved from mitochondria.

The glycosome is a membrane-enclosed organelle that contains the glycolytic enzymes. The term was first used by Scott and Still in 1968 after they realized that the glycogen in the cell was not static but rather a dynamic molecule. It is found in a few species of protozoa including the Kinetoplastida which include the suborders Trypanosomatida and Bodonina, most notably in the human pathogenic trypanosomes, which can cause sleeping sickness, Chagas's disease, and leishmaniasis. The organelle is bounded by a single membrane and contains a dense proteinaceous matrix. It is believed to have evolved from the peroxisome. This has been verified by work done on Leishmania genetics.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cell biology:

A prokaryote is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό (pro) "before" and κάρυον (karyon) "nut or kernel". Prokaryotes are divided into two domains, Archaea and Bacteria. Species with nuclei and organelles are placed in the third domain, Eukaryota. Prokaryotes reproduce without fusion of gametes. The first living organisms are thought to have been prokaryotes.

Cyanidioschyzon merolae is a small (2μm), club-shaped, unicellular haploid red alga adapted to high sulfur acidic hot spring environments. The cellular architecture of C. merolae is extremely simple, containing only a single chloroplast and a single mitochondrion and lacking a vacuole and cell wall. In addition, the cellular and organelle divisions can be synchronized. For these reasons, C. merolae is considered an excellent model system for study of cellular and organelle division processes, as well as biochemistry and structural biology. The organism's genome was the first full algal genome to be sequenced in 2004; its plastid was sequenced in 2000 and 2003, and its mitochondrion in 1998. The organism has been considered the simplest of eukaryotic cells for its minimalist cellular organization.


















