Related Research Articles

The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 3,544 meters, to the east of Crete. The Thracian Sea and the Myrtoan Sea are subdivisions of the Aegean Sea.

Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe.

The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia. It lies to the east of the Balkans in Southeast Europe, south of the East European Plain in Eastern Europe; and north and west of the South Caucasus and Anatolia in Western Asia. The Black Sea is supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper, and Don. The waters of many countries drain into the sea beyond the six that share its coast.
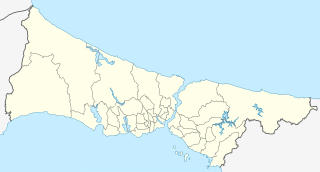
The Bosporus or Bosphorus, also known as the Strait of Istanbul, is a narrow, natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in northwestern Turkey. It forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe, and divides Turkey by separating Anatolia from Thrace. It is the world's narrowest strait used for international navigation. The Bosporus connects the Black Sea with the Sea of Marmara, and, by extension via the Dardanelles, the Aegean and Mediterranean seas, and by the Kerch Strait, the sea of Azov.

The Dardanelles, also known as Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont, is a narrow, natural strait and internationally significant waterway in northwestern Turkey that forms part of the continental boundary between Asia and Europe and separates Asian Turkey from European Turkey. Together with the Bosphorus, the Dardanelles forms the Turkish Straits.
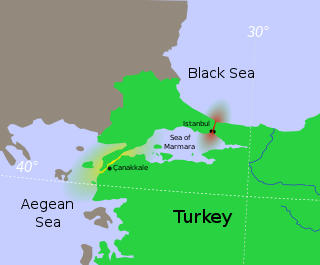
The Sea of Marmara, also known as the Marmara Sea, and in the context of classical antiquity as the Propontis, is an inland sea located entirely within the borders of Turkey. It connects the Black Sea to the Aegean Sea, separating the country's European and Asian part. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Black Sea and the Dardanelles strait to the Aegean Sea. The former also separates Istanbul's European and Asian side. The Sea of Marmara is a small sea with an area of 11,350 km2 (4,380 sq mi), and dimensions 280 km × 80 km. Its greatest depth is 1,370 m (4,490 ft).

Turkey is a large, roughly rectangular peninsula that bridges southeastern Europe and Asia. Thrace, the European portion of Turkey comprises 3% of the country and 10% of its population. Thrace is separated from Asia Minor, the Asian portion of Turkey, by the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara and the Dardanelles. İskilip, Çorum province, is considered to be the geographical center of Earth.

The Coast Guard Command is the coast guard service of Turkey. The Turkish Coast Guard is under the command of the Ministry of the Interior. However, during wartime some of its elements can be subordinated to Turkish Naval Forces by the President.

The geographical regions of Turkey comprise seven regions which were originally defined at the country's First Geography Congress in 1941. These seven regions are subdivided into twenty one sections, which are further split into numerous areas as defined by microclimate and bounded by local geographic formations.

The Marmara Region is a geographical region of Turkey.
The Turkish Straits are two internationally significant waterways in northwestern Turkey. The straits create a series of international passages that connect the Aegean and Mediterranean seas to the Black Sea. They consist of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The straits are on opposite ends of the Sea of Marmara. The straits and the Sea of Marmara are part of the sovereign sea territory of Turkey and subject to the regime of internal waters.

Greece is a country of the Balkans, in Southeastern Europe, bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cretan and the Libyan Seas, and to the west by the Ionian Sea which separates Greece from Italy.

The Kocaeli Peninsula lies in the northwest corner of Anatolia, Turkey, separating the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the Asian side of the strait of Bosphorus. Approximately one-third of Istanbul, one of the most populous cities of the world, occupies its western part, and İzmit, another big city, is at the easternmost point of the peninsula.

The Armutlu Peninsula is a peninsula extending westward into Marmara Sea in the Anatolian section of Turkey. In addition to Yalova Province, parts of Kocaeli Province and Bursa Province are on the peninsula.

The Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests is an ecoregion located in southwestern Anatolia, Turkey. It has a Mediterranean climate, and is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome.

Biga Peninsula is a peninsula in Turkey, in the northwest part of Anatolia. It is also known by its ancient name Troad (Troas).

The wildlife of Greece includes the diverse flora and fauna of Greece, a country in southern Europe. The country is mostly mountainous with a very long, convoluted coastline, consisting of peninsulas and many islands. The climate ranges from Mediterranean through temperate to alpine, and the habitats include mountains, hills, forests, rivers, lakes, coasts and cultivated land.
References
- ↑ Faik Sabri Duran, Büyük Atlas (İstanbul: Kanaat Yayınevi, 2001; ISBN 975-7537-04-7).
- ↑ Türkiye Turizm Atlası 2009 (İstanbul: Boyut Yayıncılık, 2009; ISBN 978-975-23-0634-9).
- ↑ Britannica Atlas, Encyclopædia Britannica Inc.,1977, p 121-122