
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While activation energy must be supplied to initiate combustion, the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining. The study of combustion is known as combustion science.

Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula H2O2. In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution in water for consumer use and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as both a monopropellant and an oxidizer in rocketry.

A hybrid-propellant rocket is a rocket with a rocket motor that uses rocket propellants in two different phases: one solid and the other either gas or liquid. The hybrid rocket concept can be traced back to the early 1930s.

An oxidizing agent is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "accepts"/"receives" an electron from a reducing agent. In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and the halogens.

Sodium percarbonate, or sodium carbonate peroxide is a chemical substance with formula Na
2H
3CO
6. It is an adduct of sodium carbonate and hydrogen peroxide whose formula is more properly written as 2 Na
2CO
3 · 3 H
2O
2. It is a colorless, crystalline, hygroscopic and water-soluble solid. It is sometimes abbreviated as SPC. It contains 32.5% by weight of hydrogen peroxide.

Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic.

Benzoyl peroxide is a chemical compound (specifically, an organic peroxide) with structural formula (C6H5−C(=O)O−)2, often abbreviated as (BzO)2. In terms of its structure, the molecule can be described as two benzoyl (C6H5−C(=O)−, Bz) groups connected by a peroxide (−O−O−). It is a white granular solid with a faint odour of benzaldehyde, poorly soluble in water but soluble in acetone, ethanol, and many other organic solvents. Benzoyl peroxide is an oxidizer, which is principally used in the production of polymers.
The highest specific impulse chemical rockets use liquid propellants. They can consist of a single chemical or a mix of two chemicals, called bipropellants. Bipropellants can further be divided into two categories; hypergolic propellants, which ignite when the fuel and oxidizer make contact, and non-hypergolic propellants which require an ignition source.

In organic chemistry, organic peroxides are organic compounds containing the peroxide functional group. If the R′ is hydrogen, the compounds are called hydroperoxides, which are discussed in that article. The O−O bond of peroxides easily breaks, producing free radicals of the form RO•. Thus, organic peroxides are useful as initiators for some types of polymerization, such as the acrylic, unsaturated polyester, and vinyl ester resins used in glass-reinforced plastics. MEKP and benzoyl peroxide are commonly used for this purpose. However, the same property also means that organic peroxides can explosively combust. Organic peroxides, like their inorganic counterparts, are often powerful bleaching agents.

Piranha solution, also known as piranha etch, is a mixture of sulfuric acid and hydrogen peroxide. The resulting mixture is used to clean organic residues off substrates, for example silicon wafers. Because the mixture is a strong oxidizing agent, it will decompose most organic matter, and it will also hydroxylate most surfaces, making them highly hydrophilic (water-compatible). This means the solution can also easily dissolve fabric and skin, potentially causing severe damage and chemical burns in case of inadvertent contact. It is named after the piranha fish due to its tendency to rapidly dissolve and 'consume' organic materials through vigorous chemical reactions.

The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an ortho- or para-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in base to form a benzenediol and a carboxylate. Overall, the carbonyl group is oxidised, whereas the H2O2 is reduced.

Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove colour (whitening) from fabric or fiber or to disinfect after cleaning. It often refers specifically to a dilute solution of sodium hypochlorite, also called "liquid bleach".
Flammable solids are any materials in the solid phase of matter that can readily undergo combustion in the presence of a source of ignition under standard circumstances, i.e. without:
A flammable liquid is a liquid with flash point of not more than 60.5 °C (141 °F), or any material in a liquid phase with a flash point at or above 37.8 °C (100 °F) that is intentionally heated and offered for transportation or transported at or above its flash point in a bulk packaging.
The HAZMAT Class 2 in United States law includes all gases which are compressed and stored for transportation. Class 2 has three divisions: Flammable, Non-Flammable/Non-Poisonous, and Poisonous. This classification is based on the United Nations' Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods - Model Regulations. In Canada, the Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, or TDGR, are also based on the UN Model Regulations and contain the same three divisions.
Poisonous material is a material, other than a gas, known to be so toxic to humans that it presents a health hazard during transportation.
Bleaching of wood pulp is the chemical processing of wood pulp to lighten its color and whiten the pulp. The primary product of wood pulp is paper, for which whiteness is an important characteristic. These processes and chemistry are also applicable to the bleaching of non-wood pulps, such as those made from bamboo or kenaf.

The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1⁄2 (superoxides), −1⁄3 (ozonides), 0, +1⁄2 (dioxygenyl), +1, and +2.
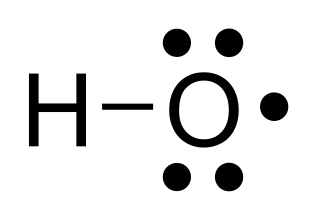
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes.

Metal peroxides are metal-containing compounds with ionically- or covalently-bonded peroxide (O2−
2) groups. This large family of compounds can be divided into ionic and covalent peroxide. The first class mostly contains the peroxides of the alkali and alkaline earth metals whereas the covalent peroxides are represented by such compounds as hydrogen peroxide and peroxymonosulfuric acid (H2SO5). In contrast to the purely ionic character of alkali metal peroxides, peroxides of transition metals have a more covalent character.
























