HMS Ganges was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched in 1782 at Rotherhithe. She was the first ship of the Navy to bear the name, and was the name ship of her class. She saw active service from 1782 to 1811, in Europe and the West Indies.

HMS Neptune was a 98-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She served on a number of stations during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and was present at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805.

HMS Captain was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 26 November 1787 at Limehouse. She served during the French revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars before being placed in harbour service in 1799. An accident caused her to burn and founder in 1813. Later that year she was raised and broken up.

HMS Northumberland was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at the yards of Barnard, Deptford and launched on 2 February 1798. She carried Napoleon to his final exile on St Helena.
HMS Ramillies was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 12 July 1785 at Rotherhithe. However, it was not actually commissioned by the Navy until February 1793. Its first Captain was Henry Harvey.

HMS Intrepid was a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 4 December 1770 at Woolwich. She was sold in 1828.
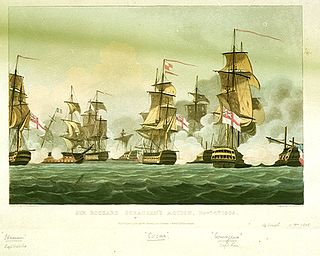
HMS Courageux was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 26 March 1800 at Deptford. She was designed by Sir John Henslow as one of the large class 74-gun ships, and was the only ship built to her draught. Unlike the middling and common class 74-gun ships, which carried 18-pounder long guns, as a large 74-gun ship, Courageux carried 24-pounders on her upper gun deck.

HMS Illustrious, a 74-gun third rate ship of the line and the second of that name, was built by Randall & Brent at Rotherhithe where her keel was laid in February 1801. Launched on 3 September 1803, she was completed at Woolwich. She was first commissioned for the Channel Fleet under Captain Sir Charles Hamilton and was involved in the Battle of the Basque Roads in 1809, in which she won a battle honour, and in the expeditions against the docks at Antwerp and render the Schelde unnavigable to French ships. On 22 November 1810, Illustrious was amongst the fleet that captured Île de France on 3 December. She then took part in the Invasion of Java (1811) in Indonesia. She was refitted at Portsmouth (1813–17) and then laid up in reserve until recommissioned in 1832. She was laid up again in 1845, and later used as a guard ship, a hospital ship and, lastly, in 1854 she became a gunnery training ship and continued as one until she was broken up in 1868 in Portsmouth.

HMS Monmouth was a 64-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 23 April 1796 at Rotherhithe. She had been designed and laid down for the East India Company, but the Navy purchased her after the start of the French Revolutionary War. She served at the Battle of Camperdown and during the Napoleonic Wars. Hulked in 1815, she was broken up in 1834.

HMS Pompee was a 74-gun ship of the line of the British Royal Navy. Built as Pompée, a Téméraire-class ship of the French Navy, she was handed over to the British at Spithead by French royalists who had fled France after the Siege of Toulon by the French Republic, only a few months after being completed. After reaching Great Britain, Pompée was registered and recommissioned as HMS Pompee and spent the entirety of her active career with the Royal Navy until she was broken up in 1817.
The Impérieuse was a 40-gun Minerve-class frigate of the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in 1793 and she served first as HMS Imperieuse and then from 1803 as HMS Unite. She became a hospital ship in 1836 and was broken up in 1858.

HMS Ethalion was a Royal Navy 36-gun frigate, launched in 1802 at Woolwich Dockyard. She was eventually broken up in 1877.
HMS Jason was a 32-gun fifth rate Thames-class frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1804 at Woolwich. She was broken up in 1815.
HMS Amaranthe was an 18-gun Royal Navy Cruizer-class brig-sloop built by John Dudman at Deptford Wharf and launched in 1804. She served in the Caribbean, taking part in an action and two campaigns that gained those members of her crew that survived until 1847 the NGSM. She was sold in 1815.
HMS Circe was a Royal Navy 32-gun fifth-rate frigate, built by Master Shipwright Joseph Tucker at Plymouth Dockyard, and launched in 1804. She served in the Caribbean during the Napoleonic Wars, and participated in an action and a campaign for which in 1847 in the Admiralty authorised the issuance of the Naval General Service Medal with clasps. The action, off the Pearl Rock, near Saint-Pierre, Martinique, was a debacle that cost Circe dearly. However, she also had some success in capturing privateers and a French brig. She was sold in 1814.

HMS Castor was a 32-gun Amazon-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. The French briefly captured her during the Atlantic Campaign of May 1794 but she spent just 20 days in French hands as a British ship retook her before her prize crew could reach a French port. Castor eventually saw service in many of the theatres of the wars, spending time in the waters off the British Isles, in the Mediterranean and Atlantic, as well as the Caribbean.

HMS Espoir was a Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy, launched in 1804. She served during the Napoleonic Wars, primarily in the Mediterranean, and then briefly on the North American station. She was broken up in April 1821.
HMS Express was the name-ship of a class of two schooner-rigged advice-boats of the Royal Navy. Express was launched in 1800 and served until she was sold in 1813. During her career she served in one action and one campaign that in 1847 qualified her surviving crew members for clasps to the Naval General Service Medal.
HMS Attentive was an Archer-class gun-brig of the Royal Navy, launched in 1804. she captured a small privateer and participated in some other captures in the Leeward Islands before returning to Britain, where she was broken up in 1812.
Ann and Amelia was a three-decker merchant ship launched in 1781. The British East India Company (EIC) twice employed her as an "extra ship", first when she went out to India to sail in trade in that market, and again in 1803 when she sailed back from India to Britain. On her return to Britain the Admiralty purchased her in June 1804 and converted her to a 44-gun fifth rate with the name HMS Mediator. The Navy converted her to a storeship in 1808, but then expended her as a fireship at the battle of the Basque Roads in April 1809.











