
Masyaf is a city in northwestern Syria. It is the center of the Masyaf District in the Hama Governorate. As of 2004, Masyaf had a religiously diverse population of approximately 22,000 Ismailis, Alawites and Christians. The city is well known for its large medieval castle, particularly its role as the headquarters of the Nizari Ismailis and their elite Assassins unit.

Mharda is a city in northern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located about 23 kilometers northwest of Hama. It is situated along the Orontes River, near the Ghab plain. Nearby localities include Halfaya and Taybat al-Imam to the east, Khitab to the southeast, Maarzaf to the south, Asilah and Jubb Ramlah to the southwest, Shaizar, Safsafiyah, Tremseh and Kafr Hud to the west and Kafr Zita and al-Lataminah to the north.
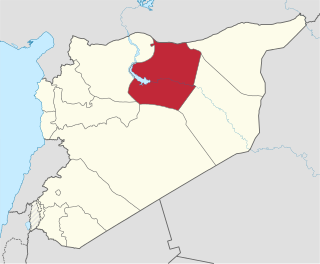
Raqqa Governorate is one of the fourteen governorates of Syria. It is situated in the north of the country and covers an area of 19,618 km2. The capital is Raqqa. The Islamic State of Iraq and Levant claimed full control of this province as of August 24, 2014 when its fighters captured Tabqa Airbase in the southwest part of the province. However, the Syrian Democratic Forces now control much of the province; all of the area north of the Euphrates River including the provincial capital of Raqqa and the city of al-Thawrah are under SDF control, with the government holding the southern part of the governorate after a successful offensive was launched with the aid of Liwa al-Quds, tribal militias and Russian air support, which resulted in the recapture of the city of Resafa, and the capture of many oil fields in Ar-Raqqah province, including various oil and gas stations.

Aleppo Governorate is one of the fourteen governorates of Syria. It is the most populous governorate in Syria with a population of more than 4,867,000, almost 23% of the total population of Syria. The governorate is the fifth in area with an area of 18,482 km2 (7,136 sq mi), or 18,498 km2, about 10% of the total area of Syria. The capital is the city of Aleppo.

Latakia Governorate, also transliterated as Ladhakia Governorate, is one of the 14 governorates of Syria. It is situated in western Syria, bordering Turkey's Hatay Province to the north, Idlib and Hama Governorates to the east, Tartus Governorate to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Its reported area varies in different sources from 2,297 km2 (887 sq mi) to 2,437 km2 (941 sq mi). The governorate has a population of 1,008,000.

The 14 governorates of Syria, or muhafazat, are divided into 65 districts, or manatiq, including the city of Damascus. The districts are further divided into 281 subdistricts, or nawahi. Each district bears the same name as its district capital.

Kafr Buhum, is a town in central Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located 9 km southwest of Hama, 210 km (130 mi) north Damascus and 160 km (99 mi) south of Aleppo. Nearby localities include al-Rabiaa and Matnin to the northwest, Tayzin to the north, al-Khalidiyah to the east, Tell Qartal to the southeast, Birin to the south and al-Muah to the southwest. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Kafr Bu had a population of 12,194 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Christian. It is 330 meters (1082 ft) above the sea level.
Al-Qadmus is a town in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Tartus Governorate, located northeast of Tartus and 14 kilometres southeast of Baniyas. Nearby localities include Kaff al-Jaa and Masyaf to the east, Wadi al-'Uyun and al-Shaykh Badr to the south, Hammam Wasel, al-Qamsiyah and Maten al-Sahel to the southwest, Taanita to the west, al-Annazeh to the northwest and Deir Mama to the northeast. It is situated just east of the Mediterranean coast and its ruined castle stands on a plateau roughly 850 metres above sea level and just above the town.
Tremseh, or in various dialects Tremseh, Treimsa, Taramsah, Taramseh in the Hama Governorate in northern Syria. It is roughly 22 miles northwest of the central city of Hama. Nearby localities include district center Mahardah and Shaizar to the east, Khunayzir to the southeast, Asilah to the south, Safsafiyah to the southwest, Asharnah and Tell Salhab to the west, al-Jalmah to the north and Kafr Hud to the northeast. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Tremseh had a population of 6,926 in the 2004 census. The town was reported to have a population of between 7,000 and 11,000.

Kafr Zita is a town in central Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located 30 kilometers (19 mi)} north of Hama. Nearby localities include Kafr Nabudah and al-Habit to the northwest, Khan Shaykhun to the northeast, Mork to the east, Suran to the southeast, al-Lataminah, Halfaya and Mahardah to the south, Tremseh to the southwest and Kirnaz and Hayalin. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, Kafr Zita had a population of 17,052 in the 2004 census. It is also the center of a nahiyah (subdistrict), part of the Mahardah District, that consists of seven localities with a combined population of 39,032 in 2004.
Al-Laqbah is a town in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located west of Hama. It is situated along the edge of the Orontes River valley, on the main road between Masyaf and northern Syria. Nearby localities include Deir Mama to the south, Jubb Ramlah and Hanjur to the northeast, Deir Shamil to the north and al-Annazah to the west. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics, al-Laqbah had a population of 1,908 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Alawites.

Abu Qubays is a former medieval castle and currently an inhabited village in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, located northwest of Hama. It is situated in the al-Ghab plain, west of the Orontes River. Nearby localities include Daliyah 21 kilometers to the west, al-Laqbah to the south, Deir Shamil to the southeast, Tell Salhab to the northeast and Nahr al-Bared further northeast. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Abu Qubays had a population of 758 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Alawites.

Khattab is a town in northwestern Syria, administratively part of the Hama Governorate, northwest of Hama located near the Orontes River River. Nearby localities include Qamhana to the east, Shihat Hama to the southeast, Kafr al-Tun to the southwest, al-Majdal to the west, Mhardeh and Halfaya to the northwest and Taybat al-Imam to the northeast. According to the Central Bureau of Statistics, Khitab had a population of 10,830 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Sunni Muslims.
Qamhana is a Syrian town located in the Hama Subdistrict of the Hama District in Hama Governorate. It is situated immediately west of the Zayn al-Abidin Mountain. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Qamhana had a population of 13,228 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Sunni Muslim.
Ba'amrah is a Syrian village located in the Ayn Halaqim Subdistrict of the Masyaf District in Hama Governorate. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Ba'amrah had a population of 508 in the 2004 census. Its inhabitants are predominantly Alawites.
The Battle of Tabqa Airbase refers to a series of clashes between the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and the Syrian Arab Army in August 2014, during the Syrian Civil War. Tabqa was the last bastion for Syrian military forces in Raqqa province, which at the end of the battle came fully under the control of the ISIL.

The Orontes River offensive was a military operation launched by the Syrian Arab Army against rebels during the Syrian Civil War on the administrative border of the Hama Governorate and Homs Governorate, along the Orontes River.
The following is a timeline of the Syrian Civil War from January to April 2017. Information about aggregated casualty counts is found at Casualties of the Syrian Civil War.

The Central Syria campaign, known as "Operation Khuzam", or "Lavender", was a large-scale military operation of the Syrian Army (SAA) against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the Syrian Civil War. Its goal was to capture the strategic oil town of Al-Sukhnah, and besiege and capture 11,000 square kilometers of ISIL territory in central Syria, after which the Syrian Army would advance towards Deir ez-Zor, and lift the three-year ISIL siege of the government's enclave in the city. Afterwards, the Syrian Army advanced towards the Islamic State's then-capital of Mayadin.
The following is a timeline of the Syrian Civil War from September to December 2017. Information about aggregated casualty counts is found at Casualties of the Syrian Civil War.




















