
St Pancras was a civil parish and metropolitan borough in London, England. It was an ancient parish in the county of Middlesex, governed by an administrative vestry. The parish was included in the area of responsibility of the Metropolitan Board of Works in 1855 and became part of the County of London in 1889. The parish of St Pancras became a metropolitan borough in 1900, following the London Government Act 1899, with the parish vestry replaced by a borough council. In 1965 the borough was abolished and its former area became part of the London Borough of Camden in Greater London.

Islington was a civil parish and metropolitan borough in London, England. It was an ancient parish within the county of Middlesex, and formed part of The Metropolis from 1855. The parish was transferred to the County of London in 1889 and became a metropolitan borough in 1900. It was amalgamated with the Metropolitan Borough of Finsbury to form the London Borough of Islington in Greater London in 1965.

The Metropolitan Borough of Hammersmith was a metropolitan borough in London, England from 1900 to 1965. It included Hammersmith, Wormwood Scrubs, Old Oak Common and Shepherd's Bush.

The Metropolis Management Act 1855 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that created the Metropolitan Board of Works, a London-wide body to co-ordinate the construction of the city's infrastructure. The Act also created a second tier of local government consisting of parish vestries and district boards of works. The Metropolitan Board of Works was the forerunner of the London County Council.

Hackney was a parish in the historic county of Middlesex. The parish church of St John-at-Hackney was built in 1792, replacing the nearby former 16th-century parish church dedicated to St Augustine. The original tower of that church was retained to hold the bells until the new church could be strengthened; the bells were finally removed to the new St John's in 1854. See details of other, more modern, churches within the original parish boundaries below.
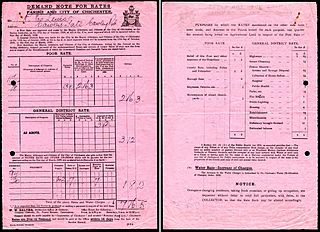
In England and Wales the poor rate was a tax on property levied in each parish, which was used to provide poor relief. It was collected under both the Old Poor Law and the New Poor Law. It was absorbed into 'general rate' local taxation in the 1920s, and has continuity with the currently existing Council Tax.

Strand was a local government district within the metropolitan area of London, England, from 1855 to 1900.

Holborn was a local government district in the metropolitan area of London to the north west of the City of London from 1855 to 1900.

St Giles District was a local government district in the metropolitan area of London, England from 1855 to 1900. The district was created by the Metropolis Management Act 1855, and comprised the civil parish of St Giles in the Fields and St George Bloomsbury, Middlesex: the two parishes had been combined for civil purposes in 1774. The district was abolished in 1900 and its former area became part of the Metropolitan Borough of Holborn. The civil parish was abolished in 1930. It is now part of the London Borough of Camden.

St George Hanover Square was a civil parish in the metropolitan area of Westminster, Middlesex, later Greater London, England. The creation of the parish accompanied the building of the Church of St George's, Hanover Square, constructed by the Commission for Building Fifty New Churches to meet the demands of the growing population. The parish was formed in 1724 from part of the ancient parish of St Martin in the Fields in the Liberty of Westminster and county of Middlesex. It included some of the most fashionable areas of the West End, including Belgravia and Mayfair. Civil parish administration, known as a select vestry, was dominated by members of the British nobility until the parish adopted the Vestries Act 1831. The vestry was reformed again in 1855 by the Metropolis Management Act. In 1889 the parish became part of the County of London and the vestry was abolished in 1900, replaced by Westminster City Council. The parish continued to have nominal existence until 1922. As created, it was a parish for both church and civil purposes, but the boundaries of the ecclesiastical parish were adjusted in 1830, 1835 and 1865.

St Margaret was an ancient parish in the City and Liberty of Westminster and the county of Middlesex. It included the core of modern Westminster, including the Palace of Westminster and the area around, but not including Westminster Abbey. It was divided into St Margaret's and St John's in 1727, to coincide with the building of the Church of St John the Evangelist, constructed by the Commission for Building Fifty New Churches in Smith Square to meet the demands of the growing population, but there continued to be a single vestry for the parishes of St Margaret and St John. This was reformed in 1855 by the Metropolis Management Act, and the two parishes formed the Westminster District until 1887. St Margaret and St John became part of the County of London in 1889. The vestry was abolished in 1900, to be replaced by Westminster City Council, but St Margaret and St John continued to have a nominal existence until 1922.
Plumstead (1855–1894) and then Lee (1894–1900) was a local government district within the metropolitan area of London from 1855 to 1900. It was formed as the Plumstead district by the Metropolis Management Act 1855 and was governed by the Plumstead District Board of Works, which consisted of elected vestrymen.
Fulham was a local government district within the metropolitan area of London, England from 1855 to 1886. It was formed by the Metropolis Management Act 1855 and was governed by the Fulham District Board of Works, which consisted of elected vestrymen. It was in the part of the county of Middlesex that was within the area of the Metropolitan Board of Works. It occupied broadly the same area as ancient parish of Fulham and that of the current London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham.

Whitechapel was a local government district within the metropolitan area of London, England from 1855 to 1900.

Wandsworth was a local government district within the metropolitan area of London, England from 1855 to 1900. It was formed by the Metropolis Management Act 1855 and was governed by the Wandsworth District Board of Works, which consisted of elected vestrymen.

The Hammersmith Metropolitan Borough Council, formally The Mayor, Aldermen and Councillors of the Metropolitan Borough of Hammersmith, was the local authority for the Metropolitan Borough of Hammersmith, which existed from 1900 to 1965.

Woolwich, also known as Woolwich St Mary, was an ancient parish containing the town of Woolwich on the south bank of the Thames and North Woolwich on the north bank. The parish was governed by its vestry from the 16th century to 1852, based in the Church of St Mary until 1842, after which in the purpose-built Woolwich Town Hall. The parish adopted the Public Health Act 1848 and was governed by the Woolwich Local Board of Health from 1852. When the parish became part of the district of the Metropolitan Board of Works in 1855 the local board was treated as if it were an incorporated vestry. It was in the county of Kent until it was transferred to London in 1889. In 1900 it was amalgamated with other parishes to form the Metropolitan Borough of Woolwich and had only nominal existence until it was abolished as a civil parish in 1930. Since 1965 it has been split between the Royal Borough of Greenwich and the London Borough of Newham.
The Hammersmith Vestry was the vestry for the parish of Hammersmith, London from 1834 to 1856 and 1886 to 1900.

The Mayor of the Metropolitan Borough of Hammersmith was the mayor of the Metropolitan Borough of Hammersmith, which existed from 1900 to 1965.

The Metropolis Management Amendment Act 1885 was a public general act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland that amended the Metropolis Management Act 1855 and other Metropolis Management Acts.

 Map of parish boundary
Map of parish boundary













