Crochet is a process of creating textiles by using a crochet hook to interlock loops of yarn, thread, or strands of other materials. The name is derived from the French term crochet, which means 'hook'. Hooks can be made from a variety of materials, such as metal, wood, bamboo, bone or even plastic. The key difference between crochet and knitting, beyond the implements used for their production, is that each stitch in crochet is completed before the next one is begun, while knitting keeps many stitches open at a time. Some variant forms of crochet, such as Tunisian crochet and broomstick lace, do keep multiple crochet stitches open at a time.

Knitting is a method for production of textile fabrics by interlacing yarn loops with loops of the same or other yarns. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done by hand or by machine.
Spinning is a twisting technique to form yarn from fibers. The fiber intended is drawn out, twisted, and wound onto a bobbin. A few popular fibers that are spun into yarn other than cotton, which is the most popular, are viscose, animal fibers such as wool, and synthetic polyester. Originally done by hand using a spindle whorl, starting in the 500s AD the spinning wheel became the predominant spinning tool across Asia and Europe. The spinning jenny and spinning mule, invented in the late 1700s, made mechanical spinning far more efficient than spinning by hand, and especially made cotton manufacturing one of the most important industries of the Industrial Revolution.

Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or other lubricants to withstand the stresses involved in sewing. Embroidery threads are yarns specifically designed for needlework. Yarn can be made of a number of natural or synthetic materials, and comes in a variety of colors and thicknesses. Although yarn may be dyed different colours, most yarns are solid coloured with a uniform hue.

Seed beads or rocailles are uniformly shaped, spheroidal beads ranging in size from under a millimeter to several millimeters. Seed bead is also a generic term for any small bead. Usually rounded in shape, seed beads are most commonly used for loom and off-loom bead weaving. They may be used for simple stringing, or as spacers between other beads in jewelry.

Textile manufacturing or textile engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.
The Crois-iarna within the textile arts, was a kind of hank reel for yarn. It was a rudimentary form of the ciud-siorraig. It consisted of a stick of a certain length, with a cross piece at each end, set at right angles to each other. The yarn is coiled on the cross pieces of the spool of the spinning wheel, so many threads or turns around the cross pieces, which threads are counted, make an old yard of cloth, i.e. 46 inches of a constant width such as the loom in use suffices to weave. It was found in Uist.

Amigurumi is the Japanese art of knitting or crocheting small, stuffed yarn creatures. The word is a compound of the Japanese words 編み ami, meaning "crocheted or knitted", and 包み kurumi, literally "wrapping", as in 縫い包み nuigurumi "(sewn) stuffed doll". Amigurumi vary in size and there are no restrictions about size or look. While the art of amigurumi has been known in Japan for several decades, the craft first started appealing to the masses in other countries, especially in the West, in 2003. By 2006, amigurumi were reported to be some of the most popular items on Etsy, an online craft marketplace, where they typically sold for $10 to $100.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns it into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.
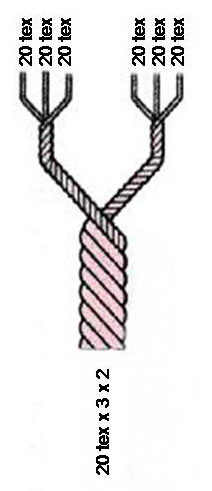
Textile fibers, threads, yarns and fabrics are measured in a multiplicity of units.

Spool knitting,loom knitting, corking,French knitting, or tomboy knitting is a form of knitting that uses a spool with a number of nails or pegs around the rim to produce a tube or sheet of fabric. The spool knitting devices are called knitting spools, knitting nancys, knitting frame, knitting loom, or French knitters.

Crochet thread is specially formulated thread usually made from mercerized cotton for crafting decorative crochet items such as doilies or filet crochet. Crochet thread produces fabric of fine gauge that may be stiffened with starch.
Hand knitting is a form of knitting, in which the knitted fabric is produced by hand using needles.

A swift is a tool used to hold a hank of yarn while it is being wound off. It has an adjustable diameter so that it can hold hanks of many sizes, and rotates around a central rod. Developed in the United States, they are generally made out of wood or metal, though other materials may also be used. In the 18th and 19th centuries, swifts were sometimes made of whale ivory and they are now sought-after antiques. Swifts are not used very much in the textile industry but are used more by knitters and crocheters who buy their yarn in hank form. The swift allows for easy balling without the yarn getting tangled and knotted.
Textile manufacturing is one of the oldest human activities. The oldest known textiles date back to about 5000 B.C. In order to make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving to create cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. Cloth is finished by what are described as wet process to become fabric. The fabric may be dyed, printed or decorated by embroidering with coloured yarns.

A bolt is a piece of cloth woven on a loom or created by a knitting machine, as it is processed, stored and/or marketed. Consequently, its dimensions are highly variable – flexible and dependent upon the manufacturing, machinery, quantity, size, thickness and quality of the product. It is a unit used in manufacturing, transport and inventory. It is also used as a descriptor for wallpaper, which uses different fabrication machinery. Being encompassing, it is by its nature a generic and ambiguous term of convenience and context, used to describe fabric and wallpaper.

A thread is a long strand of material, often composed of several filaments or fibres, used for joining, creating or decorating textiles. Ancient Egyptians were known for creating thread using plant fibers, wool and hair. Today, thread can also be made of many different materials including but not limited to cotton, wool, flax, nylon, silk, polyester etc. There are also metal threads, which can be made of fine wire.

Eisaku Noro Company, Ltd. is a yarn manufacturer located in the Aichi Prefecture of Japan. The company produces yarns for handcrafting under the Noro brand name, as well as machine yarns for textile production using the Eisaku Noro label. The company was founded over forty years ago by Eisaku Noro. The handcrafting yarns in particular are well known for their vivid colors and combinations of diverse fiber types. They differ from a number of other manufactured yarns in the industry by having lengthier spans of color in the runs, causing distinctive striping patterns, as well as being partially spun by hand versus being produced completely by machines. In 2012, Noro Knitting Magazine initiated publication, which features knit and crochet patterns specifically designed for use with the yarns.
Wet Processing Engineering is one of the major streams in Textile Engineering or Textile manufacturing which refers to the engineering of textile chemical processes and associated applied science. The other three streams in textile engineering are yarn engineering, fabric engineering, and apparel engineering. The processes of this stream are involved or carried out in an aqueous stage. Hence, it is called a wet process which usually covers pre-treatment, dyeing, printing, and finishing.

String is a long flexible structure made from fibers twisted together into a single strand, or from multiple such strands which are in turn twisted together. String is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects. It is also used as a material to make things, such as textiles, and in arts and crafts. String is a simple tool, and its use by humans is known to have been developed tens of thousands of years ago. In Mesoamerica, for example, string was invented some 20,000 to 30,000 years ago, and was made by twisting plant fibers together. String may also be a component in other tools, and in devices as diverse as weapons, musical instruments, and toys.














