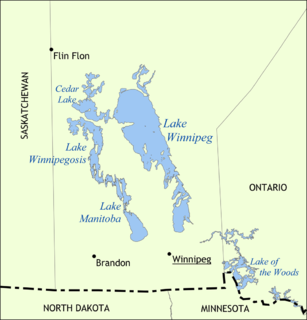
Lake Winnipeg is a very large, relatively shallow 24,514-square-kilometre (9,465 sq mi) lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about 55 kilometres (34 mi) north of the city of Winnipeg. Lake Winnipeg is Canada's sixth-largest freshwater lake and the third-largest freshwater lake contained entirely within Canada, but it is relatively shallow excluding a narrow 36 m (118 ft) deep channel between the northern and southern basins. It is the eleventh-largest freshwater lake on Earth. The lake's east side has pristine boreal forests and rivers that were in 2018 inscribed as Pimachiowin Aki, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The lake is 416 km (258 mi) from north to south, with remote sandy beaches, large limestone cliffs, and many bat caves in some areas. Manitoba Hydro uses the lake as one of the largest reservoirs in the world. There are many islands, most of them undeveloped.

Lake Winnipegosis is a large (5,370 km2) lake in central North America, in Manitoba, Canada, some 300 km northwest of Winnipeg. It is Canada's eleventh-largest lake. An alternate spelling, once common but now rare, is Lake Winipigoos or simply 'Lake Winipigis'.

The Nelson River is a river of north-central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba. The river drains Lake Winnipeg and runs 644 kilometres (400 mi) before it ends in Hudson Bay. Its full length is 2,575 kilometres (1,600 mi), it has mean discharge of 2,370 cubic metres per second (84,000 cu ft/s), and has a drainage basin of 1,072,300 square kilometres (414,000 sq mi), of which 180,000 square kilometres (69,000 sq mi) is in the United States.

The Assiniboine River is a 1,070-kilometre (660 mi) river that runs through the prairies of Western Canada in Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It is a tributary of the Red River. The Assiniboine is a typical meandering river with a single main channel embanked within a flat, shallow valley in some places and a steep valley in others. Its main tributaries are the Qu'Appelle, Souris and Whitesand Rivers. For early history and exploration see Assiniboine River fur trade.

The Souris River or Mouse River is a river in central North America. It is about 700 km (430 mi) in length and drains about 23,600 square miles (61,100 km2). It rises in the Yellow Grass Marshes north of Weyburn, Saskatchewan. It wanders south through North Dakota beyond Minot to its most southern point at the city of Velva, and then back north into Manitoba. The river passes through the communities of Melita, Hartney, Souris and Wawanesa and on to its confluence with the Assiniboine River near Treesbank, about 25 miles (40 km) southeast of Brandon. The main tributaries which flow into the Souris in Manitoba are the Antler River, the Gainsborough, and Plum Creeks.

The Pembina River is a tributary of the Red River of the North, approximately 319 miles (513 km) long, in southern Manitoba in Canada and northeastern North Dakota in the United States. It drains an area of the prairie country along the Canada–US border, threading the Manitoba-North Dakota border eastward to the Red River. Via the Red River, Lake Winnipeg and the Nelson River, it is part of the watershed of Hudson Bay.

The Winnipeg River is a Canadian river that flows roughly northwest from Lake of the Woods in the province of Ontario to Lake Winnipeg in Manitoba. This river is 235 kilometres (146 mi) long from the Norman Dam in Kenora to its mouth at Lake Winnipeg. Its watershed is 106,500 square kilometres (41,100 sq mi) in area, mainly in Canada. About 29,000 square kilometres (11,000 sq mi) of the watershed is in northern Minnesota, United States.

The Churchill River is a major river in Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba, Canada. From the head of the Churchill Lake it is 1,609 kilometres (1,000 mi) long. It was named after John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough and governor of the Hudson's Bay Company from 1685 to 1691.

The Hayes River is a river in Northern Manitoba, Canada, that flows from Molson Lake to Hudson Bay at York Factory. It was historically an important river in the development of Canada and is now a Canadian Heritage River and the longest naturally flowing river in Manitoba.
Treaty 2 was entered in to on 21 August 1871 at Manitoba House, Rupertsland, with representatives of the Queen of Great Britain and Ireland. The original Anishinaabe, who were present, constitute Treaty 2 today. It is known that many of the chiefs and leaders within the territory were at the early gathering and after the treaty was agreed to. Those who were not present were represented through Metis until they indicated where they wished their farming reserves to be established. The treaty reaffirmed the inherent rights that the Anishinaabe had prior to European contact, located where southwestern Manitoba is today and a small part of southeastern Saskatchewan.

Minago River is a river in the Hudson Bay drainage basin in Northern Manitoba, Canada. It flows in a northeasterly direction from Moon Lake into the western end of Cross Lake on the Nelson River.

The Mistik Creek is a stream in the Hudson Bay drainage basin in the Northern Region of Manitoba, Canada, approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) northeast of Bakers Narrows.

Pipestone Creek is a river in the Souris River watershed. Its flow begins in south-eastern Saskatchewan, just south of the town of Grenfell and travels in a south-eastly direction into Manitoba in the Westman Region where it empties into Oak Lake through the Oak Lake Marsh.

Oak Lake is a lake in the south-western part of the Canadian province of Manitoba in a region called Westman. Oak Lake is a kettle lake and is an aquifer supplier for numerous nearby residential areas and farms. The lake is in the RM of Sifton and sits at an elevation of 426 metres above sea level. Provincial Road 254 provides access to the lake.

Plum Creek is the primary outflow for the Plum Lakes and travels in an easterly direction for about 28 kilometres until it meets up with the Souris River, which is part of the Hudson Bay drainage basin, at the community of Souris in the Canadian province of Manitoba. Plum Lakes and the beginning of Plum Creek are in the Rural Municipality of Sifton and the mouth is in the Municipality of Souris – Glenwood.

The Red Deer River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba. It has its source at Nut Lake in east central Saskatchewan and from there, it flows east towards Manitoba where it empties into Dawson Bay of Lake Winnipegosis. To the north of Red Deer's basin is the Saskatchewan River, to the south-west is the upper Assiniboine River, and to the south-east is Swan River.
Woody River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan. The river's source is in the Porcupine Hills and Porcupine Provincial Forest of eastern Saskatchewan. From there it flows south through boreal forest and then east through Boreal Plains in the Parkland Region of Manitoba en route to Swan Lake. The river parallels the Swan River for much of its route as it travels through Swan River Valley between Duck Mountain and Porcupine Hills of the Manitoba Escarpment. Bowsman is the only notable community along the course of Woody River. Several highways cross it, including Saskatchewan's Highway 980, Manitoba's Roads 588, 587, 366, 268, and Manitoba's Highway 10.
Whitefish Lake is a lake in the Canadian province of Manitoba. It is located on the western side of the province immediately east of the border with Saskatchewan in the Porcupine Hills of the Manitoba Escarpment. The lake is in Manitoba's Porcupine Provincial Forest, which is a boreal forest. Accessed is on the east side from Provincial Road 279.
Smallfish Lake is a lake in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is located in the east-central part of the province right alongside the border with Manitoba in the Porcupine Hills and Porcupine Provincial Forest. The lake is part of the Woody River Block of Porcupine Hills Provincial Park and is situated in boreal forest surrounded by hills, other small lakes, and muskeg. Access to the lake is on the western side from Highway 980.















