
Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of Texas, as well as the seat and largest city of Travis County, with portions extending into Hays and Williamson counties. Incorporated on December 27, 1839, it is the 11th-most populous city in the United States, the fourth-most-populous city in Texas, the second-most-populous state capital city, one of two state capitals with a population of over one million people, after Phoenix, Arizona, and the most populous state capital that is not also the most populous city in its state. It has been one of the fastest growing large cities in the United States since 2010. Downtown Austin and Downtown San Antonio are approximately 80 miles (129 km) apart, and both fall along the Interstate 35 corridor. Some observers believe that the two regions may some day form a new "metroplex" similar to Dallas and Fort Worth. Austin is the southernmost state capital in the contiguous United States and is considered a "Beta −" global city as categorized by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network.

Wollemia is a genus of coniferous trees in the family Araucariaceae. It was known only through fossil records until 1994, when the Australian species Wollemia nobilis was discovered in a temperate rainforest wilderness area of the Wollemi National Park in New South Wales. It was growing in a remote series of narrow, steep-sided, sandstone gorges 150 km (93 mi) north-west of Sydney. The genus is named after the National Park.

Barton Springs Pool is a recreational outdoor swimming pool that is filled entirely with water from nearby natural springs. It is located on the grounds of Zilker Park in Austin, Texas. The pool exists within the channel of Barton Creek and utilizes water from Main Barton Spring, the fourth largest spring in Texas. The pool is a popular venue for year-round swimming, as its temperature hovers between about 68 °F (20 °C) and 74 °F (23 °C) year round.

The Austin City Limits (ACL) Music Festival is an annual music festival held in Zilker Park in Austin, Texas on two consecutive three-day weekends. Inspired by the KLRU/PBS music series of the same name, the festival is produced by Austin-based company C3 Presents, which also produces Chicago's Lollapalooza.

The Zilker Botanical Garden is a botanical garden of varied topography located on the south bank of the Colorado River at 2220 Barton Springs Road, near downtown Austin, Texas, United States.

Zilker is a neighborhood in south central Austin, Texas. It extends south of Lady Bird Lake, approximately bounded by the Union Pacific Railway to the southeast/south, Barton Skyway to the south, Rabb Road and Azie Morton Road to the west and Lady Bird Lake to the north.

Andrew Jackson Zilker (1858–1934) was a political figure and philanthropist in Austin, Texas, after whom Zilker Park was named. He was the last private owner of Barton Springs.

The Umlauf Sculpture Garden & Museum, stylized as the UMLAUF, is a museum and outdoor sculpture garden centered on the artistic works of American sculptor Charles Umlauf. Located at 605 Azie Morton Road in the Zilker neighborhood of Austin, Texas, the garden is adjacent to Austin's Zilker Park.

The Dallas–Fort Worth Metroplex sits above Cretaceous-age strata ranging from ≈145-66 Ma. These Cretaceous-aged sediments lie above the eroded Ouachita Mountains and the Fort Worth Basin, which was formed by the Ouachita Orogeny. Going from west to east in the DFW Metroplex and down towards the Gulf of Mexico, the strata get progressively younger. The Cretaceous sediments dip very gently to the east.

Plant collecting is the acquisition of plant specimens for the purposes of research, cultivation, or as a hobby. Plant specimens may be kept alive, but are more commonly dried and pressed to preserve the quality of the specimen. Plant collecting is an ancient practice with records of a Chinese botanist collecting roses over 5000 years ago.

A fossil track or ichnite is a fossilized footprint. This is a type of trace fossil. A fossil trackway is a sequence of fossil tracks left by a single organism. Over the years, many ichnites have been found, around the world, giving important clues about the behaviour of the animals that made them. For instance, multiple ichnites of a single species, close together, suggest 'herd' or 'pack' behaviour of that species.

The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center at The University of Texas at Austin is the state botanical garden and arboretum of Texas. The center features more than 900 species of native Texas plants in both garden and natural settings and is home to a breadth of educational programs and events. The center is 284 acres and located 10 miles southwest of downtown Austin, Texas just inside the edge of the distinctive Texas hill country. It straddles both Edwards Plateau and Texas Blackland Prairies ecosystems.
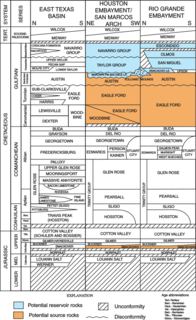
The Glen Rose Formation is a shallow marine to shoreline geological formation from the lower Cretaceous period exposed over a large area from South Central to North Central Texas. The formation is most widely known for the dinosaur footprints and trackways found in the Dinosaur Valley State Park near the town of Glen Rose, Texas, southwest of Fort Worth and at other localities in Central Texas.

Dinosaur State Park and Arboretum is a state-owned natural history preserve occupying 80 acres (32 ha) in the town of Rocky Hill, Connecticut. The state park protects one of the largest dinosaur track sites in North America. The park was created in recognition of fossil trackways embedded in sandstone from the beginning of the Jurassic period, about 200 million years ago. The facility is managed by the Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection.

Barton Hills is a neighborhood in Austin, Texas. It is located in south Austin, and encompasses part of ZIP code 78704.

Fossil Detectives is a 2008 BBC Television documentary series in which presenter Hermione Cockburn travels across Great Britain exploring fossil sites and discovering the latest scientific developments in geology and palaeontology. The show is a spin-off of Coast.
Leanderthal Lady is the skeletal remains of a prehistoric woman discovered in January 1983 by the Texas Department of Transportation at the Wilson-Leonard Brushy Creek Site in the city of Cedar Park, Texas, a suburb of Austin, the state capital. The remains were also alternatively labeled "Leanne". Both names were inspired by the proximity of the site to the town of Leander, to the north.
Allandale, Austin, Texas is a neighborhood in North Central Austin, in the U.S. State of Texas known for its large lots, mature trees, and central location.

Paleontology in Texas refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Texas. Author Marian Murray has remarked that "Texas is as big for fossils as it is for everything else." Some of the most important fossil finds in United States history have come from Texas. Fossils can be found throughout most of the state. The fossil record of Texas spans almost the entire geologic column from Precambrian to Pleistocene. Shark teeth are probably the state's most common fossil. During the early Paleozoic era Texas was covered by a sea that would later be home to creatures like brachiopods, cephalopods, graptolites, and trilobites. Little is known about the state's Devonian and early Carboniferous life. However, evidence indicates that during the late Carboniferous the state was home to marine life, land plants and early reptiles. During the Permian, the seas largely shrank away, but nevertheless coral reefs formed in the state. The rest of Texas was a coastal plain inhabited by early relatives of mammals like Dimetrodon and Edaphosaurus. During the Triassic, a great river system formed in the state that was inhabited by crocodile-like phytosaurs. Little is known about Jurassic Texas, but there are fossil aquatic invertebrates of this age like ammonites in the state. During the Early Cretaceous local large sauropods and theropods left a great abundance of footprints. Later in the Cretaceous, the state was covered by the Western Interior Seaway and home to creatures like mosasaurs, plesiosaurs, and few icthyosaurs. Early Cenozoic Texas still contained areas covered in seawater where invertebrates and sharks lived. On land the state would come to be home to creatures like glyptodonts, mammoths, mastodons, saber-toothed cats, giant ground sloths, titanotheres, uintatheres, and dire wolves. Archaeological evidence suggests that local Native Americans knew about local fossils. Formally trained scientists were already investigating the state's fossils by the late 1800s. In 1938, a major dinosaur footprint find occurred near Glen Rose. Pleurocoelus was the Texas state dinosaur from 1997 to 2009, when it was replaced by Paluxysaurus jonesi after the Texan fossils once referred to the former species were reclassified to a new genus.
This is a compendium of information on springs in Travis County, Texas, especially those with prehistoric or historic links to Texas Native Americans. Information is based primarily on Gunnar Brune's report to the Texas Water Development Board, "Major and Historical Springs of Texas", and his book, Springs of Texas. Additional sources are cited with associated springs.
















