
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body.

Karl Barry Sharpless is an American stereochemist. He is a two-time Nobel laureate in Chemistry known for his work on stereoselective reactions and click chemistry.
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide. By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to explore the mechanism of chemical reactions by tracing the path that the radioisotope follows from reactants to products. Radiolabeling or radiotracing is thus the radioactive form of isotopic labeling. In biological contexts, experiments that use radioisotope tracers are sometimes called radioisotope feeding experiments.
Pittsburgh compound B (PiB) is a radioactive analog of thioflavin T, which can be used in positron emission tomography scans to image beta-amyloid plaques in neuronal tissue. Due to this property, Pittsburgh compound B may be used in investigational studies of Alzheimer's disease.

[18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose (INN), or fluorodeoxyglucose F 18, also commonly called fluorodeoxyglucose and abbreviated [18F]FDG, 2-[18F]FDG or FDG, is a radiopharmaceutical, specifically a radiotracer, used in the medical imaging modality positron emission tomography (PET). Chemically, it is 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose, a glucose analog, with the positron-emitting radionuclide fluorine-18 substituted for the normal hydroxyl group at the C-2 position in the glucose molecule.

Tauopathies are a class of neurodegenerative diseases characterized by the aggregation of abnormal tau protein. Hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins causes them to dissociate from microtubules and form insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles. Various neuropathologic phenotypes have been described based on the anatomical regions and cell types involved as well as the unique tau isoforms making up these deposits. The designation 'primary tauopathy' is assigned to disorders where the predominant feature is the deposition of tau protein. Alternatively, diseases exhibiting tau pathologies attributed to different and varied underlying causes are termed 'secondary tauopathies'. Some neuropathologic phenotypes involving tau protein are Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal degeneration.

MK-9470 is a synthetic compound which binds to the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and functions as an inverse agonist. The 18F-labeled version, [18F]-MK-9470, is used in research as a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer for brain imaging of the CB1 receptor.
Avid Radiopharmaceuticals is an American company, founded by Dr. Daniel Skovronsky, and based at the University City Science Center research campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The company has developed a radioactive tracer called florbetapir (18F). Florbetapir can be used to detect beta amyloid plaques in patients with memory problems using positron emission tomography (PET) scans, making the company the first to bring to market an FDA-approved method that can directly detect this hallmark pathology of Alzheimer's disease.
Emission computed tomography (ECT) is a type of tomography involving radioactive or emissions. Types include positron emission tomography (PET) and Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).

Brain positron emission tomography is a form of positron emission tomography (PET) that is used to measure brain metabolism and the distribution of exogenous radiolabeled chemical agents throughout the brain. PET measures emissions from radioactively labeled metabolically active chemicals that have been injected into the bloodstream. The emission data from brain PET are computer-processed to produce multi-dimensional images of the distribution of the chemicals throughout the brain.
Radiofluorination is the process by which a radioactive isotope of fluorine is attached to a molecule and is preferably performed by nucleophilic substitution using nitro or halogens as leaving groups. Fluorine-18 is the most common isotope used for this procedure. This is due to its 97% positron emission and relatively long 109.8 min half-life. The half-life allows for a long enough time to be incorporated into the molecule and be used without causing exceedingly harmful effects. This process has many applications especially with the use of positron emission tomography (PET) as the aforementioned low positron energy is able to yield a high resolution in PET imaging.

18F-FMISO or fluoromisonidazole is a radiopharmaceutical used for PET imaging of hypoxia. It consists of a 2-nitroimidazole molecule labelled with the positron-emitter fluorine-18.
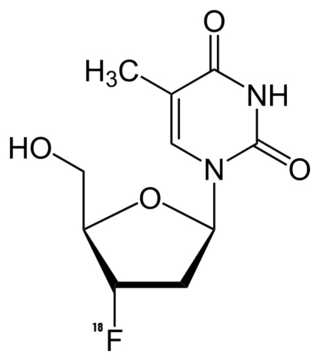
Fluorothymidine F-18 (FLT) is a tumor-specific PET tracer and radiopharmaceutical. It is an isotopologue of alovudine. FLT is suitable for monitoring how tumors respond to cytostatic therapy. FLT accumulates in proliferating cells where it indicates the activity of the enzyme thymidine kinase. Cell division can be characterized by the activity of that enzyme. FLT is phosphorylated as though it were thymidine, and is subsequently incorporated into DNA. Thymidine is essential for DNA replication. Considering that FLT lacks a 3′-hydroxy group, transcription of DNA is impeded following incorporating of FLT. FLT indicates changes in tumor cell proliferation by tracking the restoration of nucleosides from degenerated DNA.

Fluciclovine (18F), also known as anti-1-amino-3-18F-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid, and sold under the brand name Axumin, is a diagnostic agent used for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels.

Peter J. H. Scott FRSC CChem is a British and American chemist and radiochemist who is a professor of radiology, professor of pharmacology and professor of medicinal chemistry, as well as a core member of the Rogel Cancer Center at the University of Michigan in the United States. He is Chief of Nuclear Medicine and director of the University of Michigan Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Center, and runs a research group developing new radiochemistry methodology and novel PET radiotracers.
Arterial input function (AIF), also known as a plasma input function, refers to the concentration of tracer in blood-plasma in an artery measured over time. The oldest record on PubMed shows that AIF was used by Harvey et al. in 1962 to measure the exchange of materials between red blood cells and blood plasma, and by other researchers in 1983 for positron emission tomography (PET) studies. Nowadays, kinetic analysis is performed in various medical imaging techniques, which requires an AIF as one of the inputs to the mathematical model, for example, in dynamic PET imaging, or perfusion CT, or dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI).
Positron emission tomography for bone imaging, as an in vivo tracer technique, allows the measurement of the regional concentration of radioactivity proportional to the image pixel values averaged over a region of interest (ROI) in bones. Positron emission tomography is a functional imaging technique that uses [18F]NaF radiotracer to visualise and quantify regional bone metabolism and blood flow. [18F]NaF has been used for imaging bones for the last 60 years. This article focuses on the pharmacokinetics of [18F]NaF in bones, and various semi-quantitative and quantitative methods for quantifying regional bone metabolism using [18F]NaF PET images.

Flortaucipir (18F), sold under the brand name Tauvid, is a radioactive diagnostic agent indicated for use with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging to image the brain.

Julie C. Price is an American medical physicist and professor of radiology at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Harvard Medical School (HMS), as well as the director of PET Pharmacokinetic Modeling at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center at MGH. Price is a leader in the study and application of quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) methods. Prior to this, Price worked with Pittsburgh colleagues to lead the first fully quantitative pharmacokinetic evaluations of 11C-labeled Pittsburgh compound-B (PIB), one of the most widely used PET ligands for imaging amyloid beta plaques. As a principal investigator at MGH, Price continues work to validate novel PET methods for imaging biological markers of health and disease in studies of aging and neurodegeneration, including studies of glucose metabolism, protein expression, neurotransmitter system function, and tau and amyloid beta plaque burden.
Neil Vasdev is a Canadian and American radiochemist and expert in nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, particularly in the application of PET. Radiotracers developed by the Vasdev Lab are in preclinical use worldwide, and many have been translated for first-in-human neuroimaging studies. He is the director and chief radiochemist of the Brain Health Imaging Centre and director of the Azrieli Centre for Neuro-Radiochemistry at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH). He is the Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Radiochemistry and Nuclear Medicine, the endowed Azrieli Chair in Brain and Behaviour and Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Toronto. Vasdev has been featured on Global News, CTV, CNN, New York Times, Toronto Star and the Globe and Mail for his innovative research program.












