
Greece had the highest rate of male smokers in Europe in 2015: 53%. [1]
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative [2] finds that Greece is fulfilling 88.6% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. [3]

Greece had the highest rate of male smokers in Europe in 2015: 53%. [1]
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative [2] finds that Greece is fulfilling 88.6% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. [3]

Education in Papua New Guinea is managed through nineteen provinces and two district organisational units. It is tuition-free and attendance is not compulsory.

Education in Costa Rica is divided in 3 cycles: pre-education, primary education, and secondary school, which leads to higher education. School year starts between the second and third week of February, stops at the last week of June, it continues again between the third and fourth week of July and finishes between the last week of November and the second week of December. Preschool and basic education are free to the public. Elementary and secondary school are both divided in two cycles. Since 1869, education is free and compulsory.

Life expectancy in Jordan was 74 years in 2021. 99% of Jordan's population have access to clean water and sanitation despite it being one of the world's poorest in water resources. There were 203 physicians per 100,000 people in the years 2000–2004, a proportion comparable to many developed countries and higher than most of the developing world.
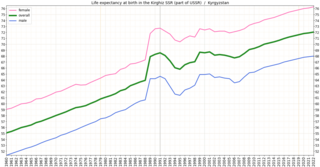
In the post-Soviet era, Kyrgyzstan's health system has suffered increasing shortages of health professionals and medicine. Kyrgyzstan must import nearly all its pharmaceuticals. The increasing role of private health services has supplemented the deteriorating state-supported system. In the early 2000s, public expenditures on health care decreased as a percentage of total expenditures, and the ratio of population to number of doctors increased substantially, from 296 per doctor in 1996 to 355 per doctor in 2001. A national primary-care health system, the Manas Program, was adopted in 1996 to restructure the Soviet system that Kyrgyzstan inherited. The number of people participating in this program has expanded gradually, and province-level family medicine training centers now retrain medical personnel. A mandatory medical insurance fund was established in 1997.

Education in Dominica is compulsory from ages 5 to 16. The gross primary enrollment rate was 100.4 percent in 1991 and 98.2 percent in 1998, and the net primary enrollment rate was 88.7 percent in 1991 and 88.8 percent in 1998. Primary school attendance rates were unavailable for Dominica as of 2001. Poor physical conditions in many primary schools affect the quality of education, while some schools are overcrowded, limiting access to primary education, particularly for children living in urban areas around the capital. Poverty and work on family banana farms during the harvest season can affect school attendance, but other employment does not pull minors out of school. There is a significant Carib Indian population in Dominica, and schools on the Carib Territory are reported to have fewer resources.
Education in Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is neither compulsory nor free, although children are usually in school until the age of 15. In 1998, the gross primary enrollment rate was 90.5 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 83.5 percent.
The Ecuadorian Constitution requires that all children attend school until they achieve a “basic level of education,” which is estimated at nine school years.
Education in Georgia is free of charge and compulsory from the age of 6 until 17–18 years. In 1996, the gross primary enrollment rate was 88.2 percent, and the net primary enrollment rate was 87 percent; 48.8 percent are girls and 51.8 percent are boys. The constitution mandates that education is free. Related expenses that include textbooks and laptops are provided by the state free of charge; in 2001, there were 47,837 children not attending primary school.

Primary education in Guinea is compulsory for 6 years. In 1997, the gross primary enrolment rate was 54.4 percent and the net primary enrolment rate was 41.8 percent. Public education in Guinea is governed by three ministries: The Ministry for Pre-University Education and Literacy; The Ministry for Technical Education and Occupational Training; and the Ministry for Higher Education, Scientific Research and Innovation.

In Ukraine, the Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that country is fulfilling 79.4% of what they should be fulfilling for the right to health, based on their level on income.
Benin faces a number of population health challenges. Apart from modern medicine, traditional medicine plays a big role too.

Ivory Coast faces multiple health challenges, caused by factors including malaria, lack of access to medicine, and healthcare staffing shortages.

Life expectancy at birth in Belarus was 69 for men and 79 for women in 2016.
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that São Tomé and Príncipe is fulfilling 80.4% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. When looking at the right to health with respect to children, São Tomé and Príncipe achieves 96.0% of what is expected based on its current income. In regards to the right to health amongst the adult population, the country achieves 91.5% of what is expected based on the nation's level of income. São Tomé and Príncipe falls into the "very bad" category when evaluating the right to reproductive health because the nation is fulfilling only 53.8% of what the nation is expected to achieve based on the resources (income) it has available.

Life expectancy in Papua New Guinea (PNG) at birth was 64 years for men in 2016 and 68 for women.
Climate change in American Samoa encompasses the effects of climate change, attributed to man-made increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide, in the U.S. territory of American Samoa. The American Samoa Environmental Protection Agency (ASEPA) notes that the territory "has a fragile ecosystem" which is "directly and immediately impacted by global climate change".
The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that Azerbaijan is fulfilling 67.3% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income. When looking at the right to health with respect to children, Azerbaijan achieves 93.5% of what is expected based on its current income. In regards to the right to health amongst the adult population, the country achieves only 91.1% of what is expected based on the nation's level of income. Azerbaijan falls into the "very bad" category when evaluating the right to reproductive health because the nation is fulfilling only 17.2% of what the nation is expected to achieve based on the resources (income) it has available.

Life expectancy in Albania was estimated at 77.59 years, in 2014, ranking 51st in the world, and outperforming a number of European Union countries, such as Hungary, Poland and the Czech Republic. In 2016 it was 74 for men and 79 for women. The most common causes of death are circulatory diseases followed by cancerous illnesses. Demographic and Health Surveys completed a survey in April 2009, detailing various health statistics in Albania, including male circumcision, abortion and more.

Sri Lanka scores higher than the regional average in healthcare having a high life expectancy and a lower maternal and infant death rate than its neighbors. In 2018 life expectancy was 72.1 for men and 78.5 for women ranking the country 70th in the world.

The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that Turkmenistan is fulfilling 74.9% of what it should be fulfilling for the right to health based on its level of income.