Related Research Articles

Demographic features of the population of Cambodia include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Demographic features of the population of Mali include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The current population of Nepal is 29,164,578 as per the 2021 census. The population growth rate is 0.92% per year.

The United States had an official estimated resident population of 334,914,895 on July 1, 2023, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This figure includes the 50 states and Washington, D.C. but excludes the population of five unincorporated U.S. territories as well as several minor island possessions. The United States is the third most populous country in the world, and the most populous in the Americas and the Western Hemisphere. The Census Bureau showed a population increase of 0.4% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2022, below the world average annual rate of 0.9%. The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2022 is 1.665 children per woman, which is below the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.1. By several metrics, including racial and ethnic background, religious affiliation, and percentage of rural and urban divide, Illinois is the most representative of the larger demography of the United States.

Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of deaths per 1,000 individuals per year; thus, a mortality rate of 9.5 in a population of 1,000 would mean 9.5 deaths per year in that entire population, or 0.95% out of the total. It is distinct from "morbidity", which is either the prevalence or incidence of a disease, and also from the incidence rate.

Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; population counts from a census, and estimation through specialized demographic techniques. The birth rate is used to calculate population growth. The estimated average population may be taken as the mid-year population.
Baychester is a neighborhood geographically located in the northeast part of the Bronx, New York City. Its boundaries are East 222nd Street to the northeast, the New England Thruway (I-95) to the east, Gun Hill Road to the southwest, and Boston Road to the northwest. Eastchester Road is the primary thoroughfare through Baychester.
Pelham Gardens is a neighborhood located in the Northeast section of the Bronx, New York City. Its boundaries, starting from the north and moving clockwise are East Gun Hill Road to the north and east, Pelham Parkway to the south, and the IRT Dyre Avenue Line to the west ending at the esplanade. Eastchester Road is the primary thoroughfare through Pelham Gardens.

Sunnyside is a neighborhood in the western portion of the New York City borough of Queens. It shares borders with Hunters Point and Long Island City to the west, Astoria to the north, Woodside to the east and Maspeth to the south. It contains the Sunnyside Gardens Historic District, one of the first planned communities in the United States.

Brooklyn Community Board 14 is a New York City community board that encompasses the Brooklyn neighborhoods of Flatbush, Midwood, Kensington, and Ocean Parkway. It is delimited by Coney Island Avenue, the Long Island Rail Road, McDonald Avenue, Avenue F and 18th Avenue on the west, Parkside Avenue on the north, Bedford Avenue, Foster Avenue and Nostrand Avenue on the east, and Kings Highway and Avenue P on the south.

India's population in 2021 as per World Bank is 1.39 billion. Being the world's most populous country and one of its fastest-growing economies, India experiences both challenges and opportunities in context of public health. India is a hub for pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries; world-class scientists, clinical trials and hospitals yet country faces daunting public health challenges like child undernutrition, high rates of neonatal and maternal mortality, growth in noncommunicable diseases, high rates of road traffic accidents and other health related issues.

Healthcare in Europe is provided through a wide range of different systems run at individual national levels. Most European countries have a system of tightly regulated, competing private health insurance companies, with government subsidies available for citizens who cannot afford coverage. Many European countries offer their citizens a European Health Insurance Card which, on a reciprocal basis, provides insurance for emergency medical treatment insurance when visiting other participating European countries.
Australia is a high income country, and this is reflected in the good status of health of the population overall. In 2011, Australia ranked 2nd on the United Nations Development Programme's Human Development Index, indicating the level of development of a country. Despite the overall good status of health, the disparities occurring in the Australian healthcare system are a problem. The poor and those living in remote areas as well as indigenous people are, in general, less healthy than others in the population, and programs have been implemented to decrease this gap. These include increased outreach to the indigenous communities and government subsidies to provide services for people in remote or rural areas.
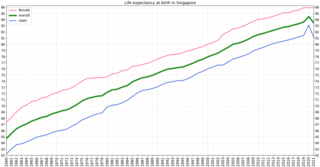
Singapore is one of the wealthiest countries in the world, with a gross domestic product (GDP) per capita of more than $57,000. Life expectancy at birth is 82.3 and infant mortality is 2.7 per 1000 live births. The population is ageing and by 2030, 20% will be over 65. However it is estimated that about 85% of those over 65 are healthy and reasonably active. Singapore has a universal health care system.

Niger is a landlocked country located in West Africa and has Libya, Chad, Nigeria, Benin, Mali, Burkina Faso, and Algeria as its neighboring countries. Niger was French territory that got its independence in 1960 and its official language is French. Niger has an area of 1.267 million square kilometres, nevertheless, 80% of its land area spreads through the Sahara Desert.
Botswana's healthcare system has been steadily improving and expanding its infrastructure to become more accessible. The country's position as an upper middle-income country has allowed them to make strides in universal healthcare access for much of Botswana's population. The majority of the Botswana's 2.3 million inhabitants now live within five kilometres of a healthcare facility. As a result, the infant mortality and maternal mortality rates have been on a steady decline. The country's improving healthcare infrastructure has also been reflected in an increase of the average life expectancy from birth, with nearly all births occurring in healthcare facilities.

Lesotho's Human development index value for 2018 was 0.518—which put the country in the low human development category—positioning it at 164 out of 189 countries and territories. Health care services in Lesotho are delivered primarily by the government and the Christian Health Association of Lesotho. Access to health services is difficult for many people, especially in rural areas. The country's health system is challenged by the relentless increase of the burden of disease brought about by AIDS, and a lack of expertise and human resources. Serious emergencies are often referred to neighbouring South Africa. The largest contribution to mortality in Lesotho are communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions.
Serbia ranked 65th in the world in life expectancy in 2018 with 73.3 years for men and 78.5 years for women. As of 2018, it had a low infant mortality rate. As of 2017, it had 2.96 practicing physicians per 1,000 people.

Brunei's healthcare system is managed by the Brunei Ministry of Health and funded by the General Treasury. It consists of around 15 health centers, ten clinics and 22 maternal facilities, considered to be of reasonable standard. There are also two private hospitals. Cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes are the leading cause of death in the country, with life expectancy around 75 years, a vast improvement from 1961. Brunei's human development index (HCI) improved from 0.81 in 2002 to 0.83 in 2021, expanding at an average annual rate of 0.14%. According to the UN's Human Development Report 2020, the HCI for girls in the country is greater than for boys, though aren't enough statistics in Brunei to break down HCI by socioeconomic classes. Brunei is the second country in Southeast Asia after Singapore to be rated 47th out of 189 nations on the UN HDI 2019 and has maintained its position in the Very High Human Development category. Being a culturally taboo subject, the rate of suicide has not been investigated.
References
- ↑ "Annual Mortality Statistics and Life Expectancy figures published". Government of Jersey. 26 September 2018. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- ↑ "Demand for mental health call-outs in Jersey has 'significantly' increased". ITV. 20 April 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2018.
- 1 2 "Births - Annual number of births to Jersey resident mothers - Government of Jersey Open Data". opendata.gov.je. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ "Births - Annual median age of mothers - Government of Jersey Open Data". opendata.gov.je. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ "Births - Crude birth rate - Government of Jersey Open Data". opendata.gov.je. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ "Births and fertility". Government of Jersey. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- 1 2 "Mortality and life expectancy". Government of Jersey. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ "Coronavirus (COVID-19) tests and cases in Jersey". Government of Jersey. Retrieved 12 March 2021.