
In the United States, Medicaid is a government program that provides health insurance for adults and children with limited income and resources. The program is partially funded and primarily managed by state governments, which also have wide latitude in determining eligibility and benefits, but the federal government sets baseline standards for state Medicaid programs and provides a significant portion of their funding.

Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States for people age 65 or older and younger people with disabilities, including those with end stage renal disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It was begun in 1965 under the Social Security Administration and is now administered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS).
TennCare is the state Medicaid program in the U.S. state of Tennessee. TennCare was established in 1994 under a federal waiver that authorized deviations from the standard Medicaid rules. It was the first state Medicaid program to enroll all Medicaid recipients in managed care. When first implemented, it also offered health insurance to other residents who did not have other insurance. Over time, the non-Medicaid component of the program was significantly reduced. Today TennCare offers a large variety of programs to better serve the citizens of Tennessee.

Medicare Part D, also called the Medicare prescription drug benefit, is an optional United States federal-government program to help Medicare beneficiaries pay for self-administered prescription drugs. Part D was enacted as part of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003 and went into effect on January 1, 2006. Under the program, drug benefits are provided by private insurance plans that receive premiums from both enrollees and the government. Part D plans typically pay most of the cost for prescriptions filled by their enrollees. However, plans are later reimbursed for much of this cost through rebates paid by manufacturers and pharmacies.
In China, the practice of medicine is a mixture of government, charitable, and private institutions, while many people rely on traditional medicine. Until reforms in the late twentieth and early twenty-first century, physicians were quasi-government employees and with little freedom in the choice of the hospital to work with. In addition, decades of planned economic policy discouraged physicians from opening their own clinics, and the practice of medicine was generally under the control of local units, such as factories, government, offices, or communes. The reforms created a largely private practice, and physicians now are encouraged to open private clinics and for-profit hospitals.

The Massachusetts health care reform, commonly referred to as Romneycare, was a healthcare reform law passed in 2006 and signed into law by Governor Mitt Romney with the aim of providing health insurance to nearly all of the residents of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
The Medicare Part D coverage gap was a period of consumer payments for prescription medication costs that lay between the initial coverage limit and the catastrophic coverage threshold when the consumer was a member of a Medicare Part D prescription-drug program administered by the United States federal government. The gap was reached after a shared insurer payment - consumer payment for all covered prescription drugs reached a government-set amount, and was left only after the consumer had paid full, unshared costs of an additional amount for the same prescriptions. Upon entering the gap, the prescription payments to date were re-set to $0 and continued until the maximum amount of the gap was reached or the then current annual period lapses. In calculating whether the maximum amount of gap had been reached, the "True-out-of-pocket" costs (TrOOP) were added together.
This article lists the healthcare statements of some candidates for president during the 2008 US presidential election.
The Oregon Health Plan is Oregon's state Medicaid program. It is overseen by the Oregon Health Authority.
In the United States, health insurance helps pay for medical expenses through privately purchased insurance, social insurance, or a social welfare program funded by the government. Synonyms for this usage include "health coverage", "health care coverage", and "health benefits". In a more technical sense, the term "health insurance" is used to describe any form of insurance providing protection against the costs of medical services. This usage includes both private insurance programs and social insurance programs such as Medicare, which pools resources and spreads the financial risk associated with major medical expenses across the entire population to protect everyone, as well as social welfare programs like Medicaid and the Children's Health Insurance Program, which both provide assistance to people who cannot afford health coverage.
Healthcare reform in the United States has a long history. Reforms have often been proposed but have rarely been accomplished. In 2010, landmark reform was passed through two federal statutes: the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), signed March 23, 2010, and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, which amended the PPACA and became law on March 30, 2010.

In the United States, health insurance coverage is provided by several public and private sources. During 2019, the U.S. population overall was approximately 330 million, with 59 million people 65 years of age and over covered by the federal Medicare program. The 273 million non-institutionalized persons under age 65 either obtained their coverage from employer-based or non-employer based sources, or were uninsured. During the year 2019, 89% of the non-institutionalized population had health insurance coverage. Separately, approximately 12 million military personnel received coverage through the Veteran's Administration and Military Health System.
Healthy San Francisco is a health access program launched in 2007 to subsidize medical care for uninsured residents of San Francisco, California operated by the San Francisco Department of Public Health. The program's stated objective is to bring universal health care to the city.
Healthcare rationing in the United States exists in various forms. Access to private health insurance is rationed on price and ability to pay. Those unable to afford a health insurance policy are unable to acquire a private plan except by employer-provided and other job-attached coverage, and insurance companies sometimes pre-screen applicants for pre-existing medical conditions. Applicants with such conditions may be declined cover or pay higher premiums and/or have extra conditions imposed such as a waiting period.
The America's Healthy Future Act was a bill proposed by Democratic Senator Max Baucus of Montana, who chaired the Senate Finance Committee, on September 16, 2009. It is also colloquially known as the Baucus Health Bill, the Baucus Health Plan, or BaucusCare. Baucus initially publicly released a 223-page summary of the proposal. It started going through the Senate mark-up process on September 22. That amendment process finished Oct. 2, and was passed by the Finance Committee on October 13 by a 14 to 9 vote,. An October CBO report stated that enacting the proposal would, on net, end up reducing the federal deficit by $81 billion over the 2010–2019 period.
There were a number of different health care reforms proposed during the Obama administration. Key reforms address cost and coverage and include obesity, prevention and treatment of chronic conditions, defensive medicine or tort reform, incentives that reward more care instead of better care, redundant payment systems, tax policy, rationing, a shortage of doctors and nurses, intervention vs. hospice, fraud, and use of imaging technology, among others.
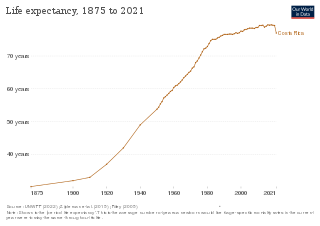
Costa Rica provides universal health care to its citizens and permanent residents. Both the private and public health care systems in Costa Rica are continually being upgraded. Statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO) frequently place Costa Rica in the top country rankings in the world for long life expectancy. WHO's 2000 survey ranked Costa Rica as having the 36th best health care system, placing it one spot above the United States at the time. In addition, the UN has ranked Costa Rica's public health system within the top 20 worldwide and the number 1 in Latin America.

Healthcare in the United States is largely provided by private sector healthcare facilities, and paid for by a combination of public programs, private insurance, and out-of-pocket payments. The U.S. is the only developed country without a system of universal healthcare, and a significant proportion of its population lacks health insurance. The United States spends more on healthcare than any other country, both in absolute terms and as a percentage of GDP; however, this expenditure does not necessarily translate into better overall health outcomes compared to other developed nations. Coverage varies widely across the population, with certain groups, such as the elderly and low-income individuals, receiving more comprehensive care through government programs such as Medicaid and Medicare.
Healthy Way LA (HWLA) was a free public health care program available to underinsured or uninsured, low-income residents of Los Angeles County from 2007 until 2014. The program, administered by the Los Angeles County Department of Health Services (LADHS), was a Low Income Health Program (LIHP) approved under the Section 1115 Medicaid Waiver. HWLA was succeeded by My Health LA, a no-cost health care program which ran from 2014 until 2024, when access to Medi-Cal was expanded.
Health care finance in the United States discusses how Americans obtain and pay for their healthcare, and why U.S. healthcare costs are the highest in the world based on various measures.




