
A Lagerstätte is a sedimentary deposit that exhibits extraordinary fossils with exceptional preservation—sometimes including preserved soft tissues. These formations may have resulted from carcass burial in an anoxic environment with minimal bacteria, thus delaying the decomposition of both gross and fine biological features until long after a durable impression was created in the surrounding matrix. Lagerstätten span geological time from the Neoproterozoic era to the present. Worldwide, some of the best examples of near-perfect fossilization are the Cambrian Maotianshan shales and Burgess Shale, the Devonian Hunsrück Slates and Gogo Formation, the Carboniferous Mazon Creek, the Jurassic Solnhofen limestone, the Cretaceous Santana, Yixian formations, the Eocene Green River Formation, and the Miocene Foulden Maar.
Aplacophora is a presumably paraphyletic taxon. This is a class of small, deep-water, exclusively benthic, marine molluscs found in all oceans of the world.
Traditionally, the Myodocopa and Podocopa have been classified as subclasses within the class Ostracoda, although there is some question about how closely related the two groups actually are. The Myodocopa are defined by possession of a poorly calcified carapace, and 8–9 articles in the exopod of the second antenna. The ventral margin of the carapace is not concave, and the valves do not overlap to a great extent.
The Silurian Lagerstätte preserved in the limestone Wenlock Series of Herefordshire, England, offers paleontologists a rare snapshot of a moment in time, about 420 Mya. In the formation, layers of fine-grained volcanic ash punctuate a sequence of carbonate muds that were accumulating in a marine environment on the outer continental shelf. In this fine-grained matrix, soft-bodied animals and delicate, lightly sclerotized chitinous shells are often preserved in three dimensions, as calcitic fossilizations within calcareous nodules. Calcitic fossilization is an unusual feature.

Megacheira is an extinct class of predatory arthropods that possessed a pair of great appendages, hence the class name as well as the common name "great appendage arthropods". Their neural structures and deutocerebral appendages resemble those of chelicerates. Most of them were found in marine environments throughout the world from the lower to middle Cambrian. Megacheirans were important components of several faunas, including the Burgess, Wheeler and Maotianshan Shales Lagerstatten.
Acaenoplax is an extinct worm-shaped mollusc known from the Wenlock Series lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England. It lived in the Silurian period. It was a couple of centimetres long and half a centimetre wide, and comprises serially repeated units with seven or eight shells, and rings of 'spines'.
Cinerocaris is an extinct genus of crustaceans which existed in the United Kingdom. It contains the species Cinerocaris magnifica.
Nasunaris flata is an extinct genus of ostracods which existed in the United Kingdom during the Silurian period. It was first named by David J. Siveter, Derek E. G. Briggs, Derek J. Siveter and Mark D. Sutton in 2010.
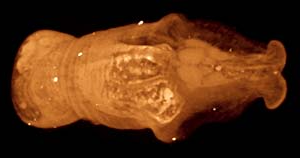
Xylokorys is a genus of marrellomorph known from two specimens from the Silurian Herefordshire lagerstatte; it filter-fed on mud particles on the sea floor. It is the only marrellomorph known from the Silurian period.
The Heloplacidae are a group of plated aplacophora known from Silurian deposits. Their best understood representative, Acaenoplax, can be taken as representative of the family; it is the only genus for which soft part anatomy is known.
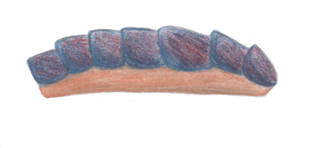
Kulindroplax perissokomos is a Silurian mollusk, known from a single fossil from the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte fauna of England. It lived during the Homerian Age. It is considered a basal aplacophoran. Unlike all modern aplacophorans, which are shell-less, Kulindroplax has a chiton-like shell, and it is considered a transitional fossil in the evolution of molluscs.
Phthipodochiton is an extinct genus of molluscs, known from several fossils from the upper Ordovician fauna of the Lady Burn Starfish beds of Girvan, Scotland. It shows a mixture of aplacophoran body plan and polyplacophoran-like valves, and it is an informative fossil in the evolution of aculiferan mollusks.
Pauline avibella is a fossil ostracod from the Silurian with unusually well preserved soft parts, including limbs, eyes, gills and alimentary system.
Pauline is a fossil genus of ostracods from the Silurian. Genus contains two species: Pauline avibella found in 425-million-year-old rocks in the Herefordshire Lagerstätte in England near the Welsh Border and Pauline nivisis, known from the Lower Silurian Pentamerus Bjerge Formation of north Greenland.
Kenostrychus is a monospecific genus of polychaete worms known from exceptional 3D fossils from the Silurian Herefordshire lagerstatten.

Aquilonifer spinosus is an extinct species of arthropod from the Silurian period. It is known from a single fossil specimen found in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England, in rocks about 430 million years old. The 1 cm long specimen is a stem-group mandibulate, not directly related to any living species. The many-legged, eyeless adult has ten unusual tethered appendages, interpreted as juveniles attached to the parent, in a unique form and previously unknown brooding behaviour.

Prosomapoda is a clade of euchelicerates including the groups Xiphosura and Planaterga, as well as several basal synziphosurid genera. The clade is defined by the lack of exopods of prosomal appendage II-V in the adult instar, where in contrast the exopods of appendage II-V are well-developed in the non-prosomapod euchelicerates Offacolus and Dibasterium.

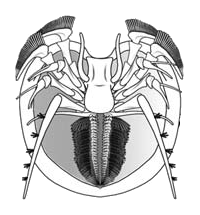
Offacolus is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Its only species, O. kingi, has been found in deposits from the Silurian period in the Wenlock Series Lagerstätte of Herefordshire, England. It is the only member of the monotypic family Offacolidae, and classified as a basal ("primitive") genus in the clade Euchelicerata, along with Dibasterium and Prosomapoda. The genus is named after Offa, a king from the ancient kingdom of Mercia, and colus, a person who dwelled among the Offa's Dyke. The species name honors Robert Joseph King, a British mineralogist who found the fossils of Offacolus.
Sollasina is an extinct genus of ophiocistioid that flourished 430 million years ago. Its fossil remains have been recovered from the Wenlock Series of the Silurian Herefordshire Lagerstätte in England.

Dibasterium is an extinct genus of euchelicerate, a group of chelicerate arthropods. Fossils of the single and type species, D. durgae, have been discovered in deposits of the Middle Silurian period in Herefordshire, England. The name of the genus is derived from the Latin words dibamos and mysterium ("mystery"), meaning "mystery on two legs" and referring to its prosomal limbs. The species name durgae comes from Durga, a Hindu goddess with many arms.








