
Texture mapping is a method for mapping a texture on a computer-generated graphic. "Texture" in this context can be high frequency detail, surface texture, or color.

In scientific visualization and computer graphics, volume rendering is a set of techniques used to display a 2D projection of a 3D discretely sampled data set, typically a 3D scalar field.
A volumetric display device is a display device that forms a visual representation of an object in three physical dimensions, as opposed to the planar image of traditional screens that simulate depth through a number of different visual effects. One definition offered by pioneers in the field is that volumetric displays create 3D imagery via the emission, scattering, or relaying of illumination from well-defined regions in (x,y,z) space.

3D scanning is the process of analyzing a real-world object or environment to collect three dimensional data of its shape and possibly its appearance. The collected data can then be used to construct digital 3D models.
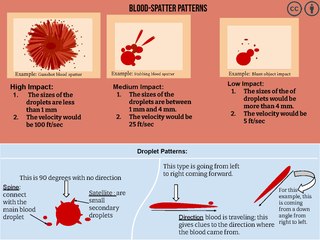
Bloodstain pattern analysis (BPA) is a forensic discipline focused on analyzing bloodstains left at known, or suspected crime scenes through visual pattern recognition and physics-based assessments. This is done with the purpose of drawing inferences about the nature, timing and other details of the crime. At its core, BPA revolves around recognizing and categorizing bloodstain patterns, a task essential for reconstructing events in crimes or accidents, verifying statements made during investigations, resolving uncertainties about involvement in a crime, identifying areas with a high likelihood of offender movement for prioritized DNA sampling, and discerning between homicides, suicides, and accidents.
Crime reconstruction or crime scene reconstruction is the forensic science discipline in which one gains "explicit knowledge of the series of events that surround the commission of a crime using deductive and inductive reasoning, physical evidence, scientific methods, and their interrelationships". Gardner and Bevel explain that crime scene reconstruction "involves evaluating the context of a scene and the physical evidence found there in an effort to identify what occurred and in what order it occurred." Chisum and Turvey explain that "[h]olistic crime reconstruction is the development of actions and circumstances based on the system of evidence discovered and examined in relation to a particular crime. In this philosophy, all elements of evidence that come to light in a given case are treated as interdependent; the significance of each piece, each action, and each event falls and rises on the backs of the others."

UCSF Chimera is an extensible program for interactive visualization and analysis of molecular structures and related data, including density maps, supramolecular assemblies, sequence alignments, docking results, trajectories, and conformational ensembles. High-quality images and movies can be created. Chimera includes complete documentation and can be downloaded free of charge for noncommercial use.

Traffic collision reconstruction is the process of investigating, analyzing, and drawing conclusions about the causes and events during a vehicle collision. Reconstructionists conduct collision analysis and reconstruction to identify the cause of a collision and contributing factors including the role of the driver(s), vehicle(s), roadway and general environment. Physics and engineering principles are the basis for these analyses and may involve the use of software for calculations and simulations. Collision reconstruction is sometimes used as the basis of expert witness testimony at trials. Collision reconstructions are performed in cases involving fatalities or personal injury. Results from collision reconstructions are also sometimes used for making roads and highways safer, as well as improving safety aspects of motor vehicle designs. Reconstructions are typically conducted by forensic engineers, specialized units in law enforcement agencies, or private consultants.

Origin is a proprietary computer program for interactive scientific graphing and data analysis. It is produced by OriginLab Corporation, and runs on Microsoft Windows. It has inspired several platform-independent open-source clones and alternatives like LabPlot and SciDAVis.

Forensic photography may refer to the visual documentation of different aspects that can be found at a crime scene. It may include the documentation of the crime scene, or physical evidence that is either found at a crime scene or already processed in a laboratory. Forensic photography differs from other variations of photography because crime scene photographers usually have a very specific purpose for capturing each image. As a result, the quality of forensic documentation may determine the result of an investigation; in the absence of good documentation, investigators may find it impossible to conclude what did or did not happen.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to forensic science:
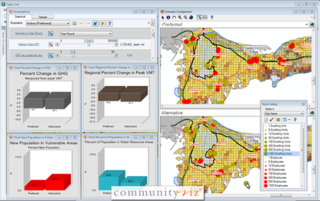
CommunityViz is the name of a group of extensions to ArcGIS Geographic Information System software. CommunityViz is an analysis tool used for, among other applications, urban planning, land use planning, geodesign, transportation planning and resource management applications. It also provides options for 3D visualization in the Scenario 3D and Scenario 360 plugins. CommunityViz also allows users to export and view their work in ArcGIS Online, Google Earth and other KML/KMZ viewers such as ArcGIS Explorer. The software was originally produced by the Orton Family Foundation and in 2005 was handed off to Placeways LLC. In 2017, the software was purchased by City Explained, Inc. where its development continues.

3D computer graphics, sometimes called CGI, 3-D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later or displayed in real time.

Forensic footwear evidence can be used in legal proceedings to help prove that a shoe was at a crime scene. Footwear evidence is often the most abundant form of evidence at a crime scene and in some cases can prove to be as specific as a fingerprint. Initially investigators will look to identify the make and model of the shoe or trainer which made an impression. This can be done visually or by comparison with evidence in a database; both methods focus heavily on pattern recognition and brand or logo marks. Information about the footwear can be gained from the analysis of wear patterns which are dependent on angle of footfall and weight distribution. Detailed examination of footwear impressions can help to link a specific piece of footwear to a footwear imprint as each shoe will have unique characteristics.

A 3D city model is digital model of urban areas that represent terrain surfaces, sites, buildings, vegetation, infrastructure and landscape elements in three-dimensional scale as well as related objects belonging to urban areas. Their components are described and represented by corresponding two- and three-dimensional spatial data and geo-referenced data. 3D city models support presentation, exploration, analysis, and management tasks in a large number of different application domains. In particular, 3D city models allow "for visually integrating heterogeneous geoinformation within a single framework and, therefore, create and manage complex urban information spaces."

Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.
Blood residue are the wet and dry remnants of blood, as well the discoloration of surfaces on which blood has been shed. In forensic science, blood residue can help investigators identify weapons, reconstruct a criminal action, and link suspects to the crime. Analysis of blood residue is also an important technique in archeology.

CrimeStat is a crime mapping software program. CrimeStat is Windows-based program that conducts spatial and statistical analysis and is designed to interface with a geographic information system (GIS). The program is developed by Ned Levine & Associates under the direction of Ned Levine, with funding by the National Institute of Justice (NIJ), an agency of the United States Department of Justice. The program and manual are distributed for free by NIJ.

C3D Toolkit is a proprietary cross-platform geometric modeling kit software developed by Russian by C3D Labs. It's written in C++. It can be licensed by other companies for use in their 3D computer graphics software products. The most widely known software in which C3D Toolkit is typically used are computer aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and computer-aided engineering (CAE) systems.
Daniel Attinger is a mechanical engineer, researcher and an academic. He owns a US-based scientific consulting company.














