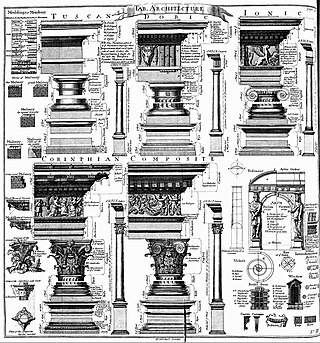
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform. Coming down to the present from Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civilization, the architectural orders are the styles of classical architecture, each distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column employed. The three orders of architecture—the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—originated in Greece. To these the Romans added, in practice if not in name, the Tuscan, which they made simpler than Doric, and the Composite, which was more ornamental than the Corinthian. The architectural order of a classical building is akin to the mode or key of classical music; the grammar or rhetoric of a written composition. It is established by certain modules like the intervals of music, and it raises certain expectations in an audience attuned to its language.

The Corinthian order is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture.

Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenics, whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC.

The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of the columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above.

The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan, and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns.

In architecture the capital or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column. It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves.

Magnesia or Magnesia on the Maeander was an ancient Greek city in Ionia, considerable in size, at an important location commercially and strategically in the triangle of Priene, Ephesus and Tralles. The city was named Magnesia, after the Magnetes from Thessaly who settled the area along with some Cretans. It was later called "on the Meander" to distinguish it from the nearby Lydian city Magnesia ad Sipylum. It was earlier the site of Leucophrys mentioned by several ancient writers.

Greek temples were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the sacrifices and rituals dedicated to the respective ouranic deity took place outside them, within the wider precinct of the sanctuary, which might be large. Temples were frequently used to store votive offerings. They are the most important and most widespread surviving building type in Greek architecture. In the Hellenistic kingdoms of Southwest Asia and of North Africa, buildings erected to fulfill the functions of a temple often continued to follow the local traditions. Even where a Greek influence is visible, such structures are not normally considered as Greek temples. This applies, for example, to the Graeco-Parthian and Bactrian temples, or to the Ptolemaic examples, which follow Egyptian tradition. Most Greek temples were oriented astronomically.

Didyma was an ancient Greek sanctuary on the coast of Ionia in the domain of the famous city of Miletus. Apollo was the main deity of the sanctuary of Didyma, also called Didymaion. But it was home to both of the temples dedicated to the twins Apollo and Artemis. Other deities were also honoured within the sanctuary. The Didymaion was well renowned in antiquity because of its famed oracle. This oracle of Apollo was situated within what was, and is, one of the world's greatest temples to Apollo. The remains of this Hellenistic temple belong to the best preserved temples of classical antiquity. Besides this temple other buildings existed within the sanctuary which have been rediscovered recently; a Greek theatre and the foundations of the above-mentioned Hellenistic temple of Artemis, to name but two.

The Tuscan order is one of the two classical orders developed by the Etruscans, the other being the composite order. It is influenced by the Doric order, but with un-fluted columns and a simpler entablature with no triglyphs or guttae. While relatively simple columns with round capitals had been part of the vernacular architecture of Italy and much of Europe since at least Etruscan architecture, the Romans did not consider this style to be a distinct architectural order. Its classification as a separate formal order is first mentioned in Isidore of Seville's Etymologies and refined during the Italian Renaissance.

Pythius, also known as Pytheos or Pythis, was a Greek architect, architecture theorist, and sculptor of the 4th century BC. He designed the Temple of Athena Polias at Priene and the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, which was regarded in antiquity among the Seven Wonders of the World. It is presumed that he came from the Greek city of Priene. The first-century BC Roman architect Vitruvius called Pythius a "celebrated builder" and referenced lost treatises on architecture written in Greek by Pythius as sources for his Latin architecture manual de Architectura (I.1.15).

A dentil is a small block used as a repeating ornament in the bedmould of a cornice. Dentils are found in ancient Greek and Roman architecture, and also in later styles such as Neoclassical, Federal, Georgian Revival, Greek Revival, Renaissance Revival, Second Empire, and Beaux-Arts architecture. Dentillation refers to use of a course of dentils.

De architectura is a treatise on architecture written by the Roman architect and military engineer Marcus Vitruvius Pollio and dedicated to his patron, the emperor Caesar Augustus, as a guide for building projects. As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first known book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture.

Teos or Teo was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, on a peninsula between Chytrium and Myonnesus. It was founded by Minyans from Orchomenus, Ionians and Boeotians, but the date of its foundation is unknown. Teos was one of the twelve cities which formed the Ionian League. The city was situated on a low hilly isthmus. Its ruins are located to the south of the modern town of Sığacık in the Seferihisar district of Izmir Province, Turkey.

Callimachus was an architect and sculptor working in the second half of the 5th century BC in the manner established by Polyclitus. He was credited with work in both Athens and Corinth and was probably from one of the two cities. According to Vitruvius (iv.1), for his great ingenuity and taste the Athenians dubbed Callimachus katatêxitechnos. His reputation in the 2nd century AD was reported in an aside by Pausanias as one "although not of the first rank of artists, was yet of unparalleled cleverness, so that he was the first to drill holes through stones"—that is, in order to enhance surface effects of light and shade in locks of hair, foliage and other details. Thus it is reported that Callimachus was known for his penchant for elaborately detailed sculptures or drapery, though few securely attributed works by him survive.
Araeostyle is one of five categories of intercolumniation described by the Roman architect Vitruvius. Of all the ancient architectural categories, the araeostyle has the widest spacing of columns, with an intercolumniation equal to four column diameters. Because of the wide span, timber rather than stone architraves were used. Vitruvius names three examples of araeostyle temples: the Temple of Ceres, Pompey's Temple of Hercules, and the Temple on the Capitoline Hill.

Bead and reel is an architectural motif, usually found in sculptures, moldings and numismatics. It consists in a thin line where beadlike elements alternate with cylindrical ones. It is found throughout the modern Western world in architectural detail, particularly on Greek/Roman style buildings, wallpaper borders, and interior moulding design. It is often used in combination with the egg-and-dart motif.
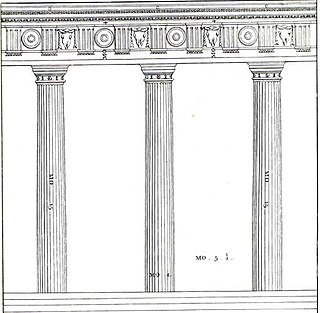
In architecture, intercolumniation is the proportional spacing between columns in a colonnade, often expressed as a multiple of the column diameter as measured at the bottom of the shaft. In Classical, Renaissance, and Baroque architecture, intercolumniation was determined by a system described by the first-century BC Roman architect Vitruvius. Vitruvius named five systems of intercolumniation, and warned that when columns are placed three column-diameters or more apart, stone architraves break. According to Vitruvius, the Hellenistic architect Hermogenes formulated these proportions ("symmetriae") and perfected the Eustyle arrangement, which has an enlarged bay in the center of the façade.

The Tholos of Delphi is among the ancient structures of the Sanctuary of Athena Pronaia in Delphi. The circular temple, a tholos, shares the immediate site with other ancient foundations of the Temple of Athena Pronaia, all located less than a mile east of the main ruins at Delphi, in the modern Greek regional unit of Phocis. The tholos is part of the Delphi UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Temple of Athena Polias in Priene was an Ionic Order temple located northwest of Priene’s agora, inside the sanctuary complex. It was dedicated to Athena Polias, also the patron deity of Athens. It was the main temple in Priene, although there was a temple of Zeus. Built around 350 BC, its construction was sponsored by Alexander the Great during his anabasis to the Persian Empire. Its ruins sit at the foot of an escarpment of mount Mycale. It was believed to have been constructed and designed by Pytheos, who was the architect of the great Mausoleum of Halikarnassos, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was one of the Hellenistic temples that was not reconstructed by Romans.


















