
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms and coined many terms in biology, including ecology, phylum, phylogeny, and Protista. Haeckel promoted and popularised Charles Darwin's work in Germany and developed the influential but no longer widely held recapitulation theory claiming that an individual organism's biological development, or ontogeny, parallels and summarises its species' evolutionary development, or phylogeny.

The Noctilucales are an order of marine dinoflagellates. They differ from most others in that the mature cell is diploid and its nucleus does not show a dinokaryotic organization. They show gametic meiosis.

Rhizostomae or Rhizostomeae is an order of jellyfish. Species of this order have neither tentacles nor other structures at the bell's edges. Instead, they have eight highly branched oral arms, along which there are suctorial minimouth orifices. These oral arms become fused as they approach the central part of the jellyfish. The mouth of the animal is also subdivided into minute pores that are linked to coelenteron.

Crown jellyfishes are the six families of true jellyfish that belong to the order Coronatae. They are distinguished from other jellyfish by the presence of a deep groove running around the umbrella, giving them the crown shape from which they take their name. Many of the species in the order inhabit deep sea environments.

Clathrina is a genus of calcareous sponge in the family Clathrinidae. Several species formerly in Clathrina were transferred to the newly erected genera Arturia, Ernstia, Borojevia, and Brattegardia in 2013. The name is derived from the Latin word "clathratus" meaning "latticed".
Levinellidae is a family of calcareous sponges in the order Clathrinida. It contains the following genera and species:
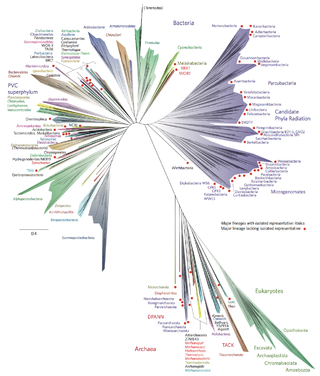
The tree of life or universal tree of life is a metaphor, model and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct, as described in a famous passage in Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species (1859).
The affinities of all the beings of the same class have sometimes been represented by a great tree. I believe this simile largely speaks the truth.
Leucosolenia is a genus of calcareous sponges belonging to the family Leucosoleniidae. Species of this genus usually appear as groups of curved vases, up to 2 cm long, each ending in an osculum. The overall shape is sometimes likened to a tiny bunch of bananas. They are most often observed in tide pools, clustered around the base of seaweeds or on rocks, and occur in a variety of colours, usually rather pale. Its canal system is of asconoid type. The colony consists of few simple vase-like, cylindrical individuals each terminating in an osculum and united at their bases by irregular horizontal tubes. Leucosolenia reproduces both asexually and sexually. asexual reproduction by budding and sexual reproduction takes place by formation of gametes, i.e., ova and sperms. Lecosolenia is hermaphrodite, because both the gametes are formed in the body of same individual. Sponges are mostly asymmetrical, but Leucosolenia is symmetrical.

Grantia is a genus of calcareous sponges belonging to the family Grantiidae. Species of the genus Grantia contain spicules and spongin fibers.

Monera (/məˈnɪərə/) is a biological kingdom that is made up of prokaryotes. As such, it is composed of single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus.

Aulosphaera is a genus of Cercozoa. The genus contains bioluminescent species. It one of two known bioluminescent phaeodarean genera, the other being Tuscaridium. The described bioluminescent species is Aulosphaera triodon Haeckel, 1887.

Sycon is a genus of calcareous sponges belonging to the family Sycettidae. These sponges are small, growing up to 7.5 cm and having length from 2.5 to7.5, and are tube-shaped and often white to cream in colour. They are known to aquarium hobbyists as "Pineapple" or "Q-Tip" sponges, and are frequent "hitchhikers" accidentally brought in.
Agalmatidae, or Agalmidae, is a family of siphonophores.

Rhizostomatidae is a family of cnidarians in the class Scyphozoa.

Ernstia is a genus of calcareous sponges in the family Clathrinidae. The genus was erected in 2013 to contain five species previously assigned to Clathrina. The genus name honors German naturalist Ernst Haeckel for his contributions towards sponge taxonomy and phylogeny.

Aeginura is a genus of hydrozoans in the family Aeginidae.
Hexacontium pachydermum is a species in the genus Hexacontium of the family Actinommidae. It was described by Eugen Honoratius Jørgensen in 1899.
Ascaltis is a genus of sponges in the family Leucascidae, first described in 1872 by Ernst Haeckel.

Actinommidae is a family of radiolarians.
Linuche is a genus of cnidarians belonging to the family Linuchidae.















