An angiogenesis inhibitor is a substance that inhibits the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Some angiogenesis inhibitors are endogenous and a normal part of the body's control and others are obtained exogenously through pharmaceutical drugs or diet.

The Hymenochaetales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. The order in its current sense is based on molecular research and not on any unifying morphological characteristics. According to one 2008 estimate, the Hymenochaetales contain around 600 species worldwide, mostly corticioid fungi and poroid fungi, but also including several clavarioid fungi and agarics. Species of economic importance include wood decay fungi in the genera Phellinus and Inonotus sensu lato, some of which may cause losses in forestry. Therapeutic properties are claimed for Inonotus obliquus ("chaga") and Phellinus linteus, both of which are now commercially marketed.
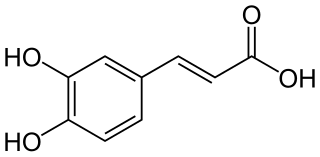
Caffeic acid is an organic compound that is classified as a hydroxycinnamic acid. This yellow solid consists of both phenolic and acrylic functional groups. It is found in all plants because it is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, one of the principal components of woody plant biomass and its residues.

Ellagic acid is a natural phenol antioxidant found in numerous fruits and vegetables. The antiproliferative and antioxidant properties of ellagic acid have prompted research into its potential health benefits. Ellagic acid is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.
G12/G13 subunits are alpha units of heterotrimeric G proteins that regulate cell processes through the use of guanine nucleotide exchange factors. These two subunits represent a fourth class of G protein alpha subunits. They are not sensitive to pertussis toxin.

GYKI-52895 is a drug which is a 2,3-benzodiazepine derivative. Unlike other similar drugs, GYKI-52895 is a selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor, which presumably would produce stimulant effects in vivo. Its DRI activity is shared by numerous addictive drugs including amphetamine and its derivatives, cocaine, and methylphenidate and its derivatives. However, dopaminergic drugs are also prone to producing emetic effects such as in the case of apomorphine.
Inhibitor of growth protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ING4 gene.

39S ribosomal protein L33, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRPL33 gene.

Protocatechuic acid (PCA) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid, a type of phenolic acid. It is a major metabolite of antioxidant polyphenols found in green tea. It has mixed effects on normal and cancer cells in in vitro and in vivo studies.

Protocatechuic aldehyde is a phenolic aldehyde, a compound released from cork stoppers into wine.
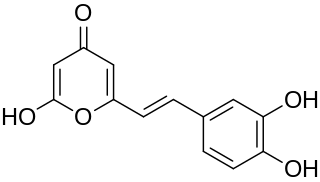
Hispidin is a natural substance. It can also be synthesized.

Phellinus ellipsoideus is a species of polypore fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae, a specimen of which produced the largest fungal fruit body ever recorded. Found in China, the fruit bodies produced by the species are brown, woody basidiocarps that grow on dead wood, where the fungus feeds as a saprotroph. The basidiocarps are perennial, allowing them to grow very large under favourable circumstances. They are resupinate, measuring 30 centimetres (12 in) or more in length, though typically extending less than a centimetre from the surface of the wood. P. ellipsoideus produces distinct ellipsoidal spores, after which it is named, and unusual setae. These two features allow it to be readily differentiated microscopically from other, similar species. Chemical compounds isolated from the species include several steroidal compounds. These may have pharmacological applications, but further research is needed.

Phellinstatin is an enoyl-ACP reductase inhibitor isolated from the fungus Phellinus linteus.

Hypholomine B is a neuraminidase inhibitor isolated from the fungus Phellinus linteus.
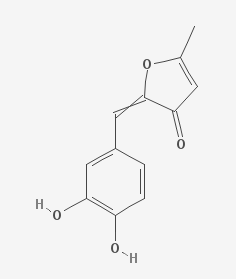
Inotilone is a chemical compound isolated from Phellinus linteus.
Inoscavins are chemical compounds isolated from Phellinus linteus.

Inoscavin A is an antioxidant isolated from the mushroom Inonotus xeranticus.
Tropicoporus tropicalis is part of the Hymenochaetaceae family, and was recently renamed to Tropicoporus tropicalis from Inonotus tropicalis, which is part of the Inonotus clade B. Tropicoporus tropicalis is a wood-decaying basidiomycetes that rarely causes disease in animals and human, and is commonly found in humid climate such as Brazil. In its natural environment, the fungus is associated with white rot woody angiosperms, and has its annual fruiting body on tree trunks and branches. Tropicoporus tropicalis has two kinds of hyphae, generative and skeletal, that lack clamp connections.














