Related Research Articles

Paraguay is a country in South America, bordering Argentina, Bolivia and Brazil. The Paraguay River divides the country into strikingly different eastern and western regions. Both the eastern region and the western region gently slope toward and are drained into the Paraguay River, which separates and unifies the two regions. With the Paraneña region reaching southward and the Chaco extending to the north, Paraguay straddles the Tropic of Capricorn and experiences both subtropical and tropical climates.

Paraguayan foreign policy has concentrated on maintaining good relations with its neighbors, and it has been an active proponent of regional co-operation. It is a member of the United Nations and has served one term in the UN Security Council in 1967-1969. It maintains membership in several international financial institutions, including the World Bank, the Inter-American Development Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. It also belongs to the Organization of American States, the Latin American Integration Association (ALADI), the Rio Group, INTERPOL, MERCOSUR and UNASUR.
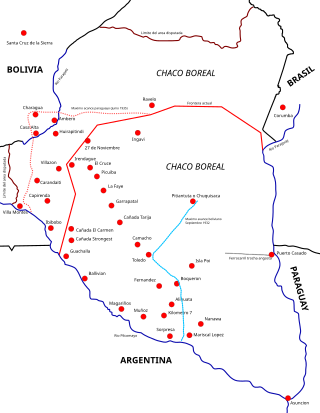
The Chaco War was fought from 1932 to 1935 between Bolivia and Paraguay, over the control of the northern part of the Gran Chaco region of South America, which was thought to be rich in oil. The war is also referred to as La Guerra de la Sed in literary circles since it was fought in the semi-arid Chaco. The bloodiest interstate military conflict fought in South America in the 20th century, it was fought between two of its poorest countries, both of which had lost territory to neighbours in 19th-century wars.

Asunción is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay. The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay of Asunción in the northwest separate the city from the Occidental Region of Paraguay and from Argentina in the south part of the city. The rest of the city is surrounded by the Central Department.
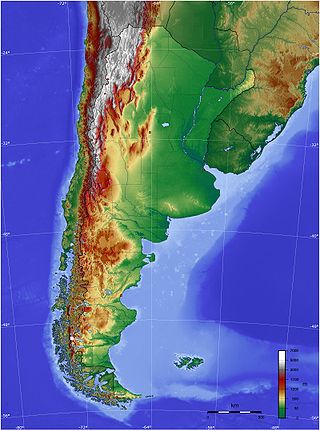
The geography of Argentina is heavily diverse, consisting of the Andes Mountains, pampas, and various rivers and lakes. Bordered by the Andes in the west and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, its neighbouring countries are Chile to the west, Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, and Brazil and Uruguay to the northeast.

Bolivia traditionally has maintained normal diplomatic relations with all hemispheric states except Chile. Foreign relations are handled by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, headed by the Chancellor of Bolivia, Rogelio Mayta.

Chaco, officially the Province of Chaco, is one of the 23 provinces in Argentina. Its capital and largest city, is Resistencia. It is located in the north-east of the country.

Pilcomayo is a river in central South America. At 1,100 kilometres (680 mi) long, it is the longest western tributary of the Paraguay River. Its drainage basin is 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi) in area, and its mean discharge is 200 cubic metres per second (7,100 cu ft/s).

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland tropical dry broadleaf forest natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.
The Paraguayan Chaco or Región Occidental is a semi-arid region in Paraguay, with a very low population density. The area is being rapidly deforested. Consisting of more than 60% of Paraguay's land area, but with less than 3% of the population, the Chaco is one of the most sparsely inhabited areas in South America.

Tarija or San Bernardo de la Frontera de Tarixa is a city in southern Bolivia. Founded in 1574, Tarija is the largest city and capital and municipality within the Tarija Department, with an airport offering regular service to primary Bolivian cities, as well as a regional bus terminal with domestic and international connections. Its climate is semi-arid (BSh) with generally mild temperatures in contrast to the harsh cold of the Altiplano and the year-round humid heat of the Amazon Basin. Tarija has a population of 234,442.

Spanish is the language that is predominantly understood and spoken as a first or second language by nearly all of the population of Argentina. According to the latest estimations, the population is currently greater than 45 million.

José Falcón is a district in Presidente Hayes Department of Paraguay, located 48 km North of Asuncion, which one can go from, through the Route 12.
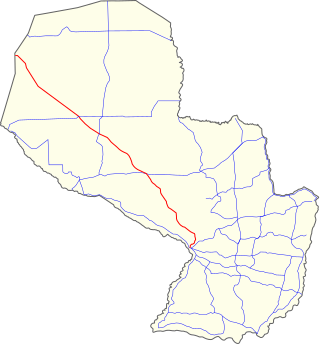
National Route 9 is a national highway in Paraguay, which crosses the Paraguayan Chaco, crossing the departments of Presidente Hayes, and Boquerón. It starts at the Argentinian border in José Falcón and ends at the Bolivian border in Fortín Sgto. Rodríguez, traversing 780 km (485 mi).

The Argentina–Paraguay border is the line that limits the territories of Argentina and Paraguay. This boundary is solely defined by three major rivers: the Pilcomayo, Paraná and Paraguay, being one of the largest natural borders in the world. The capital of Paraguay, Asunción, lies on one of the banks of the Paraguay River, which borders Argentina. The capital of Argentina is Buenos Aires, which lies on one of the banks of the River Plate, made by major Paraguayan tributaries. Argentina is the country which Paraguay has the largest border with, being about 1,689 km long. It is Argentina's second largest border, after the Argentina–Chile border.

The Machain–Irigoyen Treaty was a border treaty signed in Buenos Aires on 3 February 1876 between Paraguay and Argentina. Concluded in the aftermath of the Paraguayan War, it was signed by Facundo Machaín and Bernardo de Irigoyen.
The Chaco Basin is a major sedimentary basin in Central South America around the borders of Argentina, Bolivia and Paraguay. The basin forms part of the larger Paraná Basin. Superficially, the Chaco Basin is an alluvial basin composed of land-derived material, mostly fine sand and clays of Paleogene, Neogene and Quaternary age. On deeper levels the Paraguayan Chaco is made up by four sub-basins, the Pirizal, Pilar, Carandaity and Curupaity basins.
Bahía Negra is a district in the department of Alto Paraguay, Paraguay. Located on the right bank of the Paraguay River its population count is estimated to be around 2537, as of 2023.

The Bolivian–Peruvian territorial dispute was a territorial dispute between Bolivia and Peru that lasted from the former's independence in 1825 to the signing of the Polo–Bustamante Treaty in 1909.
References
- ↑ "Diario Digital abc de Paraguay - A 130 años de la decisión, los entretelones del laudo Hayes.". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2020-02-07.
- ↑ Ministerio de Justicia y Derechos Humanos, Presidencia de la Nación Argentina. Aprobación complementario de límites con Paraguay. Tratado 12.600. [ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Historia general de las relaciones exteriores de la República Argentina. Las relaciones de la Argentina con Bolivia y Paraguay.